muscle protein synthesis rates during temperature acclimation in a
... reached in the plasma which allows rates of protein synthesis to be calculated in a similar manner to that used for measuring muscle protein synthesis using the constant infusion method. This method has the advantage of procedural simplicity and also it expands the free amino acid pool so that error ...
... reached in the plasma which allows rates of protein synthesis to be calculated in a similar manner to that used for measuring muscle protein synthesis using the constant infusion method. This method has the advantage of procedural simplicity and also it expands the free amino acid pool so that error ...
POND MANAGEMENT - Aquatic Environmental Services
... Known as bream to many, they are the backbone of forage production for largemouth bass ponds. Bluegill are very prolific, reproducing multiple times a season (3-5 times/year). This provides largemouth bass with a large quantity of food while still allowing themselves to sustain a healthy thriving po ...
... Known as bream to many, they are the backbone of forage production for largemouth bass ponds. Bluegill are very prolific, reproducing multiple times a season (3-5 times/year). This provides largemouth bass with a large quantity of food while still allowing themselves to sustain a healthy thriving po ...
j.0022-1112.2005.00934.x.doc
... relationships, as would have been the case if depth had been used as a continuous variable. Patterns in microhabitat use were analysed using generalized linear models (GLMs) for CPUE (Crawley, 2002) and ANOVA for fish size (Copp & Jurajda, 1999). Since CPUE is a variable derived from count data, Poi ...
... relationships, as would have been the case if depth had been used as a continuous variable. Patterns in microhabitat use were analysed using generalized linear models (GLMs) for CPUE (Crawley, 2002) and ANOVA for fish size (Copp & Jurajda, 1999). Since CPUE is a variable derived from count data, Poi ...
On the different nature of top-down and bottom
... Gilliam (1984) on size-structured fish populations, the two disparate quantities have often been compared successfully when they were converted to the common currency of fitness. Dynamic modelling of state-dependent decision-making under the risk of predation has been successfully developed to tackl ...
... Gilliam (1984) on size-structured fish populations, the two disparate quantities have often been compared successfully when they were converted to the common currency of fitness. Dynamic modelling of state-dependent decision-making under the risk of predation has been successfully developed to tackl ...
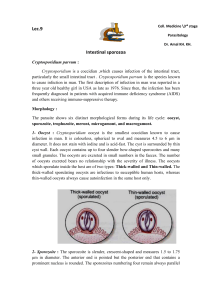
mechanisms used by some parasitic protozoa to evade the immune
... forming parasite nests or pseudocysts, particularly in cardiac muscle fibres. The disease is frequently lethal in children and infants, but in adults the initial infection often turns into a chronic disease, sometimes after a long interval, causing an illness characterized by megacardia with megacol ...
... forming parasite nests or pseudocysts, particularly in cardiac muscle fibres. The disease is frequently lethal in children and infants, but in adults the initial infection often turns into a chronic disease, sometimes after a long interval, causing an illness characterized by megacardia with megacol ...
important considerations for the management of demersal fisheries
... high gravel or mud content. Plaice density was positively correlated with the density of emergent epifauna, which could be due to the fact that complex habitats provide a multitude of niche spaces for mobile epifauna, that form an important part of their diet. By contrast, stations of high sole dens ...
... high gravel or mud content. Plaice density was positively correlated with the density of emergent epifauna, which could be due to the fact that complex habitats provide a multitude of niche spaces for mobile epifauna, that form an important part of their diet. By contrast, stations of high sole dens ...
Coho- Integrated - Northwest Power and Conservation Council
... Fish should be released at an optimum time and size that has been determined by a site-specific survival study. Fish should be released at sizes and life history stages similar to those of natural fish of the same species. ...
... Fish should be released at an optimum time and size that has been determined by a site-specific survival study. Fish should be released at sizes and life history stages similar to those of natural fish of the same species. ...
Lake Manager`s Handbook: Alien Invaders
... dispersal mechanisms, and a range of species remain restricted to the water bodies they were first introduced into (see section 4). Alien fish species currently in New Zealand are mostly unable to spread between catchments naturally, unless they are tolerant of saltwater (for example, chinook salmon ...
... dispersal mechanisms, and a range of species remain restricted to the water bodies they were first introduced into (see section 4). Alien fish species currently in New Zealand are mostly unable to spread between catchments naturally, unless they are tolerant of saltwater (for example, chinook salmon ...
parasite
... pressure hosts and parasites impose on each other has caused both of their populations to evolve. ...
... pressure hosts and parasites impose on each other has caused both of their populations to evolve. ...
Disturbance and trajectory of change in a stream fish community
... we assess the Brier Creek fish community, over four decades, to test applicability of our framework in a system in which some of the most extraordinary, and repeated, disturbances (flood and drought) on record have occurred. To test predictions of any theoretical constructs about communities, long-t ...
... we assess the Brier Creek fish community, over four decades, to test applicability of our framework in a system in which some of the most extraordinary, and repeated, disturbances (flood and drought) on record have occurred. To test predictions of any theoretical constructs about communities, long-t ...
Tuna Fishery - National Fisheries Authority
... The government’s policy on tuna fishing is one geared towards domestication and onshore investment. How to get a Tuna Fishing License. In general, only commercial fishing vessels require licences. Small scale operations do not. To get a fishing license for tuna, the applicant has to submit a fishing ...
... The government’s policy on tuna fishing is one geared towards domestication and onshore investment. How to get a Tuna Fishing License. In general, only commercial fishing vessels require licences. Small scale operations do not. To get a fishing license for tuna, the applicant has to submit a fishing ...
YSISPUBS - Yakima/Klickitat Fisheries Project
... McMichael, G. A., T. N. Pearsons, and S. A. Leider. 1999. Minimizing ecological impacts of hatchery-reared juvenile steelhead on wild salmonids in a Yakima basin tributary. Pages ...
... McMichael, G. A., T. N. Pearsons, and S. A. Leider. 1999. Minimizing ecological impacts of hatchery-reared juvenile steelhead on wild salmonids in a Yakima basin tributary. Pages ...
Myxobolus cerebralis

Myxobolus cerebralis is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids (salmon, trout, and their allies) that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations. It was first described in rainbow trout in Germany a century ago, but its range has spread and it has appeared in most of Europe (including Russia), the United States, South Africa and other countries. In the 1980s, M. cerebralis was found to require a tubificid oligochaete (a kind of segmented worm) to complete its life cycle. The parasite infects its hosts with its cells after piercing them with polar filaments ejected from nematocyst-like capsules.Whirling disease afflicts juvenile fish (fingerlings and fry) and causes skeletal deformation and neurological damage. Fish ""whirl"" forward in an awkward, corkscrew-like pattern instead of swimming normally, find feeding difficult, and are more vulnerable to predators. The mortality rate is high for fingerlings, up to 90% of infected populations, and those that do survive are deformed by the parasites residing in their cartilage and bone. They act as a reservoir for the parasite, which is released into water following the fish's death. M. cerebralis is one of the most economically important myxozoans in fish, as well as one of the most pathogenic. It was the first myxosporean whose pathology and symptoms were described scientifically. The parasite is not transmissible to humans.