1 History of Astronomy - Journigan-wiki
... eternally unchanging. All objects in the heavens were supposed to be perfect circles, except for stars, which were featureless points of light. ...
... eternally unchanging. All objects in the heavens were supposed to be perfect circles, except for stars, which were featureless points of light. ...
Animated Planets PowerPoint Presentation
... magnitude of 9.5 during that orbit. The orbital period of Comet Faye is 7.55 years Its next perihelion will occur on May 29, 2014. During this next appearance, its apparent magnitude is expected to be around 12. The appearance of Comet Faye will come a few short months after what many expected to be ...
... magnitude of 9.5 during that orbit. The orbital period of Comet Faye is 7.55 years Its next perihelion will occur on May 29, 2014. During this next appearance, its apparent magnitude is expected to be around 12. The appearance of Comet Faye will come a few short months after what many expected to be ...
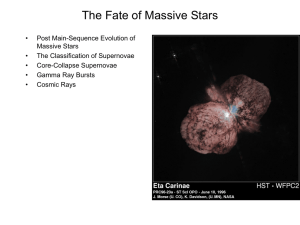
The Fate of Massive Stars
... increased opacity due to presence of various Ions (including Fe) in stellar atmosphere Diagonal upper-luminosity cutoff that is temperature dependent Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM ...
... increased opacity due to presence of various Ions (including Fe) in stellar atmosphere Diagonal upper-luminosity cutoff that is temperature dependent Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM ...
Kaler`s MEASURING THE SKY
... than 12 hours), nights longer (greater than 12 hours). On December 22, the Sun reaches its most southerly extent, at a declination of 23.4 degrees south, at the Winter Solstice to begin northernhemisphere winter (southern hemisphere summer). It then rises as far south of east and sets as far south o ...
... than 12 hours), nights longer (greater than 12 hours). On December 22, the Sun reaches its most southerly extent, at a declination of 23.4 degrees south, at the Winter Solstice to begin northernhemisphere winter (southern hemisphere summer). It then rises as far south of east and sets as far south o ...
Eyeing the retina nebula
... Planetary nebulae are the multicolored remnants of dead stars. When a star about the size of the Sun runs out of nuclear fuel, the core collapses to form a much smaller dwarf star and the outer layers are ejected to form an expanding cloud of dust and gas. Intense radiation from the collapsed star i ...
... Planetary nebulae are the multicolored remnants of dead stars. When a star about the size of the Sun runs out of nuclear fuel, the core collapses to form a much smaller dwarf star and the outer layers are ejected to form an expanding cloud of dust and gas. Intense radiation from the collapsed star i ...
Summer 2014 Mercury - Astronomical Society of the Pacific
... by making it much sharper. He proposed a three-lens form, which later evolved into the four-lens form that is still sometimes used. Thus we see Galileo, Rheita, Marius, and Gassendi all involved in convoluted ways with one another in the development of astronomy during the 1600s. The new Marius Port ...
... by making it much sharper. He proposed a three-lens form, which later evolved into the four-lens form that is still sometimes used. Thus we see Galileo, Rheita, Marius, and Gassendi all involved in convoluted ways with one another in the development of astronomy during the 1600s. The new Marius Port ...
Properties of Stars: The H
... We can also determine the abundances of many elements in stars by using the `atomic fingerprints’ seen in spectral absorption lines. This is a tricky business! We already know that the strength and even presence of absorption lines is strongly temperature dependent. To use absorption line strengths ...
... We can also determine the abundances of many elements in stars by using the `atomic fingerprints’ seen in spectral absorption lines. This is a tricky business! We already know that the strength and even presence of absorption lines is strongly temperature dependent. To use absorption line strengths ...
Lecture 9/10 Stellar evolution Ulf Torkelsson 1 Main sequence stars
... the large expansion of the surface area the star is able to radiate its energy at a lower effective temperature than before. Once the temperature in the outer layers go down its opacity will go up and the star forms a thick outer convection zone. The star then becomes a red giant that moves up the H ...
... the large expansion of the surface area the star is able to radiate its energy at a lower effective temperature than before. Once the temperature in the outer layers go down its opacity will go up and the star forms a thick outer convection zone. The star then becomes a red giant that moves up the H ...
A brightening Sun will boil the seas and bake the continents a billion
... gravity will be so weak that the solar wind will blow a million times stronger than it does today. During the course of its redgiant phase, the Sun will lose approximately 10 percent of its total mass. This gradual mass loss will reduce the Sun’s overall gravitational pull, so it no longer will hol ...
... gravity will be so weak that the solar wind will blow a million times stronger than it does today. During the course of its redgiant phase, the Sun will lose approximately 10 percent of its total mass. This gradual mass loss will reduce the Sun’s overall gravitational pull, so it no longer will hol ...
Stellar Physics - Craigie High School
... A dense star with a sufficiently large mass/small radius could have an escape velocity greater than 3 x 108 m s-1. This means that light emitted from its surface could not escape - hence the name black hole. The physics of the black hole cannot be explained using Newton’s Theory. The correct theory ...
... A dense star with a sufficiently large mass/small radius could have an escape velocity greater than 3 x 108 m s-1. This means that light emitted from its surface could not escape - hence the name black hole. The physics of the black hole cannot be explained using Newton’s Theory. The correct theory ...
