The Celestial Sphere
... First Point of Aries (Υ) The point on the celestial sphere where the ecliptic cuts the equinoctial when the sun just passes the equinoctial from south to north, also known as the vernal equinox position of the sun, which occurs on 21st of March. First Point of Libra The point on the celestial sph ...
... First Point of Aries (Υ) The point on the celestial sphere where the ecliptic cuts the equinoctial when the sun just passes the equinoctial from south to north, also known as the vernal equinox position of the sun, which occurs on 21st of March. First Point of Libra The point on the celestial sph ...
proper motion
... The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as ...
... The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as ...
Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars How do we measure stellar
... those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: white dwarfs. ...
... those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: white dwarfs. ...
Stars
... Sun) is Sirius. It is 2.6 pc from Earth. How long does it take light from Sirius to reach us? ...
... Sun) is Sirius. It is 2.6 pc from Earth. How long does it take light from Sirius to reach us? ...
StarIntro_sb12
... whole number) for an amount greater than or (X a decimal number) for an amount less than the AM of the Sun. ...
... whole number) for an amount greater than or (X a decimal number) for an amount less than the AM of the Sun. ...
doc - Jnoodle
... In the center we have the sun, our closest star. There are so far 9 known planets, of which the 5 inner have been known since ancient times, Uranus was discovered in the 18th and Neptune in the 19th century, Pluto as late as 1930. The gravitational disturbances on the orbits of thus far known planet ...
... In the center we have the sun, our closest star. There are so far 9 known planets, of which the 5 inner have been known since ancient times, Uranus was discovered in the 18th and Neptune in the 19th century, Pluto as late as 1930. The gravitational disturbances on the orbits of thus far known planet ...
Chapter21
... In most other introductory astronomy textbooks, binary stars are covered in a piecemeal fashion in several different chapters. There are several reasons why I decided to cover binary stars in a single coherent chapter. First, most stars are in binary or multiple systems, so it isn’t reasonable to tr ...
... In most other introductory astronomy textbooks, binary stars are covered in a piecemeal fashion in several different chapters. There are several reasons why I decided to cover binary stars in a single coherent chapter. First, most stars are in binary or multiple systems, so it isn’t reasonable to tr ...
poster
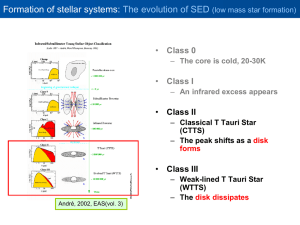
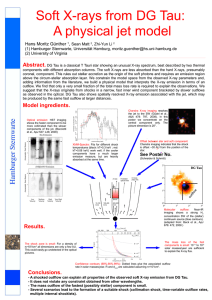
... Abstract. DG Tau is a classical T Tauri star showing an unusual X-ray spectrum, best described by two thermal components with different absorption columns. The soft X-rays are less absorbed than the hard X-rays, presumably coronal, component. This rules out stellar accretion as the origin of the sof ...
... Abstract. DG Tau is a classical T Tauri star showing an unusual X-ray spectrum, best described by two thermal components with different absorption columns. The soft X-rays are less absorbed than the hard X-rays, presumably coronal, component. This rules out stellar accretion as the origin of the sof ...
Stars
... million miles (1 AU) from Earth. • It is estimated to reach about 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees ...
... million miles (1 AU) from Earth. • It is estimated to reach about 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees ...
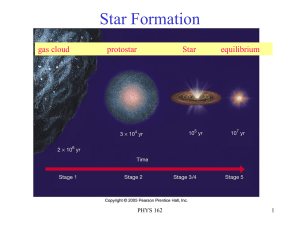
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
Measuring The Parallax of Barnard's Star
... established rate of proper motion of 10.37 arcseconds per year. And, the velocity in arcseconds per year times the distance in parsecs gives the velocity in astronomical units (au) per year. Using our derived numbers we get that the projected velocity is 19.3 au/yr. A natural question to ask is: why ...
... established rate of proper motion of 10.37 arcseconds per year. And, the velocity in arcseconds per year times the distance in parsecs gives the velocity in astronomical units (au) per year. Using our derived numbers we get that the projected velocity is 19.3 au/yr. A natural question to ask is: why ...
Iron does not burn.
... spin (i.e., anti-parallel). The energy state of an electron spinning anti-parallel is slightly lower than the energy state of a parallel-spin electron. Remember that the atom always wants to be in the lowest energy state possible, so the electron will eventually flip to the antiparallel spin directi ...
... spin (i.e., anti-parallel). The energy state of an electron spinning anti-parallel is slightly lower than the energy state of a parallel-spin electron. Remember that the atom always wants to be in the lowest energy state possible, so the electron will eventually flip to the antiparallel spin directi ...