* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
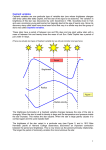
Survey of the Universe Tom Burbine [email protected] • • • • HW #6 Due this Wednesday You will make a quiz covering material up to April 8th You need to have answers for each question 70 points – Use a similar style to my previous quizzes • Cumulative • You can’t use (or be too similar to) previous questions on quizzes • You can’t use questions used by other students (no collaboration with other students in making your quiz) • I will use the “best” quiz as your next quiz • If you are unhappy with any of your grades: • You can write a 10 page paper on an astronomical subject to replace it • 12 point font • Times New Roman font • Double space • No figures or plots • Due by May 1st • Star expands quickly • Becomes more luminous because the star becomes bigger • Because the star is expanding, the energy coming from the interior becomes more spread out • The surface becomes cooler Helium Fusion • Helium can fuse into Carbon at temperatures above 100 million kelvin Degenerate gas • Core compresses • But can only compress so far since electrons can not occupy the same space if they have the same energy • This is called a degenerate gas • Stars less than 0.5 solar mass can’t compress any more • Stars from 0.5-2 solar masses get so compressed that gravitational contraction and radiation from the fusion shell releases energy that is absorbed by some of the electrons • The core can then compress more • Helium fusion can occur Variable Star • Star whose luminosity changes over time Lightcurves • Lightcurves plot brightness of a star versus time • Period is the interval of time where a pattern of brightness repeats Different Types of Variable Stars • RR Lyrae Variables – Mass comparable to Sun but ~40 times more luminous • Mira Variables – Red cool supergiants that have periods of many months to years • Cepheid Variables –Yellow supergiants that are more massive than the Sun and ~10,000 times more luminous • T-Tauri Irregular Variables – Pre-main sequence stars that appear to brighten as material falls sporadically onto the forming star • Giant stars pulsate because their atmospheres trap their radiated energy • Heats their outer layers that expand • The expanded gas cools and pressure drops • Gravity then recompresses the gas Cepheid Variables • Obey a period-luminosity relation • The more luminous a Cepheid is, the slower it pulsates Why is there a relationship? • Larger Cepheid Variables have weaker surface gravities than the smaller Cepheid Variables • Gravity pulls Larger Cepheid Variables inward slower than smaller Cepheid Variables • So Larger ones pulsate slower Cepheids as Standard Candles • Can be used as standard candle • So luminous that you can determine distances to galaxies that are millions of light years distant • • • • You determine the pulsation period You can then determine its luminosity You can measure its brightness Then determine distance from inverse-square law B = L/4d2 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iyisAjHdhas Any Questions?