* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Amplification systems: Hearing aids
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
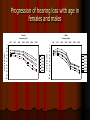
Noise induced hearing loss Predisposing factors: Drug use (aspirin) Gender Cause: Exposure to noise Acoustic trauma: Damage due to loud impulsive noise Two forms of NIHL Temporary threshold shift (TTS) Permanent threshold shift (PTS) Relationship between noise level and duration of exposure (OSHA, 1983) 85 dB A: 8 hours 90 dB A: 4 hours 95 dB A: 2 hours 105 dB A: 30 minutes Audiometric findings Sensorineural hearing loss Usually progressive with continued noise exposure Characteristic notch around 4000 Hz Tinnitus matched to frequencies around 3-6 kHz Measures to prevent NIHL Avoid noise exposure, especially if on certain types of medication Hearing protection Monitor hearing loss periodically Presbycusis Age-related hearing loss Progressive, sensorineural Effects first seen in high frequencies Age-related changes occur not only in cochlea Often: Speech-understanding difficulties Progression of hearing loss with age in females and males 500 Males Frequency (Hz) Frequency (Hz) 1000 2000 4000 6000 8000 250 0 0 10 10 20 20 30 40 60-64 50 65-69 70-74 60 75-79 70 80-84 80 85-89 dB HL (ANSI, 1969) dB HL (ANSI, 1969) 250 Females 500 1000 2000 4000 6000 8000 30 60-64 40 50 65-69 70-74 60 75-79 70 80-84 80 90 90 100 100 85-89 Méniére disease Disease that originates in the labyrinth Classic symptoms: Hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo Symptoms can be paroxysmal, and are usually progressive. Probable causes: Endolymphatic hydrops, others Treatment: Diuretics to limit fluid retention, diet control, sedatives, vestibular suppressants, surgery.