Astronomy Triemester Review Sheet 2015
... 6. What fuel source is used to power stars? What happens when that first source is used? 7. Describe how small and large stars move through their life cycles and die. Use the terms: red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, supergiant, super nova, neutron star, black hole, main sequence 8. What is t ...
... 6. What fuel source is used to power stars? What happens when that first source is used? 7. Describe how small and large stars move through their life cycles and die. Use the terms: red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, supergiant, super nova, neutron star, black hole, main sequence 8. What is t ...
Earth and Space Science - Standards Aligned System
... learn about early Earth by studying objects in the solar system such as lunar rocks, asteroids, comets, and meteorites, which have changed ...
... learn about early Earth by studying objects in the solar system such as lunar rocks, asteroids, comets, and meteorites, which have changed ...
draft - Standards Aligned System
... The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted physical processes and laws. The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted ...
... The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted physical processes and laws. The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted ...
Ch 11c and 12 ( clusters 3-31-11)
... •Young stars near clouds of gas and dust •Contraction and heating of clouds into protostars • Hydrogen fusion stops collapse II. Leaving the Main Sequence: Hydrogen fusion stops 1. Low mass stars (M < 0.4 solar masses) Not enough mass to ever fuse any element heavier than Hydrogen → white dwarf 2.In ...
... •Young stars near clouds of gas and dust •Contraction and heating of clouds into protostars • Hydrogen fusion stops collapse II. Leaving the Main Sequence: Hydrogen fusion stops 1. Low mass stars (M < 0.4 solar masses) Not enough mass to ever fuse any element heavier than Hydrogen → white dwarf 2.In ...
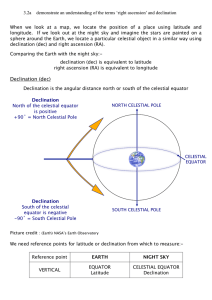
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... effect represents the hours (angular distance eastwards) from the reference point that a particular celestial object will be. As an example, the celestial coordinates of the star BETELGEUSE in the constellation Orion are:Right Ascension = 5 hours 52 minutes : Declination = +7 degrees 24 minutes. ...
... effect represents the hours (angular distance eastwards) from the reference point that a particular celestial object will be. As an example, the celestial coordinates of the star BETELGEUSE in the constellation Orion are:Right Ascension = 5 hours 52 minutes : Declination = +7 degrees 24 minutes. ...
The Sky is holy
... These are most common opinions about Sky and celestial bodies. But how this holyness reflects in ethnoastronomy, especially in constellation names and where are the roots of these names. The classic star map has only some constellations with hidden Olympic roots (Orion – as god of war, Cygnus – as Z ...
... These are most common opinions about Sky and celestial bodies. But how this holyness reflects in ethnoastronomy, especially in constellation names and where are the roots of these names. The classic star map has only some constellations with hidden Olympic roots (Orion – as god of war, Cygnus – as Z ...
“extras” available for your scope?
... transmits a range of light near the two strong spectral lines of doubly ionized oxygen (designated OIII) while blocking all other light. An OIII filter works best for emission and planetary nebulae. This filter, coupled with an 8-inch or larger telescope under a moderately light-polluted sky, will s ...
... transmits a range of light near the two strong spectral lines of doubly ionized oxygen (designated OIII) while blocking all other light. An OIII filter works best for emission and planetary nebulae. This filter, coupled with an 8-inch or larger telescope under a moderately light-polluted sky, will s ...
Determining the Origin of Inner Planetary System Debris Orbiting the
... objects, then we reject the original assumption that the dust is being produced in an active planetesimal belt and instead conclude that the dust was produced in a transient event connected to the formation of a rocky planet. For the systems considered by our team, the copious amounts of dust are st ...
... objects, then we reject the original assumption that the dust is being produced in an active planetesimal belt and instead conclude that the dust was produced in a transient event connected to the formation of a rocky planet. For the systems considered by our team, the copious amounts of dust are st ...
Nemesis - The Evergreen State College
... test the 19MJupiter that I have earlier presented. First, assuming that all planets in the Solar System have negligible effects on the Sun, a Saturn size Nemesis would also have a negligible effect on Sol and therefor be undetectable. To test the 19 MJupiter we will use Kepler’s First law to find th ...
... test the 19MJupiter that I have earlier presented. First, assuming that all planets in the Solar System have negligible effects on the Sun, a Saturn size Nemesis would also have a negligible effect on Sol and therefor be undetectable. To test the 19 MJupiter we will use Kepler’s First law to find th ...
The Sun: Example of Radiation Laws
... High-mass stars (M > 8M⊙ ) evolve into both red and blue giants and supergiants as their cores burn heavier and heavier elements. ...
... High-mass stars (M > 8M⊙ ) evolve into both red and blue giants and supergiants as their cores burn heavier and heavier elements. ...
English Summary
... wavelength the elements emit. These wavelengths are normally very small and are measured in units such as nanometers (1 nm = 0.000000001 meters). Since the light that we see is a combination of many wavelengths from different elements, how can we distinguish them? Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) solved ...