Binary Star - Armagh Observatory
... galaxies. They're bright and distinctly disk-shaped, with star-forming gas, dust and bright stars in the spiral arms. Because spiral galaxies are bright, they make up most of the visible galaxies, but they're thought to make up only about 20 percent of the galaxies in the Universe. ...
... galaxies. They're bright and distinctly disk-shaped, with star-forming gas, dust and bright stars in the spiral arms. Because spiral galaxies are bright, they make up most of the visible galaxies, but they're thought to make up only about 20 percent of the galaxies in the Universe. ...
Comparing the Chemical Compositions of the Sun and Earth
... rational to use Si has disappeared. For example, with a silicon normalization, the Earth is enriched relative to the Sun in all the elements which are more refractory than Si (e.g. Fe, Mg, Ni, Ca, Al, Cr, Ti, V, Sr Zr). However, when normalized to Al we see that the Earth is not enriched in anything ...
... rational to use Si has disappeared. For example, with a silicon normalization, the Earth is enriched relative to the Sun in all the elements which are more refractory than Si (e.g. Fe, Mg, Ni, Ca, Al, Cr, Ti, V, Sr Zr). However, when normalized to Al we see that the Earth is not enriched in anything ...
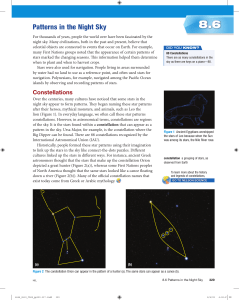
Patterns in the Night Sky
... A star map is a map of the night sky that shows the relative positions of the stars in a particular part of the sky (Figure 4). Some star maps show only those objects that can be seen with the unaided eye, while others show objects that can only be viewed using a telescope or other instrument. A sta ...
... A star map is a map of the night sky that shows the relative positions of the stars in a particular part of the sky (Figure 4). Some star maps show only those objects that can be seen with the unaided eye, while others show objects that can only be viewed using a telescope or other instrument. A sta ...
Sun - UNT Physics
... The preceding chapter gave us a quick overview of the universe, and chapters later in the book will discuss the details. This chapter and the next help us understand what the universe looks like seen from the surface of our spinning planet. But appearances are deceiving. We will see in Chapter 4 how ...
... The preceding chapter gave us a quick overview of the universe, and chapters later in the book will discuss the details. This chapter and the next help us understand what the universe looks like seen from the surface of our spinning planet. But appearances are deceiving. We will see in Chapter 4 how ...
here - ESA Science
... turn means that comparisons can be made between measurements of the same object taken at different times, at different locations and in different wavelengths. Astrometry measurements are instrumental for time keeping. Universal Time is calculated by synchronizing atomic time to the Earth’s rotation. ...
... turn means that comparisons can be made between measurements of the same object taken at different times, at different locations and in different wavelengths. Astrometry measurements are instrumental for time keeping. Universal Time is calculated by synchronizing atomic time to the Earth’s rotation. ...
Starbursts – from 30 Doradus to Lyman
... the Hubble tuning fork, but now from M82-like starbursts via ultraluminous infrared galaxies to the recently discovered SCUBA galaxies, as well as from Lyman-break galaxies through luminous compact blue galaxies, perhaps down to dwarf ellipticals. It appears that the frequency of starbursts was larg ...
... the Hubble tuning fork, but now from M82-like starbursts via ultraluminous infrared galaxies to the recently discovered SCUBA galaxies, as well as from Lyman-break galaxies through luminous compact blue galaxies, perhaps down to dwarf ellipticals. It appears that the frequency of starbursts was larg ...
HR Diagram
... __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. If star Large and star Small were the same temperature, explain why Large would appear brighter. __________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. If star Large and star Small were the same temperature, explain why Large would appear brighter. __________________ ...
03jan13.ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... • It takes time for the more direct sunlight to heat up the land and water. • Therefore, July & August are typically hotter than June. ...
... • It takes time for the more direct sunlight to heat up the land and water. • Therefore, July & August are typically hotter than June. ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
... If there is not enough material in the protostar, one possible outcome is a brown dwarf (a large, not-veryluminous celestial body having a mass between 1028 kg and 84 x 1028 kg). A Newborn Star: When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction ...
... If there is not enough material in the protostar, one possible outcome is a brown dwarf (a large, not-veryluminous celestial body having a mass between 1028 kg and 84 x 1028 kg). A Newborn Star: When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction ...
o - Salem State University
... 1.Let's say we find a star that is located on the following points or circles in the sky. Then, on the same night we move to a location on Earth that is some significant distance from our first location. There will now be a different star at or on: a. the celestial north pole b. the zenith c. the ce ...
... 1.Let's say we find a star that is located on the following points or circles in the sky. Then, on the same night we move to a location on Earth that is some significant distance from our first location. There will now be a different star at or on: a. the celestial north pole b. the zenith c. the ce ...
CHAP
... - They are made up mainly of ________ and produce __________ through nuclear fusion. - The nuclear energy released from the nuclear fusion is ___________ into electromagnetic radiation. - This conversion of energy makes stars shine ____________. - Astronomers classify stars according to their physic ...
... - They are made up mainly of ________ and produce __________ through nuclear fusion. - The nuclear energy released from the nuclear fusion is ___________ into electromagnetic radiation. - This conversion of energy makes stars shine ____________. - Astronomers classify stars according to their physic ...