Student Literacy
... You have probably wondered how far away from Earth are the celestial bodies you see in the universe, the space that consists of all matter, all light and all forms of radiation and energy. Stars are so far away that our present mode of space travel would take more than a lifetime to reach the neares ...
... You have probably wondered how far away from Earth are the celestial bodies you see in the universe, the space that consists of all matter, all light and all forms of radiation and energy. Stars are so far away that our present mode of space travel would take more than a lifetime to reach the neares ...
High-Speed Ballistic Stellar Interlopers
... approach between two binary star systems—or a binary system and a third star. In such cases, one or more of the stars can pick up enough energy through gravitational interaction with the others to be thrown from the system. Determining how many stars have been ejected from their neighbors is importa ...
... approach between two binary star systems—or a binary system and a third star. In such cases, one or more of the stars can pick up enough energy through gravitational interaction with the others to be thrown from the system. Determining how many stars have been ejected from their neighbors is importa ...
Powerpoint for today
... Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes cloud want to collapse. ...
... Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes cloud want to collapse. ...
HR Diagram and Stellar Fusion
... • …Ejnar Hertzsprung and H. N. Russell, graph (see illustration) showing the luminosity of a star as a function of its surface temperature. The luminosity, or absolute magnitude, increases upwards on the vertical axis; the temperature (or some temperature-dependent characteristic such as spectral cl ...
... • …Ejnar Hertzsprung and H. N. Russell, graph (see illustration) showing the luminosity of a star as a function of its surface temperature. The luminosity, or absolute magnitude, increases upwards on the vertical axis; the temperature (or some temperature-dependent characteristic such as spectral cl ...
Luminosity Classes
... These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
... These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
The First Stars - Amazon Web Services
... In the century that followed, astronomers measured the masses of many stars, typically by using the orbits in binary systems, and confirmed Eddington’s reasoning. The smaller balls of gas make the planets. The massive stars explode, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, because their masses are so la ...
... In the century that followed, astronomers measured the masses of many stars, typically by using the orbits in binary systems, and confirmed Eddington’s reasoning. The smaller balls of gas make the planets. The massive stars explode, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, because their masses are so la ...
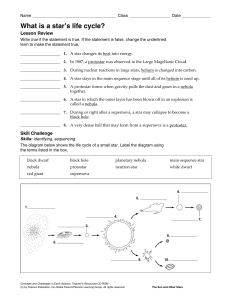
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Chapter 24
... • Final stage depends on mass • Possibilities • Massive star • Over 3 solar masses • Short life span • Terminates in a brilliant explosion called a supernova • Interior condenses • May produce a hot, dense object that is either a neutron star or a black hole ...
... • Final stage depends on mass • Possibilities • Massive star • Over 3 solar masses • Short life span • Terminates in a brilliant explosion called a supernova • Interior condenses • May produce a hot, dense object that is either a neutron star or a black hole ...
ph512-10-lec5
... motion that cause the positions to change with time, and corrections to the positions due to distortions in the optics, atmosphere refraction, and aberration caused by the Earth’s motion. Astronomers use astrometric techniques for the tracking of nearEarth objects. It has been also been used to dete ...
... motion that cause the positions to change with time, and corrections to the positions due to distortions in the optics, atmosphere refraction, and aberration caused by the Earth’s motion. Astronomers use astrometric techniques for the tracking of nearEarth objects. It has been also been used to dete ...
starevolution - Global Change Program
... Nebula. For a detailed view of the Crab Nebula, look at the recent Hubble Telescope image. This supernova remnant is 6,500 light years away. Another beautiful example of a supernova remnant is the Cygnus Loop, lying about 2,500 light years away (on right). The evolution of even more massive stars pr ...
... Nebula. For a detailed view of the Crab Nebula, look at the recent Hubble Telescope image. This supernova remnant is 6,500 light years away. Another beautiful example of a supernova remnant is the Cygnus Loop, lying about 2,500 light years away (on right). The evolution of even more massive stars pr ...
EMS, HR, Star Lives classwork/homework
... 10. State how Barnard’s star and Mira are similar. 11. Name the stars on the diagram that are blue or blue-white. 12. Describe three features of the star Deneb. 13.Suppose you wanted to observe the star Aldebaran. What clues would you use to help you identify it? ...
... 10. State how Barnard’s star and Mira are similar. 11. Name the stars on the diagram that are blue or blue-white. 12. Describe three features of the star Deneb. 13.Suppose you wanted to observe the star Aldebaran. What clues would you use to help you identify it? ...
PPT - UBC
... A few 1000 visible to the naked eye Polaris (North Star) not brightest (only 50th) Sirius is brightest ...
... A few 1000 visible to the naked eye Polaris (North Star) not brightest (only 50th) Sirius is brightest ...
properties of stars 2012
... Variable Stars are those whose luminosity varies. A PULSATING variable is a star that is swelling and shrinking. As it swells, the same energy is spread over a larger area, the star cools and appears dimmer. (also, star cols because less pressure allows energy to escape) As it shrinks, it heats up ...
... Variable Stars are those whose luminosity varies. A PULSATING variable is a star that is swelling and shrinking. As it swells, the same energy is spread over a larger area, the star cools and appears dimmer. (also, star cols because less pressure allows energy to escape) As it shrinks, it heats up ...
Basic Properties of Stars
... sense. According to the blackbody law, hot things emit more light. But a star’s brightness also depends on its size – the larger the area, the more square centimeters are emitting and the more light you get. The relationship between ...
... sense. According to the blackbody law, hot things emit more light. But a star’s brightness also depends on its size – the larger the area, the more square centimeters are emitting and the more light you get. The relationship between ...
The origin, life, and death of stars
... The life cycle of a star is determined by its mass More massive stars have greater gravity, and this speeds up the rate of fusion O and B stars can consume all of their core hydrogen in a few million years, while very low mass stars can take hundreds of billions of years. ...
... The life cycle of a star is determined by its mass More massive stars have greater gravity, and this speeds up the rate of fusion O and B stars can consume all of their core hydrogen in a few million years, while very low mass stars can take hundreds of billions of years. ...
Chapter20
... Black holes are gravity wells that can not only draw mater in but can spin it as well. This effect, called framedragging, is most prominent near massive, fast spinning objects. Matter in this system gets caught up and spun around the black hole. Such discoveries help scientists better understand gra ...
... Black holes are gravity wells that can not only draw mater in but can spin it as well. This effect, called framedragging, is most prominent near massive, fast spinning objects. Matter in this system gets caught up and spun around the black hole. Such discoveries help scientists better understand gra ...
CARBON STARS
... and lines in spectra make it difficult to determine Teff accurately • N-stars ~ 2200-3300K ...
... and lines in spectra make it difficult to determine Teff accurately • N-stars ~ 2200-3300K ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram Star Data Table
... Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell discovered a relationship between the brightness of a star and the surface temperature of a star. The graph of a star’s absolute magnitude versus its temperature is called an ...
... Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell discovered a relationship between the brightness of a star and the surface temperature of a star. The graph of a star’s absolute magnitude versus its temperature is called an ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.