Support worksheet – Topic 3 Questions
... Two stars have the same apparent brightness but the distance from Earth to star X is L double the distance from Earth to star Y. Calculate the ratio of luminosities X . LY ...
... Two stars have the same apparent brightness but the distance from Earth to star X is L double the distance from Earth to star Y. Calculate the ratio of luminosities X . LY ...
Star
... -Since different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, elements can be determined. -Stars are made up of gas elements. (Hydrogen is the most common!) ...
... -Since different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, elements can be determined. -Stars are made up of gas elements. (Hydrogen is the most common!) ...
THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... between them is of no consequence to day-to-day observations. We therefore imagine the stars to remain fixed on a sphere of very large radius with the earth at its centre. We call this sphere the celestial sphere. At any point of time we can only see the upper half of the celestial sphere. The point ...
... between them is of no consequence to day-to-day observations. We therefore imagine the stars to remain fixed on a sphere of very large radius with the earth at its centre. We call this sphere the celestial sphere. At any point of time we can only see the upper half of the celestial sphere. The point ...
Solar System Project
... 8th Grade Science Mrs. Hickle, Mrs. Kirts, Mr. Powell Due starting April 27-28 (full credit) April 29 (-20 pts) April 30 (-30 pts & final day) We are all made of star material. The atoms of some of the elements that make up our bodies were created in the stars. And just like living things, stars are ...
... 8th Grade Science Mrs. Hickle, Mrs. Kirts, Mr. Powell Due starting April 27-28 (full credit) April 29 (-20 pts) April 30 (-30 pts & final day) We are all made of star material. The atoms of some of the elements that make up our bodies were created in the stars. And just like living things, stars are ...
The illustration shows the Sun just after it has made the transition to
... It is tricky to explain the reason why the atmospheres of stars “boil” outwards – and cool off in the process to a “red” or at least “orange” color – as the star gets brighter. Let me put it this way. If the atmosphere of the star was perfectly transparent, then it would not boil outwards. The extra ...
... It is tricky to explain the reason why the atmospheres of stars “boil” outwards – and cool off in the process to a “red” or at least “orange” color – as the star gets brighter. Let me put it this way. If the atmosphere of the star was perfectly transparent, then it would not boil outwards. The extra ...
main sequence star
... • The outer gases are lost, which allows us to see the core of the star. The white dwarf is very dense and hot. The emit (release) less light than they did when they were stars. • As these white dwarfs cool they become fainter. • When there is no more energy being emitted (released), they are called ...
... • The outer gases are lost, which allows us to see the core of the star. The white dwarf is very dense and hot. The emit (release) less light than they did when they were stars. • As these white dwarfs cool they become fainter. • When there is no more energy being emitted (released), they are called ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects ...
... giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects ...
molecular clouds
... Molecular Clouds In these nebulae much of the hydrogen is in the molecular (H2) form, so these nebulae are called molecular clouds. The largest such formations are called giant molecular clouds (GMC). ...
... Molecular Clouds In these nebulae much of the hydrogen is in the molecular (H2) form, so these nebulae are called molecular clouds. The largest such formations are called giant molecular clouds (GMC). ...
Lecture 14 - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy CASA
... Blows completely apart. All that remains is an expanding shell of gas that used to be a white dwarf and the companion star slingshot into space. ...
... Blows completely apart. All that remains is an expanding shell of gas that used to be a white dwarf and the companion star slingshot into space. ...
Science 9 – Space Exploration
... called the Heliocentric model. Galileo Galilei later confirmed his model, in his observations with one of the first telescope. But it was this Johannes Kepler, who put in place what was missing from Copernicus’ model. He realized that the orbits of the planets were … A. circular B. geocentric C. int ...
... called the Heliocentric model. Galileo Galilei later confirmed his model, in his observations with one of the first telescope. But it was this Johannes Kepler, who put in place what was missing from Copernicus’ model. He realized that the orbits of the planets were … A. circular B. geocentric C. int ...
The Effects of Gravity
... protons to create neutrons. These neutron stars are also called “pulsars” because they release light energy as radio waves, sending “mysterious” signals. ...
... protons to create neutrons. These neutron stars are also called “pulsars” because they release light energy as radio waves, sending “mysterious” signals. ...
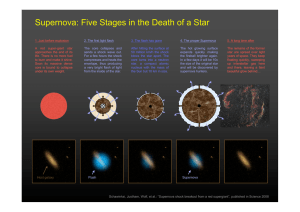
Supernova: Five Stages in the Death of a Star
... Soon its massive dense core is bound to collapse under its own weight. ...
... Soon its massive dense core is bound to collapse under its own weight. ...