Sequencing the Stars
... two-frame mosaic. My mosaic doesn’t cover the entire cluster but I captured a big central part of it. I actually made three separate mosaics, using short exposures (0.08 seconds), medium exposures (8 seconds), and long exposures (80 seconds). Then, I used the freeware program S OURCE E XTRACTOR, com ...
... two-frame mosaic. My mosaic doesn’t cover the entire cluster but I captured a big central part of it. I actually made three separate mosaics, using short exposures (0.08 seconds), medium exposures (8 seconds), and long exposures (80 seconds). Then, I used the freeware program S OURCE E XTRACTOR, com ...
Basic Properties of the Stars
... The Danish astronomer Hertzsprung and the American astronomer Russell noted that a majority of stars had absolute magnitudes that correlated with their spectral types. In a plot of MV vs. spectral type most stars traced out a band from the upper left of the diagram to the lower right. Astronomers ca ...
... The Danish astronomer Hertzsprung and the American astronomer Russell noted that a majority of stars had absolute magnitudes that correlated with their spectral types. In a plot of MV vs. spectral type most stars traced out a band from the upper left of the diagram to the lower right. Astronomers ca ...
Fulltext PDF
... up of spiral arms where young stars are forming even now, as it is gas rich. This is where we find open star clusters which are looser aggregates of stars with typical lifetimes of a few 100 Myr1 . The nuclear bulge contains the highest density of stars in the galaxy. The primary population of stars ...
... up of spiral arms where young stars are forming even now, as it is gas rich. This is where we find open star clusters which are looser aggregates of stars with typical lifetimes of a few 100 Myr1 . The nuclear bulge contains the highest density of stars in the galaxy. The primary population of stars ...
Chapter10 (with interactive links)
... Eclipsing binary: the total light coming from the star system decreases when one star passes in front of the other. This allows us to determine the relative sizes of the two stars. ...
... Eclipsing binary: the total light coming from the star system decreases when one star passes in front of the other. This allows us to determine the relative sizes of the two stars. ...
Starlight and Atoms - School District of Clayton
... b. The upper layers of a star contain hot low-density gases that produce bright lines at precisely the same wavelengths as the dark lines, thus making them invisible. c. Hot hydrogen and helium gas in the interstellar medium produces bright lines to fill in the dark lines. d. The resolution of many ...
... b. The upper layers of a star contain hot low-density gases that produce bright lines at precisely the same wavelengths as the dark lines, thus making them invisible. c. Hot hydrogen and helium gas in the interstellar medium produces bright lines to fill in the dark lines. d. The resolution of many ...
Stars - WhatisOutThere
... helium. These are the two lightest elements. They shine by burning the hydrogen into helium in their cores, then later in life they create heavier elements. Most stars have heavy elements, like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron but only small amounts. These elements came from the stars that existed ...
... helium. These are the two lightest elements. They shine by burning the hydrogen into helium in their cores, then later in life they create heavier elements. Most stars have heavy elements, like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron but only small amounts. These elements came from the stars that existed ...
Distance, Size, and Temperature of a Star
... Because blue stars are large, and compact, they burn their fuel quickly, which gives them a very high temperature. These stars often run out of fuel in only 10,000 - 100,000 years. A blue giant is very bright. Like a lighthouse, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are ra ...
... Because blue stars are large, and compact, they burn their fuel quickly, which gives them a very high temperature. These stars often run out of fuel in only 10,000 - 100,000 years. A blue giant is very bright. Like a lighthouse, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are ra ...
E-AQA Mark Scheme P1 long answer questions
... centre) can gain the first point only below the point of suspension accept ‘(vertically) below Y’ at the centre (of the lifebelt) accept ‘in the middle’ (because) the lifebelt / it is symmetrical or (because) the mass / weight is evenly ...
... centre) can gain the first point only below the point of suspension accept ‘(vertically) below Y’ at the centre (of the lifebelt) accept ‘in the middle’ (because) the lifebelt / it is symmetrical or (because) the mass / weight is evenly ...
Name Date Life and Death of a Star 2015 1. In the main
... 29. When helium fusion takes over in a star's core, what happens? A. the energy output decreases B. energy output stays the same C. the energy output increases 30. A star that is gravitationally bound to another may be a A. binary B. red giant C. white dwarf D. constellation 31. A type II supernova ...
... 29. When helium fusion takes over in a star's core, what happens? A. the energy output decreases B. energy output stays the same C. the energy output increases 30. A star that is gravitationally bound to another may be a A. binary B. red giant C. white dwarf D. constellation 31. A type II supernova ...
Inquiry Lab: Exploring the Spectrum Intended Learning Outcomes: 1
... rays). In the case of light, the effect is difficult to demonstrate without using sophisticated instrumentation, because of the very high speed with which light moves. Therefore, while light is the wave of interest to astronomers, this activity will focus primarily on simulations to demonstrate the ...
... rays). In the case of light, the effect is difficult to demonstrate without using sophisticated instrumentation, because of the very high speed with which light moves. Therefore, while light is the wave of interest to astronomers, this activity will focus primarily on simulations to demonstrate the ...
