PSC100 Summary Chapters 1 to Chapter 9
... frequency components and spectra elements of these signals. If we do, we can achieve phenomenal insights into the complex structure and evolution of things that are billions of light years away from us in space and which we will never be able to visit or experiment on first hand. When we study the u ...
... frequency components and spectra elements of these signals. If we do, we can achieve phenomenal insights into the complex structure and evolution of things that are billions of light years away from us in space and which we will never be able to visit or experiment on first hand. When we study the u ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do NOT evolve to the Wolf-Rayet stage: they never completely lose the hydrogen in their outer layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining cor ...
... Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do NOT evolve to the Wolf-Rayet stage: they never completely lose the hydrogen in their outer layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining cor ...
slides - Indico
... studied at higher resolution to understand detailed predictions of nucleosynthesis models ...
... studied at higher resolution to understand detailed predictions of nucleosynthesis models ...
There He Goes Again - GeocentrismDebunked.org
... Magellanic Cloud, neighbouring the Milky Way, which, cosmically speaking, is in our backyard. The distance of the Large Magellanic Cloud using the appropriate techniques of the Cosmic Distance Ladder matches this geometric measurement perfectly. The concept of a small (10,000 light years radius) Uni ...
... Magellanic Cloud, neighbouring the Milky Way, which, cosmically speaking, is in our backyard. The distance of the Large Magellanic Cloud using the appropriate techniques of the Cosmic Distance Ladder matches this geometric measurement perfectly. The concept of a small (10,000 light years radius) Uni ...
Theoretical Predictions for Mass Loss Rates: Rotation & Pulsation
... Hot star winds: pulsations & waves • Cranmer (1996, 2007) showed that low-frequency modes that are evanescent in the photosphere can leak out into a CAK-type stellar wind. ...
... Hot star winds: pulsations & waves • Cranmer (1996, 2007) showed that low-frequency modes that are evanescent in the photosphere can leak out into a CAK-type stellar wind. ...
Week 2
... 1. Start on the day that star time and solar time match up at midnight (Sept. 21) 2. Determine star time at midnight on the day you want 3. Determine star time for the clock time you want 4. Stars having RA within about 6 h of that star time will be visible ...
... 1. Start on the day that star time and solar time match up at midnight (Sept. 21) 2. Determine star time at midnight on the day you want 3. Determine star time for the clock time you want 4. Stars having RA within about 6 h of that star time will be visible ...
Slide 1
... giant and apply the method of spectroscopic parallax to determine its distance. How does this affect your distance estimate? a. Betelgeuse is closer than your estimate. b. Betelgeuse is farther than your estimate. c. The distance estimate is not affected by ...
... giant and apply the method of spectroscopic parallax to determine its distance. How does this affect your distance estimate? a. Betelgeuse is closer than your estimate. b. Betelgeuse is farther than your estimate. c. The distance estimate is not affected by ...
Studying Variable stars using Small Telescopes Observational
... believed that there should also exist a systematic long-term variations. These long-term variations or Stellar Activity Cycles are very similar to the solar 11-year sunspot cycle or 22-year magnetic cycle. The study of stellar activity is one of important areas where knowledge of existence of activi ...
... believed that there should also exist a systematic long-term variations. These long-term variations or Stellar Activity Cycles are very similar to the solar 11-year sunspot cycle or 22-year magnetic cycle. The study of stellar activity is one of important areas where knowledge of existence of activi ...
astro-ph/0504597 PDF
... and electrons are pushed together to form neutrons and neutrinos. Even though neutrinos don’t interact easily with matter, at densities as high as they are here, they exert a tremendous outward pressure. The other is, outer layers fall inward when the iron core collapses. When the core stops collaps ...
... and electrons are pushed together to form neutrons and neutrinos. Even though neutrinos don’t interact easily with matter, at densities as high as they are here, they exert a tremendous outward pressure. The other is, outer layers fall inward when the iron core collapses. When the core stops collaps ...
ASTRONOMICAL SURVEYING - I - IDC
... Celestial Sphere. The millions of stars that we see in the sky on a clear cloudless night are all at varying distances from us. Since we are concerned with their relative distance rather than their actual distance from the observer. It is exceedingly convenient to picture the stars as distributed ov ...
... Celestial Sphere. The millions of stars that we see in the sky on a clear cloudless night are all at varying distances from us. Since we are concerned with their relative distance rather than their actual distance from the observer. It is exceedingly convenient to picture the stars as distributed ov ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... Classical indicators of what is going on: The limit of the Balmer series and the blending of the high-order Balmer lines produces a discontinuity of the spectrum blueward of 3650°A. (the Balmer break) –more important in young populations, The break amplitude and position is a proxy for the age of th ...
... Classical indicators of what is going on: The limit of the Balmer series and the blending of the high-order Balmer lines produces a discontinuity of the spectrum blueward of 3650°A. (the Balmer break) –more important in young populations, The break amplitude and position is a proxy for the age of th ...
Complete the “Assess Your Understanding” including
... Complete the “Assess Your Understanding” including “got it” on page 107. How does gravity help form planets, stars, and solar systems? Scientists think that _________________ helps form solar systems by __________ __________________________________________________________________. Accretion is _____ ...
