Ia 超新星的
... of Hamuy et al. (2003): why hydrogen has been detected only in case of SN 2002ic since there exist about 100 spectra of Sne Ia? The main problem of this scenario is that one would expect to observe a range of Ha lines in Sne Ia, depending on the amount of circunstellar material (in turn, determined ...
... of Hamuy et al. (2003): why hydrogen has been detected only in case of SN 2002ic since there exist about 100 spectra of Sne Ia? The main problem of this scenario is that one would expect to observe a range of Ha lines in Sne Ia, depending on the amount of circunstellar material (in turn, determined ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... different temperatures, from O0 (hottest) to M9 (coolest). The reason for the changes between the classes was to do with some atoms becoming ionised at various temperature and at cooler temperature the light may not have sufficient energy to excite the atoms to create spectral lines. This meant th ...
... different temperatures, from O0 (hottest) to M9 (coolest). The reason for the changes between the classes was to do with some atoms becoming ionised at various temperature and at cooler temperature the light may not have sufficient energy to excite the atoms to create spectral lines. This meant th ...
The Milky Way
... • You ARE responsible for understanding the topics covered in class (including details in the book that I may not have mentioned). • You are NOT responsible for other stuff in these chapters not covered at all in lecture. ...
... • You ARE responsible for understanding the topics covered in class (including details in the book that I may not have mentioned). • You are NOT responsible for other stuff in these chapters not covered at all in lecture. ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... • Larger, more luminous stars will pulsate with longer periods than the smaller, fainter stars – because gravity takes longer to pull the more extended outer layers of the larger stars back ...
... • Larger, more luminous stars will pulsate with longer periods than the smaller, fainter stars – because gravity takes longer to pull the more extended outer layers of the larger stars back ...
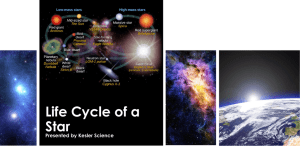
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary Low mass stars – • Half as massive as the Sun • Can live 80 to 100 billion years in Main ...
... Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary Low mass stars – • Half as massive as the Sun • Can live 80 to 100 billion years in Main ...
The magnitudes of stars
... Apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude How bright a star looks when viewed from the Earth is given by its apparent magnitude. However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but ...
... Apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude How bright a star looks when viewed from the Earth is given by its apparent magnitude. However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but ...
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets
... these step by step below. It turns out that 51 Peg is about the same mass as the sun so to measure the semi-major axis, we can use Kepler’s 3rd Law (without Newton’s modification). If the period is measured in years, then we obtain the semi-major axis in A.U. from P2 = a3. a. Calculate the semi-majo ...
... these step by step below. It turns out that 51 Peg is about the same mass as the sun so to measure the semi-major axis, we can use Kepler’s 3rd Law (without Newton’s modification). If the period is measured in years, then we obtain the semi-major axis in A.U. from P2 = a3. a. Calculate the semi-majo ...
Full Press Release - The Open University
... surface into interstellar space during the final phases of their life. Dust is formed in the ejected gas, and this mixture of gas and dust expands outward and escapes from the star. This “mass loss” process is so important that it may well determine the final stage of the star’s life. Stars with mas ...
... surface into interstellar space during the final phases of their life. Dust is formed in the ejected gas, and this mixture of gas and dust expands outward and escapes from the star. This “mass loss” process is so important that it may well determine the final stage of the star’s life. Stars with mas ...
HR Diagram and Stellar Fusion
... black dwarf, as cold as Pluto and the size of Earth destined for every to orbit the galaxy as a really big hard sphere of carbon—some astronomers think that because diamonds are just dense lumps of carbon the Sun will be a diamond forever. ...
... black dwarf, as cold as Pluto and the size of Earth destined for every to orbit the galaxy as a really big hard sphere of carbon—some astronomers think that because diamonds are just dense lumps of carbon the Sun will be a diamond forever. ...
Stars - Mrs. Tosh`s class
... A star is made up of different elements in the form of gases. The inner layers of a star are very dense and hot. But the outer layers of a star, or a star's atmosphere, are made up of cool gases. ...
... A star is made up of different elements in the form of gases. The inner layers of a star are very dense and hot. But the outer layers of a star, or a star's atmosphere, are made up of cool gases. ...