AJAstroProject
... • M105 is an elliptical galaxy that is about 32.0 million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec expo ...
... • M105 is an elliptical galaxy that is about 32.0 million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec expo ...
NASA`s Spitzer Images Out-of-This
... Technology in Pasadena. "Some theories hold that the black hole might quiet down and eventually enter a more dormant state like our Milky Way black hole." The ring around the black hole is bursting with new star formation. An inflow of material toward the central bar of the galaxy is causing the rin ...
... Technology in Pasadena. "Some theories hold that the black hole might quiet down and eventually enter a more dormant state like our Milky Way black hole." The ring around the black hole is bursting with new star formation. An inflow of material toward the central bar of the galaxy is causing the rin ...
Clusters of galaxies
... Estimate 3 parameters: weighted age; [Z/H]; [α/Fe] (or [E/Fe]) by fitting line pairs of index measurements onto model grids. [α/Fe] tells you something about the timescale of star formation. ...
... Estimate 3 parameters: weighted age; [Z/H]; [α/Fe] (or [E/Fe]) by fitting line pairs of index measurements onto model grids. [α/Fe] tells you something about the timescale of star formation. ...
PPT - ICRA
... 2) ``Melting’’ phase transition: the nucleon matter core, nuclei matter surroundings. 3) Super-critical electric field on the surface of collapsing core. 4) Electron-positron-photon plasma (dyadosphere) formed in gravitational collapses. 5) Hydrodynamic expansion of Electron-positron-photon plasma. ...
... 2) ``Melting’’ phase transition: the nucleon matter core, nuclei matter surroundings. 3) Super-critical electric field on the surface of collapsing core. 4) Electron-positron-photon plasma (dyadosphere) formed in gravitational collapses. 5) Hydrodynamic expansion of Electron-positron-photon plasma. ...
Chapter 29: Stars - Mr. Pelton Science
... using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, with the O class stars being the hottest and the M class stars being the coolest. ...
... using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, with the O class stars being the hottest and the M class stars being the coolest. ...
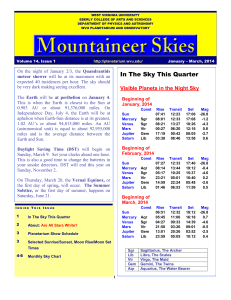
January-February-March - WVU Planetarium
... Orion, the Hunter, the star that marks his upper left hand shoulder is called Betelgeuse (most usually pronounced “Beetlejuice” in English like the movie of some years ago) and is clearly not white, but somewhat reddish. Okay, so what? Does the color mean anything? It does indeed. The color of a sta ...
... Orion, the Hunter, the star that marks his upper left hand shoulder is called Betelgeuse (most usually pronounced “Beetlejuice” in English like the movie of some years ago) and is clearly not white, but somewhat reddish. Okay, so what? Does the color mean anything? It does indeed. The color of a sta ...
Power-point slides for Lecture 2
... does greatly affect everything – the explosion, light curve, nucleosynthesis and remnant properties. A massive hydrogen envelope may also make the star more difficult to explode. 3) Mass loss sets an upper bound to the luminosity of red supergiants. This limit is metallicity dependent. For solar met ...
... does greatly affect everything – the explosion, light curve, nucleosynthesis and remnant properties. A massive hydrogen envelope may also make the star more difficult to explode. 3) Mass loss sets an upper bound to the luminosity of red supergiants. This limit is metallicity dependent. For solar met ...
Return both exam and scantron sheet when you
... (a) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (b) photons of certain wavelengths are absorbed. (c) it is redshifted. (d) it is blueshifted. 28. What is the second most abundant chemical element in the main sequence stars? (a) Oxygen (O). (b) Hydrogen (H). (c) Carbon (C). (d) Helium (He) 29. To dete ...
... (a) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (b) photons of certain wavelengths are absorbed. (c) it is redshifted. (d) it is blueshifted. 28. What is the second most abundant chemical element in the main sequence stars? (a) Oxygen (O). (b) Hydrogen (H). (c) Carbon (C). (d) Helium (He) 29. To dete ...
a new isotopic abundance anomaly in chemically peculiar stars
... stars, the notorious Przybylski’s star, appeared to show the 48Ca shifts. When another spectrum of the same star, obtained with a different spectrograph also indicated 48Ca, they decided to measure additional spectra, concentrating on magnetic CP stars, but including a few other exotic types. Eventu ...
... stars, the notorious Przybylski’s star, appeared to show the 48Ca shifts. When another spectrum of the same star, obtained with a different spectrograph also indicated 48Ca, they decided to measure additional spectra, concentrating on magnetic CP stars, but including a few other exotic types. Eventu ...
Astr604-Ch1
... depends on the wavelength interval at which we observe. Originally, photographic plates were sensitive only to blue light, and the term photographic magnitude (mpg) still refers to magnitude centered at 420 nm (in the blue region of the spectrum). Similarly, because the human eye is most sensitive t ...
... depends on the wavelength interval at which we observe. Originally, photographic plates were sensitive only to blue light, and the term photographic magnitude (mpg) still refers to magnitude centered at 420 nm (in the blue region of the spectrum). Similarly, because the human eye is most sensitive t ...