Producing Electric Current
... DC- Direct Current- Flows in only one direction. AC- Alternating current- reverses the direction of ...
... DC- Direct Current- Flows in only one direction. AC- Alternating current- reverses the direction of ...
Part 1 * Creating an Electric Field
... but the internal field gave them some trouble. Students were quick to realize that Gauss’s Law should work, but the problem came when determining the enclosed charge. In questions (iii) and (iv) most students remembered that the curl of E was zero but not the expression for the divergence of E. Most ...
... but the internal field gave them some trouble. Students were quick to realize that Gauss’s Law should work, but the problem came when determining the enclosed charge. In questions (iii) and (iv) most students remembered that the curl of E was zero but not the expression for the divergence of E. Most ...
Electricity – Uses of Electromagnetism
... increases voltage? STEP-UP Transformer What do we call a transformer that decreases voltage? STEP-DOWN Transformer © Boardworks Ltd 2003 ...
... increases voltage? STEP-UP Transformer What do we call a transformer that decreases voltage? STEP-DOWN Transformer © Boardworks Ltd 2003 ...
Teacher Guide: UDL Electricity
... thinking about where it comes from, what it is, or how it works. Because we see the results of what is happening with electrical current, but not the actual movement, understanding electricity can be an elusive topic to understand, especially in 3rd and 4th grade. Atoms are made up of charged and un ...
... thinking about where it comes from, what it is, or how it works. Because we see the results of what is happening with electrical current, but not the actual movement, understanding electricity can be an elusive topic to understand, especially in 3rd and 4th grade. Atoms are made up of charged and un ...
Displacement Current Does Not Exist
... Any one of these flaws would be sufficient to cast doubt on this and all of the other similar derivations. All of the flaws, when taken together, should be enough to negate the derivation. Why hasn’t this happened? It hasn’t happened, because there was no real need to do so. Remember that the time c ...
... Any one of these flaws would be sufficient to cast doubt on this and all of the other similar derivations. All of the flaws, when taken together, should be enough to negate the derivation. Why hasn’t this happened? It hasn’t happened, because there was no real need to do so. Remember that the time c ...
Electrical Power Generation - Bartlesville Public Schools
... The purpose of any power plant boiler is to heat water into steam. Here we see Briggs by one of the plant's coal boilers. It burns coal to heat water to 1000 degree Fahrenheit steam. Not all of the coal entering the boiler can be burned. The unburned heavy ash falls to the bottom of the boiler and i ...
... The purpose of any power plant boiler is to heat water into steam. Here we see Briggs by one of the plant's coal boilers. It burns coal to heat water to 1000 degree Fahrenheit steam. Not all of the coal entering the boiler can be burned. The unburned heavy ash falls to the bottom of the boiler and i ...
Can the amount of current change?
... Can the amount of current change? Yes it can…… So remember……. The amount of current depends on: 1. The amount of wire 2. The size of the magnet 3. And how fast the magnet moves ...
... Can the amount of current change? Yes it can…… So remember……. The amount of current depends on: 1. The amount of wire 2. The size of the magnet 3. And how fast the magnet moves ...
MPE Science Highlight
... of the Hall current to the meridional closure of the field-aligned current (FAC), and the coupling between the FAC and the electrojet (EJ) flowing along the arc. ALADYN is illustrated with a wide, stable, winter evening arc, as seen in the ‘Data’ panels. The ionospheric electric field (IEF), potenti ...
... of the Hall current to the meridional closure of the field-aligned current (FAC), and the coupling between the FAC and the electrojet (EJ) flowing along the arc. ALADYN is illustrated with a wide, stable, winter evening arc, as seen in the ‘Data’ panels. The ionospheric electric field (IEF), potenti ...
Faraday`s Law - Rutgers Physics
... fixed electromagnet is at the bottom, while a rotating electromagnet (also called the armature) is affixed to the shaft above the bottom one. ...
... fixed electromagnet is at the bottom, while a rotating electromagnet (also called the armature) is affixed to the shaft above the bottom one. ...
Magnetism can produce current.
... the second coil has fewer loops than the first, as in the illustration, the voltage is decreased. This is called a step-down transcoil of wire former. On the other hand, if the second coil has more loops than the first, the voltage in the second circuit will be higher than the original voltage. This ...
... the second coil has fewer loops than the first, as in the illustration, the voltage is decreased. This is called a step-down transcoil of wire former. On the other hand, if the second coil has more loops than the first, the voltage in the second circuit will be higher than the original voltage. This ...
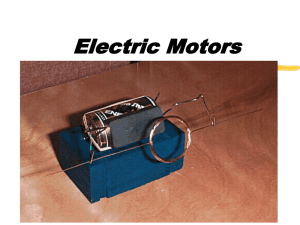
Electric Motors
... Electric Circuits An electric circuit is an electrical path that begins at a power source and ends up back at the power source. The component that is being powered by the source is called the load. ...
... Electric Circuits An electric circuit is an electrical path that begins at a power source and ends up back at the power source. The component that is being powered by the source is called the load. ...
Class 10 - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... Electric Potential Energy (UE) and Electric Potential (“voltage”) (V) In the study and harnessing of electrical energy, it is convenient to express the electrical potential energy on a per-unit-charge basis. This is called the electric potential or voltage, and is denoted by V. Electric potential i ...
... Electric Potential Energy (UE) and Electric Potential (“voltage”) (V) In the study and harnessing of electrical energy, it is convenient to express the electrical potential energy on a per-unit-charge basis. This is called the electric potential or voltage, and is denoted by V. Electric potential i ...
Electromagnetism - Physical Science
... Strength of an Electromagnet • 2 things affect the strength of an electromagnet(same 2 things that affect the strength of a magnetic field): 1. Amount of Current 2. # of turns of wire(# of coils) ...
... Strength of an Electromagnet • 2 things affect the strength of an electromagnet(same 2 things that affect the strength of a magnetic field): 1. Amount of Current 2. # of turns of wire(# of coils) ...
How transformers work
... your table how transformers work. Remember the following: • They only work with an a.c. current • They need to have an iron core • They use electromagnetic induction to work ...
... your table how transformers work. Remember the following: • They only work with an a.c. current • They need to have an iron core • They use electromagnetic induction to work ...
Electric potential
... is the energy required to move a unit charge between two specified points. An electric field has the special property that it is conservative, which means that the path taken by the test charge is irrelevant: all paths between two specified points expend the same energy, and thus a unique value for ...
... is the energy required to move a unit charge between two specified points. An electric field has the special property that it is conservative, which means that the path taken by the test charge is irrelevant: all paths between two specified points expend the same energy, and thus a unique value for ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.