... wavelength the elements emit. These wavelengths are normally very small and are measured in units such as nanometers (1 nm = 0.000000001 meters). Since the light that we see is a combination of many wavelengths from different elements, how can we distinguish them? Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) solved ...
Open Houses at the Campus Observatory Astronomical Horizons Lecture
... left behind by a massive-star supernova Degeneracy pressure of neutrons supports a neutron star against gravity ...
... left behind by a massive-star supernova Degeneracy pressure of neutrons supports a neutron star against gravity ...
Astronomy Part 1 - Malvern Troop 7
... You will be standing relatively still for possible a long time. In cold weather, dress as if it was 10 – 20 F colder than it actually is. In the summer, make sure to wear insect repellant, no open toe shoes (sandals). Ideally, survey the area you are going to be observing in during daylight. Bring f ...
... You will be standing relatively still for possible a long time. In cold weather, dress as if it was 10 – 20 F colder than it actually is. In the summer, make sure to wear insect repellant, no open toe shoes (sandals). Ideally, survey the area you are going to be observing in during daylight. Bring f ...
The Galactic Halo The Galactic Disk Height and Thickness of MW
... young stars, but old stars are also present. rich in dust and gas. star formation is ongoing. stars moving in circular orbits around the Galactic center. ...
... young stars, but old stars are also present. rich in dust and gas. star formation is ongoing. stars moving in circular orbits around the Galactic center. ...
What is X-ray Astronomy? - Extreme Universe Laboratory
... …and much more efficient X-ray Astronomy tries to find out what could cause such extraordinary power ...
... …and much more efficient X-ray Astronomy tries to find out what could cause such extraordinary power ...
Coordinates and Time - University of Florida Astronomy
... The modern standard time is based upon the SI second, which is defined in terms of the oscillations for a particular transition of 133Cs rather than astronomical measures. One second = 9192631770 oscillations. IAT is effectively the atomic equivalent of UT, based upon atomic clocks instead of mean s ...
... The modern standard time is based upon the SI second, which is defined in terms of the oscillations for a particular transition of 133Cs rather than astronomical measures. One second = 9192631770 oscillations. IAT is effectively the atomic equivalent of UT, based upon atomic clocks instead of mean s ...
The Big Dipper is a
... If your astrological sign is Aries, the Sun should be in the constellation Aries on your birthday. The dates, according to astrological tradition, during which the Sun is in the constellation Aries are: March 21 to April 20th. In which constellation is the Sun actually in, during this time period? a ...
... If your astrological sign is Aries, the Sun should be in the constellation Aries on your birthday. The dates, according to astrological tradition, during which the Sun is in the constellation Aries are: March 21 to April 20th. In which constellation is the Sun actually in, during this time period? a ...
Earth in Space - Learning Outcomes
... A dense star with a sufficiently large mass/small radius could have an escape velocity greater than 3 x 108 m s-1. This means that light emitted from its surface could not escape - hence the name black hole. The physics of the black hole cannot be explained using Newton’s Theory. The correct theory ...
... A dense star with a sufficiently large mass/small radius could have an escape velocity greater than 3 x 108 m s-1. This means that light emitted from its surface could not escape - hence the name black hole. The physics of the black hole cannot be explained using Newton’s Theory. The correct theory ...
Making Heavier Metals
... have not yet evolved to the AGB phase. Hence they are totally unable to produce heavy elements. So how can there be heavy elements in the CH-stars? This mystery was solved when it was realized that the CH-stars all belong to binary systems and that they therefore have a companion star [5]. That comp ...
... have not yet evolved to the AGB phase. Hence they are totally unable to produce heavy elements. So how can there be heavy elements in the CH-stars? This mystery was solved when it was realized that the CH-stars all belong to binary systems and that they therefore have a companion star [5]. That comp ...
The Death of High Mass Stars
... hundred light years across) in our Galaxy (the Interstellar Medium stuff between the stars). The atoms and molecules in these clouds are moving with speeds according to the temperature of the cloud. If the cloud is cold enough, the particles will begin to come together due to the attractive force of ...
... hundred light years across) in our Galaxy (the Interstellar Medium stuff between the stars). The atoms and molecules in these clouds are moving with speeds according to the temperature of the cloud. If the cloud is cold enough, the particles will begin to come together due to the attractive force of ...
The Constellations
... • Stars do move back a nd forth (a teeny-tiny bit) in the sky over the course of the year also, due to the revolution of Earth around the Sun (stellar parallax). Note that this motion is not possible to observe without the help of modern telescopes. • Position of stars is different at different loca ...
... • Stars do move back a nd forth (a teeny-tiny bit) in the sky over the course of the year also, due to the revolution of Earth around the Sun (stellar parallax). Note that this motion is not possible to observe without the help of modern telescopes. • Position of stars is different at different loca ...
AWG recommendation on Cosmic Vision
... first census of the frequency of Earth-like planets. GAIA will deliver important insights into the frequency of giant planets; the existence and location of such planets is crucial for the possible existence of Earth-like planets in the habitable zone. GAIA will also further improve our understandin ...
... first census of the frequency of Earth-like planets. GAIA will deliver important insights into the frequency of giant planets; the existence and location of such planets is crucial for the possible existence of Earth-like planets in the habitable zone. GAIA will also further improve our understandin ...