Charcteristic of Stars Powerpoint C
... approximately 695,000 km, or about 109 times the radius of Earth. So the sun would equal 1 solar radius. • In comparison white dwarfs are about the same size as Earth and would equal 0.01 solar radius. Supergiants can have sizes up to 1,000 solar radii. ...
... approximately 695,000 km, or about 109 times the radius of Earth. So the sun would equal 1 solar radius. • In comparison white dwarfs are about the same size as Earth and would equal 0.01 solar radius. Supergiants can have sizes up to 1,000 solar radii. ...
Binary Stars - Mid-Pacific Institute
... What is a binary star? a star system made up of usually two stars that orbit around one center of mass, where the mass is most concentrated A binary star is not to be confused with two stars that appear close together to the naked eye from Earth, but in reality are very far apart ...
... What is a binary star? a star system made up of usually two stars that orbit around one center of mass, where the mass is most concentrated A binary star is not to be confused with two stars that appear close together to the naked eye from Earth, but in reality are very far apart ...
Evolution of High
... degenerate pressure of the newly formed neutron core, if the star is not too heavy. • The core becomes a neutron star with a mass of about 1 Msun, with a size of just a few kilometer! (Chapter 13) • If the mass of the star is high enough to overcome the neutron degenerate pressure, then the core col ...
... degenerate pressure of the newly formed neutron core, if the star is not too heavy. • The core becomes a neutron star with a mass of about 1 Msun, with a size of just a few kilometer! (Chapter 13) • If the mass of the star is high enough to overcome the neutron degenerate pressure, then the core col ...
Stars III - Indiana University Astronomy
... has occurred since the creation of the universe, only 2% of the ordinary matter in the universe is now in the form of heavy elements. Most is still hydrogen and helium ...
... has occurred since the creation of the universe, only 2% of the ordinary matter in the universe is now in the form of heavy elements. Most is still hydrogen and helium ...
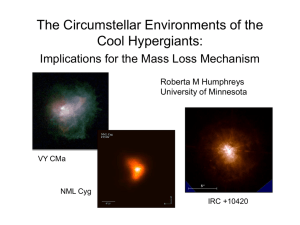
Circumstellar
... IRC +10420 – excellent candidate for post– red supergiant evolution In post RSG evolution, these stars will enter a region (6000-9000 K) of increased dynamical instability, high mass loss, increasing opacity – deJager’s “yellow void” HST/STIS spatially resolved spectroscopy – Halpha – uniform outfl ...
... IRC +10420 – excellent candidate for post– red supergiant evolution In post RSG evolution, these stars will enter a region (6000-9000 K) of increased dynamical instability, high mass loss, increasing opacity – deJager’s “yellow void” HST/STIS spatially resolved spectroscopy – Halpha – uniform outfl ...
elementary measuring stars
... Answer: Pick almost any stellar property to measure (mass, luminosity, size, temperature), and the Sun resides near the geometric mean of the range. However, in terms of absolute numbers of stars, small stars are much more ...
... Answer: Pick almost any stellar property to measure (mass, luminosity, size, temperature), and the Sun resides near the geometric mean of the range. However, in terms of absolute numbers of stars, small stars are much more ...
Chapter 13 section 3
... What is a white dwarf? The star’s core contracts even more after it uses much of its helium and the outer layers escape into space. This leaves only the hot, dense core. At this stage in a star’s life cycle, it is about the size of Earth. It is called a white dwarf. In time, the white dwarf will coo ...
... What is a white dwarf? The star’s core contracts even more after it uses much of its helium and the outer layers escape into space. This leaves only the hot, dense core. At this stage in a star’s life cycle, it is about the size of Earth. It is called a white dwarf. In time, the white dwarf will coo ...
Stars
... toward each other by gravity • Many stars orbit each other • More than 50% of stars occur in pairs or multiples. • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate – It’s mass ...
... toward each other by gravity • Many stars orbit each other • More than 50% of stars occur in pairs or multiples. • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate – It’s mass ...
H-R Diagram
... such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the Star collection. Information about each star is displayed on the right side of th ...
... such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the Star collection. Information about each star is displayed on the right side of th ...
Star Basics
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
Chapter 10: Measuring the Stars - Otto
... • (If sun were 10 pc from us, its apparent magnitude would be 4.8, which is faint) ...
... • (If sun were 10 pc from us, its apparent magnitude would be 4.8, which is faint) ...
notes
... Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) for ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995. 1,500 galaxies at various stages of evolution. Most of the galaxies are so faint (nearly 30th magnitude or about four-billion times fainter than can be seen by the human eye) they have never before b ...
... Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) for ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995. 1,500 galaxies at various stages of evolution. Most of the galaxies are so faint (nearly 30th magnitude or about four-billion times fainter than can be seen by the human eye) they have never before b ...
What is an astrolabe
... instrument representing the movement of the sun and the stars. •The astrolabe became symbolic of astronomy and ...
... instrument representing the movement of the sun and the stars. •The astrolabe became symbolic of astronomy and ...
Homework No. 2 Solutions
... Go to the Wikipedia article on spectroscopy (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spectroscopy) and scroll down to the section on “Fluorescence” and examine the spectrum shown there from a fluorescent light (the long tube type of lights or the new compact ones that are tubes in a spiral shape). Answer q ...
... Go to the Wikipedia article on spectroscopy (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spectroscopy) and scroll down to the section on “Fluorescence” and examine the spectrum shown there from a fluorescent light (the long tube type of lights or the new compact ones that are tubes in a spiral shape). Answer q ...
Astronomy 21 – Test 2 – Answers
... There are at least two options, you only need to mention one for full credit (and repeating silhouettes does not earn points). (a) Dust will get heated by proto-stars that are inside those dark clouds. The temperatures of the dust may rise to a few hundred degrees Kelvin. Warm dust grains then emit ...
... There are at least two options, you only need to mention one for full credit (and repeating silhouettes does not earn points). (a) Dust will get heated by proto-stars that are inside those dark clouds. The temperatures of the dust may rise to a few hundred degrees Kelvin. Warm dust grains then emit ...