PH213GeneralPhysicsCalculus_CrsOutline2012
... products, portfolios, juried performances, quizzes and exams, or other appropriate measure of performance. ...
... products, portfolios, juried performances, quizzes and exams, or other appropriate measure of performance. ...
SUMMARY 1. Define motor and generator. A motor is a device
... A motor is a device which converts electrical energy to mechanical energy (or motion). A generator is a device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. 2. What does the term “magnetic field” describe? The region surrounding a magnet where magnetic effects can be detected. A compass n ...
... A motor is a device which converts electrical energy to mechanical energy (or motion). A generator is a device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. 2. What does the term “magnetic field” describe? The region surrounding a magnet where magnetic effects can be detected. A compass n ...
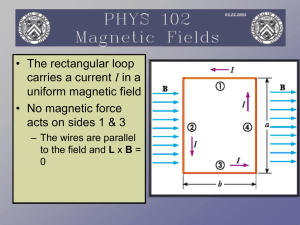
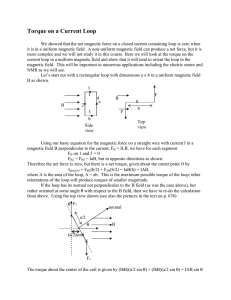
Torque on a Current Loop
... of the nucleus may depend on its local environment, since the other atoms nearby may produce small B fields themselves due to their circulating currents. NMR is so sensitive to this that it can measure a signal that tells the numbers of nuclei from atoms in different local environments. The signal l ...
... of the nucleus may depend on its local environment, since the other atoms nearby may produce small B fields themselves due to their circulating currents. NMR is so sensitive to this that it can measure a signal that tells the numbers of nuclei from atoms in different local environments. The signal l ...
magnet Any material that attracts iron and materials that contain iron
... of all atoms are lined up in the same direction. ...
... of all atoms are lined up in the same direction. ...
Standard 6.P.3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of
... The objective of this indicator is to develop and use models to exemplify how magnetic fields produced by electrical energy flow in a circuit are interrelated in electromagnets, generators, and simple electrical motors. Therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be to model how the flow of el ...
... The objective of this indicator is to develop and use models to exemplify how magnetic fields produced by electrical energy flow in a circuit are interrelated in electromagnets, generators, and simple electrical motors. Therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be to model how the flow of el ...
HG B J4C ELECTROMAGNETISM 10 credits
... Module Aims This module introduces electromagnetism by appealing to familiar concepts such as charge and current. The fluxes of these quantities are related to fields via the Maxwell equations. These equations are obtained in differential and integral form and applied to examine the behaviour of the ...
... Module Aims This module introduces electromagnetism by appealing to familiar concepts such as charge and current. The fluxes of these quantities are related to fields via the Maxwell equations. These equations are obtained in differential and integral form and applied to examine the behaviour of the ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength) Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin electric and magnetic fields are two interrelate ...
... given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength) Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin electric and magnetic fields are two interrelate ...