... Complete the “Assess Your Understanding” including “got it” on page 107. How does gravity help form planets, stars, and solar systems? Scientists think that _________________ helps form solar systems by __________ __________________________________________________________________. Accretion is _____ ...
Astronomy - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... questions about science, technology and global issues. Students will be challenged and encouraged to take risks and to develop critical thinking Skills as they apply to real-world experiences. Course Description: This course will provide an overview of fundamental concepts in Astronomy, from its his ...
... questions about science, technology and global issues. Students will be challenged and encouraged to take risks and to develop critical thinking Skills as they apply to real-world experiences. Course Description: This course will provide an overview of fundamental concepts in Astronomy, from its his ...
8th Grade Earth Science Objectives
... By plotting the path of two hurricanes, students investigate the travel paths and destruction of hurricanes. Global atmospheric movement is a hurricane helping to dissipate some of Earth’s atmospheric heat and energy. Students keep track of Oklahoma’s changing weather for a period of two weeks. They ...
... By plotting the path of two hurricanes, students investigate the travel paths and destruction of hurricanes. Global atmospheric movement is a hurricane helping to dissipate some of Earth’s atmospheric heat and energy. Students keep track of Oklahoma’s changing weather for a period of two weeks. They ...
虚拟天文台引领天文学网络化协同工作 - Chinese Virtual Observatory
... • Candidate Milky Way satellites in the Galactic halo(Liu et al., 2008, A&A) • SDSS DR5 photometric data were searched for new Milky Way companions or substructures in the Galactic halo. • Data analysis procedures were based on the VO-DAS. • Five candidates are identified as over-dense faint stellar ...
... • Candidate Milky Way satellites in the Galactic halo(Liu et al., 2008, A&A) • SDSS DR5 photometric data were searched for new Milky Way companions or substructures in the Galactic halo. • Data analysis procedures were based on the VO-DAS. • Five candidates are identified as over-dense faint stellar ...
the life cycles of stars (5) - U3A Bendigo Courses / Activities
... billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Our sun emits a solar wind of protons and electrons which can cause aurorae and in ce ...
... billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Our sun emits a solar wind of protons and electrons which can cause aurorae and in ce ...
Basics – II. Time, Magnitudes and Spectral types
... It is convenient for many human pursuits to use the Earth’s diurnal and annual motion (the day and year) as a basis for time-keeping. The rotation of the Earth on its axis is fundamental to us; our waking and sleeping cycles are determined by it. It is, however, not strictly constant. Perhaps the ea ...
... It is convenient for many human pursuits to use the Earth’s diurnal and annual motion (the day and year) as a basis for time-keeping. The rotation of the Earth on its axis is fundamental to us; our waking and sleeping cycles are determined by it. It is, however, not strictly constant. Perhaps the ea ...
Unit 11: Stellar Evolution
... • Chemical nature: mostly hydrogen, most of the rest is helium, and some heavier elements. • Physical nature: mostly gas, some solid particles. ...
... • Chemical nature: mostly hydrogen, most of the rest is helium, and some heavier elements. • Physical nature: mostly gas, some solid particles. ...
CHAPTER 14
... 11. The star slowly enters a new red giant phase and its position on the H-R diagram moves to the right and upward. 12. Stars more massive than 2 solar masses do not experience a helium flash. Their cores make a smooth transition to helium burning without becoming degenerate. When their helium suppl ...
... 11. The star slowly enters a new red giant phase and its position on the H-R diagram moves to the right and upward. 12. Stars more massive than 2 solar masses do not experience a helium flash. Their cores make a smooth transition to helium burning without becoming degenerate. When their helium suppl ...
Standing in Awe - Auckland Astronomical Society
... Libra lies prominently in the June sky, preceding the Scorpion across the sky. At 538° square in size, Libra is one of the larger constellations, though its stars are poorly shown, the brightest attaining magnitude 2.6. In fact, Libra is one of the poorer adorned constellations, there being only 2.4 ...
... Libra lies prominently in the June sky, preceding the Scorpion across the sky. At 538° square in size, Libra is one of the larger constellations, though its stars are poorly shown, the brightest attaining magnitude 2.6. In fact, Libra is one of the poorer adorned constellations, there being only 2.4 ...
The Lives of Stars
... moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
... moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
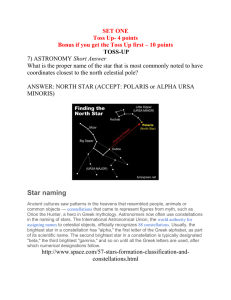
TOSS-UP 7) ASTRONOMY Short Answer
... Ancient cultures saw patterns in the heavens that resembled people, animals or common objects — constellations that came to represent figures from myth, such as Orion the Hunter, a hero in Greek mythology. Astronomers now often use constellations in the naming of stars. The International Astronomica ...
... Ancient cultures saw patterns in the heavens that resembled people, animals or common objects — constellations that came to represent figures from myth, such as Orion the Hunter, a hero in Greek mythology. Astronomers now often use constellations in the naming of stars. The International Astronomica ...