Do you know how we hear
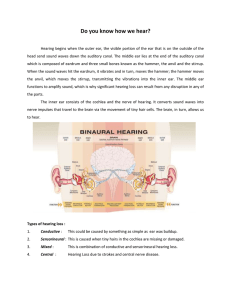
... The inner ear consists of the cochlea and the nerve of hearing. It converts sound waves into nerve impulses that travel to the brain via the movement of tiny hair cells. The brain, in turn, allows us to hear. ...
... The inner ear consists of the cochlea and the nerve of hearing. It converts sound waves into nerve impulses that travel to the brain via the movement of tiny hair cells. The brain, in turn, allows us to hear. ...
John Rubin - "Friends, Romans Countrymen...."
... short wavelengths and therefore do not travel as far? We then looked at a concerning table of industrial standards in exposure to sound; exposure to a relatively quiet 50 dB conversation at 3 metres is considered safe for 4 hours. At the other end of the scale, the 105 dB of a rock concert is safe f ...
... short wavelengths and therefore do not travel as far? We then looked at a concerning table of industrial standards in exposure to sound; exposure to a relatively quiet 50 dB conversation at 3 metres is considered safe for 4 hours. At the other end of the scale, the 105 dB of a rock concert is safe f ...
Activity 14-4 activity_14
... Guided Reading Activity – 14.4 1. What are the three main sections of the ear? 2. Describe the function of each part of the outer ear: auricle, external auditory canal, hairs and wax, and tympanic membrane. 3. What are the auditory ossicles? 4. What does the Eustachian tube do? 5. Describe the labyr ...
... Guided Reading Activity – 14.4 1. What are the three main sections of the ear? 2. Describe the function of each part of the outer ear: auricle, external auditory canal, hairs and wax, and tympanic membrane. 3. What are the auditory ossicles? 4. What does the Eustachian tube do? 5. Describe the labyr ...
Table 2.Delay progressive factors
... Table 2. Factors associated with delayed diagnosis of hearing loss and contributing to late intervention for infants who pass newborn hearing screening. Adapted from Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (2007). _______________________________________________________________ ...
... Table 2. Factors associated with delayed diagnosis of hearing loss and contributing to late intervention for infants who pass newborn hearing screening. Adapted from Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (2007). _______________________________________________________________ ...
Vision Problems are Common in Children with Hearing Loss
... Vision Problems are Common in Children with Hearing Loss About one-fifth of children who have a particular type of hearing loss also have visual disorders, according to a recent study. An estimated one to three children per 1,000 has some degree of sensorineural hearing loss, which occurs as a resul ...
... Vision Problems are Common in Children with Hearing Loss About one-fifth of children who have a particular type of hearing loss also have visual disorders, according to a recent study. An estimated one to three children per 1,000 has some degree of sensorineural hearing loss, which occurs as a resul ...
Hearing - AP Psychology
... the crest of the wave is the louder the sound is. It is measured in decibels. ...
... the crest of the wave is the louder the sound is. It is measured in decibels. ...
Sensorineural hearing loss

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss, or deafness, in which the root cause lies in the inner ear (cochlear), vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), or central processing centers of the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total.The great majority of human sensorineural hearing loss is caused by abnormal structure or function of the hair cells of the organ of Corti in the cochlea. There are also very unusual sensorineural hearing impairments that involve the eighth cranial nerve (the vestibulocochlear nerve) or the auditory portions of the brain. In the rarest of these sorts of hearing loss, only the auditory centers of the brain are affected. In this situation, cortical deafness, sounds may be heard at normal thresholds, but the quality of the sound perceived is so poor that speech cannot be understood.Sensory hearing loss is due to poor hair cell function. The hair cells may be abnormal at birth, or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, like noise trauma and infection, and intrinsic abnormalities, like deafness genes.Neural hearing loss occurs because of damage to the cochlear nerve (CVIII). This damage may affect the initiation of the nerve impulse in the cochlear nerve or the transmission of the nerve impulse along the nerve. Hearing loss that results from abnormalities of the central auditory system in the brain is called central hearing impairment. Since the auditory pathways cross back and forth on both sides of the brain, deafness from a central cause is unusual.Sensory hearing loss can also be caused by prolonged exposure to very loud noise, for example, being in a loud workplace without wearing protection, or having headphones set to high volumes for a long period. Exposure to a very loud noise such as a bomb blast can cause noise-induced hearing loss.