6. ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION IN EARTH`S CRUST AND
... and magnetic fields at the surface. The traditional development, which we will follow, works with the electric field E rather than with B. As in the previous section we use a flat-Earth approximation and a uniform exciting field above the ground; the only difference is that now the conductivity is a ...
... and magnetic fields at the surface. The traditional development, which we will follow, works with the electric field E rather than with B. As in the previous section we use a flat-Earth approximation and a uniform exciting field above the ground; the only difference is that now the conductivity is a ...
The Displacement Current and Maxwell`s Equations
... over a volume (Gauss’ Law for E and B ) or over a surface (Faraday induction and Ampere’s Law with displacement current) and then applying two theorems from vector calculus, the Divergence Theorem and Stokes’ Theorem respectively. You will soon learn this approach in your study of vector calculus. T ...
... over a volume (Gauss’ Law for E and B ) or over a surface (Faraday induction and Ampere’s Law with displacement current) and then applying two theorems from vector calculus, the Divergence Theorem and Stokes’ Theorem respectively. You will soon learn this approach in your study of vector calculus. T ...
Solutions to Problem Sheet 8
... positive x-axis. The protons are travelling along the y-axis at with a velocity of 1.5 X 105 ms-1. What is the magnitude of the force and along which direction does the force act? F=q X VII X B = 1.6x10-19 X 1.5x105 X 4 =9.6x10-14 N. Force acts long the z-axis, but is it positive or negative? 3. A b ...
... positive x-axis. The protons are travelling along the y-axis at with a velocity of 1.5 X 105 ms-1. What is the magnitude of the force and along which direction does the force act? F=q X VII X B = 1.6x10-19 X 1.5x105 X 4 =9.6x10-14 N. Force acts long the z-axis, but is it positive or negative? 3. A b ...
Physics Form 5 Syllabus
... give out radiation to get rid of excess energy, and are said to be radioactive Appreciate that an element may change into another element when radioactivity ...
... give out radiation to get rid of excess energy, and are said to be radioactive Appreciate that an element may change into another element when radioactivity ...
Digital Design
... “It is well known that if we attempt to apply Maxwell's electro-dynamics, as conceived at the present time, to moving bodies, we are led to asymmetry which does not agree with observed phenomena. Let us think of the mutual action between a magnet and a conductor. The observed phenomena in this case ...
... “It is well known that if we attempt to apply Maxwell's electro-dynamics, as conceived at the present time, to moving bodies, we are led to asymmetry which does not agree with observed phenomena. Let us think of the mutual action between a magnet and a conductor. The observed phenomena in this case ...
Maxwell`s equations
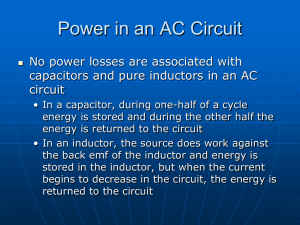
... current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it. The induced magnetic field inside any loop of wire always acts to keep the magnetic flux in the loop constant. In the examples below, if the B field is increasing, the induced field acts in opposition to it. If it is decreasing, the ...
... current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it. The induced magnetic field inside any loop of wire always acts to keep the magnetic flux in the loop constant. In the examples below, if the B field is increasing, the induced field acts in opposition to it. If it is decreasing, the ...
intro electromagnetism
... to the spin of the atom’s electrons. Groups of atoms join so that their magnetic fields are all going in the same direction These areas of atoms are called “domains” ...
... to the spin of the atom’s electrons. Groups of atoms join so that their magnetic fields are all going in the same direction These areas of atoms are called “domains” ...


![L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015457348_1-45ec1c6d8804a0bbd57ecd8a52999a34-300x300.png)