Section 2 Electricity and Magnetism
... Look at the magnetic field lines around the coils of wire in Figure 9B. The magnetic fields around each coil of wire add together to form a stronger magnetic field inside the coil. When the coils are wrapped around an iron core, the magnetic field of the coils magnetizes the iron. The iron then beco ...
... Look at the magnetic field lines around the coils of wire in Figure 9B. The magnetic fields around each coil of wire add together to form a stronger magnetic field inside the coil. When the coils are wrapped around an iron core, the magnetic field of the coils magnetizes the iron. The iron then beco ...
Lightning Strokes
... polarity as in terrestrial clouds. Observations of thunderclouds shows a typical tripolar structure with a small positively charge area at the bottom of the clouds. Once the charge is build up, an electrical field is developed. To bridge the distance between the bottom of the clouds and the Earth’s ...
... polarity as in terrestrial clouds. Observations of thunderclouds shows a typical tripolar structure with a small positively charge area at the bottom of the clouds. Once the charge is build up, an electrical field is developed. To bridge the distance between the bottom of the clouds and the Earth’s ...
CAPACITORS: are any physical objects that can store charge. I
... net charge is really zero, but we still say it’s “charged” up!) These two plates have a voltage difference between them. (It takes WORK to move a little test charge from one plate to the other). Let's think about this: What if you double Q on both plates? => you'll double the number of E field lines ...
... net charge is really zero, but we still say it’s “charged” up!) These two plates have a voltage difference between them. (It takes WORK to move a little test charge from one plate to the other). Let's think about this: What if you double Q on both plates? => you'll double the number of E field lines ...
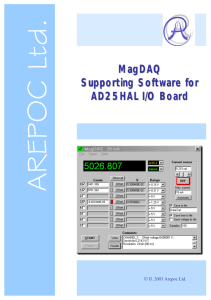
MagDAQ Supporting Software for AD25HAL I/O Board
... data acquisition board acquires a single sample from each selected channel. In the Continual mode the DAQ board acquires one or more samples from selected channels. The number of acquired samples must be selected in the Samples box of the Main window (see Save to file section). Reading time interval ...
... data acquisition board acquires a single sample from each selected channel. In the Continual mode the DAQ board acquires one or more samples from selected channels. The number of acquired samples must be selected in the Samples box of the Main window (see Save to file section). Reading time interval ...
Teaching of Electric Circuits Theories in Introductory Courses: How
... Abstract. At the beginnings of electrical sciences the terminology used by the scientists was varied and vague. There was no system of units for measuring the various aspects of electricity, described by terms as tension, voltaic excitation, electric virtue, etc. Using an historical approach, this p ...
... Abstract. At the beginnings of electrical sciences the terminology used by the scientists was varied and vague. There was no system of units for measuring the various aspects of electricity, described by terms as tension, voltaic excitation, electric virtue, etc. Using an historical approach, this p ...
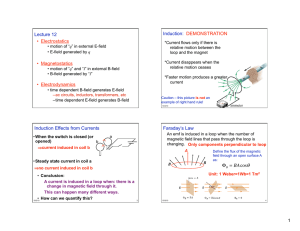
Electromagnetic induction
... 2. The faster the movement, the bigger the current. 3. Changing the direction of the movement changes the direction of the current, 4. The stronger the magnet, the bigger the current. 5. The more coils of wire, the bigger the current. Numbers 3, 4 and 5 form the basis of Faraday’s Law If you work ou ...
... 2. The faster the movement, the bigger the current. 3. Changing the direction of the movement changes the direction of the current, 4. The stronger the magnet, the bigger the current. 5. The more coils of wire, the bigger the current. Numbers 3, 4 and 5 form the basis of Faraday’s Law If you work ou ...
Homework 11
... A long solenoid has n = 400 turns per meter and curries current given by I = 30A⋅(1-e-1.6t). Inside the solenoid and coaxial with is a coil that has a radius of 6 cm and consists of a total of N = 250 turns of fine wire. What emf is induced in the coil by the changing current? ...
... A long solenoid has n = 400 turns per meter and curries current given by I = 30A⋅(1-e-1.6t). Inside the solenoid and coaxial with is a coil that has a radius of 6 cm and consists of a total of N = 250 turns of fine wire. What emf is induced in the coil by the changing current? ...
Chapter 16: Electromagnets and Induction
... Parallel wires can be bundled together. (10 wires, each with 1 A of current, create a magnetic field 10X as strong as 1 wire carrying 1 A). ...
... Parallel wires can be bundled together. (10 wires, each with 1 A of current, create a magnetic field 10X as strong as 1 wire carrying 1 A). ...
File
... assembly allows the whole loop to spin freely). The electricity produced by this type of generator is called alternating current because it changes direction (in North America it changes direction 120 times per second – giving 60 Hertz or complete waves each second. In large AC generators many loops ...
... assembly allows the whole loop to spin freely). The electricity produced by this type of generator is called alternating current because it changes direction (in North America it changes direction 120 times per second – giving 60 Hertz or complete waves each second. In large AC generators many loops ...
3D Finite Element Analysis for Arcing Chamber Optimization
... 2.1 The physical model of the arcing chamber In Fig.2 is presented the construction plan of the current path which includes the output terminals A, B, the conducting bars 1,2, the brake contacts 3 (lasting contacts) and 4 (arc brake contacts), the slopes 5, 6 placed in the arcing chamber CS. Within ...
... 2.1 The physical model of the arcing chamber In Fig.2 is presented the construction plan of the current path which includes the output terminals A, B, the conducting bars 1,2, the brake contacts 3 (lasting contacts) and 4 (arc brake contacts), the slopes 5, 6 placed in the arcing chamber CS. Within ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.