Interesting Articles
... between elevated workplace noise and hypertension. Regular exposure to excess noise at work not only harms the structure of the ear, but also creates unhealthy stress. The immediate damage called acoustic trauma, a particular risk for members of the military, is different from the insidious harm tha ...
... between elevated workplace noise and hypertension. Regular exposure to excess noise at work not only harms the structure of the ear, but also creates unhealthy stress. The immediate damage called acoustic trauma, a particular risk for members of the military, is different from the insidious harm tha ...
Cochlear Implants
... Future of the Cochlear Implant A new product called the Electric Acoustic Stimulation ...
... Future of the Cochlear Implant A new product called the Electric Acoustic Stimulation ...
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
... hear. NIHL slowly progresses into lower tones. Once these are affected, you may have problems hearing people when they speak. What kind of noise is too loud? The noise is too loud if you have to raise your voice to talk to a person who is only an arm’s length away. The loudness of sound is measured ...
... hear. NIHL slowly progresses into lower tones. Once these are affected, you may have problems hearing people when they speak. What kind of noise is too loud? The noise is too loud if you have to raise your voice to talk to a person who is only an arm’s length away. The loudness of sound is measured ...
Hearing Module 14 - Clayton Valley Charter High School
... Because we have two ears sounds that reach one ear faster than the other makes us localize the sound. ...
... Because we have two ears sounds that reach one ear faster than the other makes us localize the sound. ...
Children with congenital unilateral sensorineural hearing loss: The
... Marlin Johansson, Division of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases [email protected] ...
... Marlin Johansson, Division of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases [email protected] ...
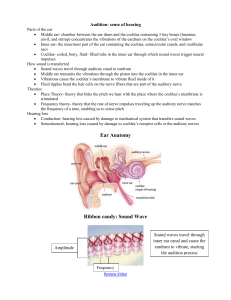
Hearing
... basilar membrane when they different pitches. • So some hairs vibrate when they hear high and other vibrate when they hear low pitches. • But this doesn’t explain low-pitch since we haven’t found specific positions for those on the BM ...
... basilar membrane when they different pitches. • So some hairs vibrate when they hear high and other vibrate when they hear low pitches. • But this doesn’t explain low-pitch since we haven’t found specific positions for those on the BM ...
JJWhite Letterhead 072913
... The middle ear amplifies the vibrations and sends them to the inner ear. The vibrations stimulate hair cells in the inner ear and create an electrical impulse. Sensory hearing loss cannot be corrected medically or surgically. It is permanent! Follow the manufactures instructions to properly wear you ...
... The middle ear amplifies the vibrations and sends them to the inner ear. The vibrations stimulate hair cells in the inner ear and create an electrical impulse. Sensory hearing loss cannot be corrected medically or surgically. It is permanent! Follow the manufactures instructions to properly wear you ...
Newsletter Vol 1 Issue 2, March, 2015
... impaired hearing. But shrinkage has also been noticed in those areas of the brain responsible for memory and sensory integration and have been shown to be involved in the early stages of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Hearing loss also leads ...
... impaired hearing. But shrinkage has also been noticed in those areas of the brain responsible for memory and sensory integration and have been shown to be involved in the early stages of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Hearing loss also leads ...
Presbyacusis - The Medical Post
... CSOM, Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuroma, cochlear otosclerosis, ear trauma & ototoxic drug ...
... CSOM, Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuroma, cochlear otosclerosis, ear trauma & ototoxic drug ...
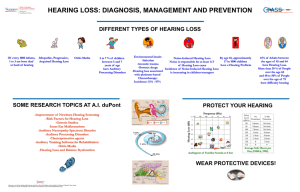
hearingloss
... suction the softened wax out Hearing Aids—makes sounds stronger and easer to hear Cochlear Implants—amplifies sound and directs it into ear canal; compensates for damaged or nonworking parts of the inner ear ...
... suction the softened wax out Hearing Aids—makes sounds stronger and easer to hear Cochlear Implants—amplifies sound and directs it into ear canal; compensates for damaged or nonworking parts of the inner ear ...
Document
... affecting the transmission of sound from the environment to the cochlea Maximum loss of 50-60 dBHL, therefore no more than mild/moderate ...
... affecting the transmission of sound from the environment to the cochlea Maximum loss of 50-60 dBHL, therefore no more than mild/moderate ...
AUDIOLOGISTS ICD-9 CODE DESCRIPTION 389.00 Conductive
... Conductive hearing loss, unspecified Sensorineural hearing loss, unspecified Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss Unspecified hearing loss, deafness NOS Unspecified disorder of middle ear and mastoid Unspecified disorder of external ear Abnormal auditory perception, unspecified ...
... Conductive hearing loss, unspecified Sensorineural hearing loss, unspecified Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss Unspecified hearing loss, deafness NOS Unspecified disorder of middle ear and mastoid Unspecified disorder of external ear Abnormal auditory perception, unspecified ...
Sensorineural hearing loss

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss, or deafness, in which the root cause lies in the inner ear (cochlear), vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), or central processing centers of the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total.The great majority of human sensorineural hearing loss is caused by abnormal structure or function of the hair cells of the organ of Corti in the cochlea. There are also very unusual sensorineural hearing impairments that involve the eighth cranial nerve (the vestibulocochlear nerve) or the auditory portions of the brain. In the rarest of these sorts of hearing loss, only the auditory centers of the brain are affected. In this situation, cortical deafness, sounds may be heard at normal thresholds, but the quality of the sound perceived is so poor that speech cannot be understood.Sensory hearing loss is due to poor hair cell function. The hair cells may be abnormal at birth, or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, like noise trauma and infection, and intrinsic abnormalities, like deafness genes.Neural hearing loss occurs because of damage to the cochlear nerve (CVIII). This damage may affect the initiation of the nerve impulse in the cochlear nerve or the transmission of the nerve impulse along the nerve. Hearing loss that results from abnormalities of the central auditory system in the brain is called central hearing impairment. Since the auditory pathways cross back and forth on both sides of the brain, deafness from a central cause is unusual.Sensory hearing loss can also be caused by prolonged exposure to very loud noise, for example, being in a loud workplace without wearing protection, or having headphones set to high volumes for a long period. Exposure to a very loud noise such as a bomb blast can cause noise-induced hearing loss.