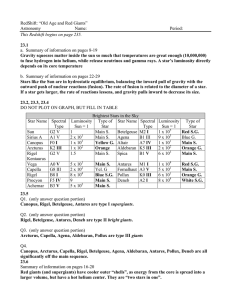
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
Stars and their Properties
... We know the most about the Sun than any other star Closest stars (besides the Sun) are hundreds of thousands of times further away than the Sun Stars are so far away so it’s safe to look at them All stars are made up of 75% hydrogen and 25% helium Parallax – Apparent movement of an object based on y ...
... We know the most about the Sun than any other star Closest stars (besides the Sun) are hundreds of thousands of times further away than the Sun Stars are so far away so it’s safe to look at them All stars are made up of 75% hydrogen and 25% helium Parallax – Apparent movement of an object based on y ...
pptx
... astronomers normally use units of the Sun’s mass, radius, etc. instead of units like kilograms and kilometers. The symbol for the Sun is . For instance, if a star has a mass 10 times greater than the Sun’s mass, then its mass is 10 M, which is read as “10 solar masses”. If a star has radius that i ...
... astronomers normally use units of the Sun’s mass, radius, etc. instead of units like kilograms and kilometers. The symbol for the Sun is . For instance, if a star has a mass 10 times greater than the Sun’s mass, then its mass is 10 M, which is read as “10 solar masses”. If a star has radius that i ...
NASC 1100
... The total energy production rate falls from its red giant phase peak. This reduces the star’s luminosity and decreases the star’s radius, making its surface hotter. In the H-R diagram, the star goes down and to the left. All low-mass stars fuse helium into carbon at nearly the same rate they have ...
... The total energy production rate falls from its red giant phase peak. This reduces the star’s luminosity and decreases the star’s radius, making its surface hotter. In the H-R diagram, the star goes down and to the left. All low-mass stars fuse helium into carbon at nearly the same rate they have ...
here - Boise State University
... 4. What kind of writing assignment did your teacher give you? 5. In your writing, assignment, what specific things are you required to write about? Click on the “Research Process” page and answer the questions below: 6. What is a star and what two gases make up a star? 7. As you watched the Youtube ...
... 4. What kind of writing assignment did your teacher give you? 5. In your writing, assignment, what specific things are you required to write about? Click on the “Research Process” page and answer the questions below: 6. What is a star and what two gases make up a star? 7. As you watched the Youtube ...
www.if.ufrgs.br
... Drake et al. point out that this NS may in fact be a quark star (astro-ph/0204159) because of its small radius, which they argue is in the range between ...
... Drake et al. point out that this NS may in fact be a quark star (astro-ph/0204159) because of its small radius, which they argue is in the range between ...
Homework 5
... Be sure to have your paper topic selections ready to hand in on Wednesday May 8. Start rooting around for a topic now! The first four problems are from Shu’s book; they’re embedded in a magnificent chapter on stellar structure as applied to the sun. 1) Shu problem 5.11 2) Shu problem 5.12 3) Shu pro ...
... Be sure to have your paper topic selections ready to hand in on Wednesday May 8. Start rooting around for a topic now! The first four problems are from Shu’s book; they’re embedded in a magnificent chapter on stellar structure as applied to the sun. 1) Shu problem 5.11 2) Shu problem 5.12 3) Shu pro ...
PHY216_lect1_2014 - Astrophysics Research Institute
... If the length of the sides are very small (compared to the radius of the sphere), then sin a ~ a etc. (small angle approximation). The spherical sine rule then becomes: ...
... If the length of the sides are very small (compared to the radius of the sphere), then sin a ~ a etc. (small angle approximation). The spherical sine rule then becomes: ...
Name Date ______ Period _____ Earth Science Chapter 25 Study
... What is the relationship between a magnitude number and the brightness of a star? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ The difference in the brightness of two stars with the same surface temperature is a ...
... What is the relationship between a magnitude number and the brightness of a star? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ The difference in the brightness of two stars with the same surface temperature is a ...
Stellar Structure - Astronomy Centre
... (see blackboard) • Is a star solid, liquid or gaseous? • Mean density and surface temperature (see blackboard) ...
... (see blackboard) • Is a star solid, liquid or gaseous? • Mean density and surface temperature (see blackboard) ...
Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers
... Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers 1. (a) The star is nearly a blackbody, the spectrum of a star can be approximated as a blackbody radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position ...
... Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers 1. (a) The star is nearly a blackbody, the spectrum of a star can be approximated as a blackbody radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... B: shifted to the blue C: shifted to the red D: much brighter than if it were at rest E: much fainter than if it were at rest ...
... B: shifted to the blue C: shifted to the red D: much brighter than if it were at rest E: much fainter than if it were at rest ...
Chapter 13 - USD Home Pages
... a white dwarf might be at several hundred million K, but this extremely high temperature contributes only a small amount of the pressure, compared to EDP. As a result, as a white dwarf cools down, the decrease in total pressure (EDP plus thermodynamic) is slight, so the white dwarf does not shrink a ...
... a white dwarf might be at several hundred million K, but this extremely high temperature contributes only a small amount of the pressure, compared to EDP. As a result, as a white dwarf cools down, the decrease in total pressure (EDP plus thermodynamic) is slight, so the white dwarf does not shrink a ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... collaboration with other students in making your quiz) • I will use the “best” quiz as your next quiz ...
... collaboration with other students in making your quiz) • I will use the “best” quiz as your next quiz ...
Star and Sun Properties
... Day 1: What Are Stars? A star is a large celestial body that is composed of hot gas and that emits light; the sun is a typical star • The Sun, our closest star, is 93 million miles from Earth. • The next closest star is 4.3 lighter years away. • By mass, the Sun is 71 % Hydrogen, 27% helium and t ...
... Day 1: What Are Stars? A star is a large celestial body that is composed of hot gas and that emits light; the sun is a typical star • The Sun, our closest star, is 93 million miles from Earth. • The next closest star is 4.3 lighter years away. • By mass, the Sun is 71 % Hydrogen, 27% helium and t ...
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit-
... Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement is used to compare distances between other astronomical bodies. AuroraA bright display of changing colorful light caused by ...
... Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement is used to compare distances between other astronomical bodies. AuroraA bright display of changing colorful light caused by ...