Electricity and Magnetism - Unit 1
... the release of static electricity as charges move off an object 2 examples of electric discharge: 1. Walking across carpet and touching a metal doorknob 2. Lightning ...
... the release of static electricity as charges move off an object 2 examples of electric discharge: 1. Walking across carpet and touching a metal doorknob 2. Lightning ...
EE302 Lesson 1: Introduction
... Voltage source is turned on ->large current begins to flow through wire VDC I Rrail ...
... Voltage source is turned on ->large current begins to flow through wire VDC I Rrail ...
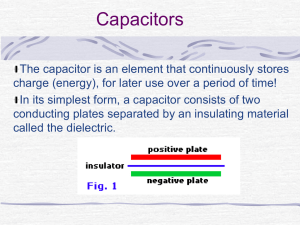
Capacitors - Honors Physics Website (Blue 5)
... material (typically waxed paper) between them. This material is called a dielectric. ...
... material (typically waxed paper) between them. This material is called a dielectric. ...
SA Power Networks 1 Electric and Magnetic Fields
... Electric fields are found wherever voltage is present. The higher the voltage and nearer the source, the stronger the field. As long as an appliance is plugged into an active power outlet, it emits an electric field. The appliance doesn’t need to be running. Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found ...
... Electric fields are found wherever voltage is present. The higher the voltage and nearer the source, the stronger the field. As long as an appliance is plugged into an active power outlet, it emits an electric field. The appliance doesn’t need to be running. Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found ...
TEM Wave Electrodynamics Feb 18 2012
... Electric current, i, doesn’t have any physical job to do. It only acts as an accounting device. Electric current inside a wire has never been measured. A magnetic field is measured outside the wire, then electric current is hypothesized to be inside the ...
... Electric current, i, doesn’t have any physical job to do. It only acts as an accounting device. Electric current inside a wire has never been measured. A magnetic field is measured outside the wire, then electric current is hypothesized to be inside the ...
final paper work for county science fair is due 01/09/2013
... Students will be able to describe how electrical charges flow through electric circuits. ...
... Students will be able to describe how electrical charges flow through electric circuits. ...
Homework 8
... (iv) Now let’s go to the inversion region. In the inversion region where you work with only the (np0/pp0)e term, which can be rewritten as eThe left side can be written as d(-2B)/dx. Thus, we have a differential equation describing how fast (2B) varies. Solve this equation with boun ...
... (iv) Now let’s go to the inversion region. In the inversion region where you work with only the (np0/pp0)e term, which can be rewritten as eThe left side can be written as d(-2B)/dx. Thus, we have a differential equation describing how fast (2B) varies. Solve this equation with boun ...
ppt document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... After it is accelerated across the gap, the speed will be larger, and from (r = mv/qB), the radius of the semicircle will be larger. During the time it is inside the half cylinder (one of the dees), the voltage across the two dees will be switched in polarity. Thus, when the charge again approaches ...
... After it is accelerated across the gap, the speed will be larger, and from (r = mv/qB), the radius of the semicircle will be larger. During the time it is inside the half cylinder (one of the dees), the voltage across the two dees will be switched in polarity. Thus, when the charge again approaches ...
Capacitors
... that a capacitor can dump its entire charge in a tiny fraction of a second, where a battery would take minutes to completely discharge itself. That's why the electronic flash on a camera uses a capacitor -- the battery charges up the flash's capacitor over several seconds, and then the capacitor dum ...
... that a capacitor can dump its entire charge in a tiny fraction of a second, where a battery would take minutes to completely discharge itself. That's why the electronic flash on a camera uses a capacitor -- the battery charges up the flash's capacitor over several seconds, and then the capacitor dum ...
Subject Description Form Subject Code ENG237 Subject Title Basic
... Concept of ideal transformer (assuming sinusoidal voltages and currents). Dot convention. Analyze circuit with ideal transformer. Calculate reflected sources and impedances across ideal transformers. Applications in galvanic isolation and voltage/current level conversion. 4. Steady-state Analysis of ...
... Concept of ideal transformer (assuming sinusoidal voltages and currents). Dot convention. Analyze circuit with ideal transformer. Calculate reflected sources and impedances across ideal transformers. Applications in galvanic isolation and voltage/current level conversion. 4. Steady-state Analysis of ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.