CSD 3000 DEAFNESS IN SOCIETY
... 1. Hearing by air conduction across frequency in each ear tells us if hearing is normal or not 2. If hearing by air conduction is NOT normal, the thresholds tell us the degree of hearing loss 3. Differences between hearing by air conduction and hearing by bone conduction tell us the type of hearing ...
... 1. Hearing by air conduction across frequency in each ear tells us if hearing is normal or not 2. If hearing by air conduction is NOT normal, the thresholds tell us the degree of hearing loss 3. Differences between hearing by air conduction and hearing by bone conduction tell us the type of hearing ...
Hearing Screening - New Mexico School Health Manual
... Conductive affects outer and / or middle ear -Most common causes: Otitis media -Correctable with treatment or surgery Sensorineural affects the inner ear or auditory nerve -This generally cannot be corrected with surgery or medical treatment Mixed Affects the outer/middle ear as well as the in ...
... Conductive affects outer and / or middle ear -Most common causes: Otitis media -Correctable with treatment or surgery Sensorineural affects the inner ear or auditory nerve -This generally cannot be corrected with surgery or medical treatment Mixed Affects the outer/middle ear as well as the in ...
the auditory system
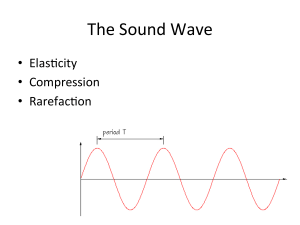
... The frequency of a sound wave determines the _______________________ of the sound we perceive. The amplitude of a sound wave determines the _______________________ of the sound we perceive. The waveform of a sound wave determines the _______________________ of the sound we perceive. Hearing the Soun ...
... The frequency of a sound wave determines the _______________________ of the sound we perceive. The amplitude of a sound wave determines the _______________________ of the sound we perceive. The waveform of a sound wave determines the _______________________ of the sound we perceive. Hearing the Soun ...
ETR Evaluation Team Report
... words and pertinent information are presented in the presence of background noise. Use of a personal FM system will help with discrimination, in the presence of background noise. Students with pre-lingual sensorineural hearing losses have not had the exposure to auditory information at the same time ...
... words and pertinent information are presented in the presence of background noise. Use of a personal FM system will help with discrimination, in the presence of background noise. Students with pre-lingual sensorineural hearing losses have not had the exposure to auditory information at the same time ...
bridget_shield_glossary_
... in the other ear is either the same or lower. Conductive hearing loss Hearing loss caused by a problem in the outer or middle ear, resulting in the inability of sound to be conducted to the inner ear. Congenital hearing loss Hearing loss present from birth. It may or may not be inherited. DeciBel dB ...
... in the other ear is either the same or lower. Conductive hearing loss Hearing loss caused by a problem in the outer or middle ear, resulting in the inability of sound to be conducted to the inner ear. Congenital hearing loss Hearing loss present from birth. It may or may not be inherited. DeciBel dB ...
Handy Handouts® Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
... of time around the noise or to increase the distance from the source of the noise. If, after leaving a potentially noise-harmful area, you experience tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or if the people talking to you sound like they are mumbling, you could be experiencing temporary hearing loss due to ...
... of time around the noise or to increase the distance from the source of the noise. If, after leaving a potentially noise-harmful area, you experience tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or if the people talking to you sound like they are mumbling, you could be experiencing temporary hearing loss due to ...
Dr Jane Madell
... Dear Colleague, Listed below is an audiology lecture being offered by the RIDBC Renwick Centre. Please direct any enquiries about this program to Trudy Smith on (02) 9872 0302 or [email protected] ...
... Dear Colleague, Listed below is an audiology lecture being offered by the RIDBC Renwick Centre. Please direct any enquiries about this program to Trudy Smith on (02) 9872 0302 or [email protected] ...
Normally if an audiologist can see a hearing loss shift between
... die. It has been assumed that SGN death is attributable to loss of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) derived from hair cells or supporting cells in the organ of Corti (OC). We used quantitative PCR (qPCR) to assay NTF expression—neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), BDNF, GDNF, neurturin, artemin, and CNTF—in the OC and ...
... die. It has been assumed that SGN death is attributable to loss of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) derived from hair cells or supporting cells in the organ of Corti (OC). We used quantitative PCR (qPCR) to assay NTF expression—neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), BDNF, GDNF, neurturin, artemin, and CNTF—in the OC and ...
Amplification/Sensory Systems
... • Compression: circuitry or programming to reduce the amplification of loud sounds to keep them below UCL • Tele-coil: direct pick up from a telephone’s electromagnetic field ...
... • Compression: circuitry or programming to reduce the amplification of loud sounds to keep them below UCL • Tele-coil: direct pick up from a telephone’s electromagnetic field ...
Sensorineural hearing loss

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss, or deafness, in which the root cause lies in the inner ear (cochlear), vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), or central processing centers of the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total.The great majority of human sensorineural hearing loss is caused by abnormal structure or function of the hair cells of the organ of Corti in the cochlea. There are also very unusual sensorineural hearing impairments that involve the eighth cranial nerve (the vestibulocochlear nerve) or the auditory portions of the brain. In the rarest of these sorts of hearing loss, only the auditory centers of the brain are affected. In this situation, cortical deafness, sounds may be heard at normal thresholds, but the quality of the sound perceived is so poor that speech cannot be understood.Sensory hearing loss is due to poor hair cell function. The hair cells may be abnormal at birth, or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, like noise trauma and infection, and intrinsic abnormalities, like deafness genes.Neural hearing loss occurs because of damage to the cochlear nerve (CVIII). This damage may affect the initiation of the nerve impulse in the cochlear nerve or the transmission of the nerve impulse along the nerve. Hearing loss that results from abnormalities of the central auditory system in the brain is called central hearing impairment. Since the auditory pathways cross back and forth on both sides of the brain, deafness from a central cause is unusual.Sensory hearing loss can also be caused by prolonged exposure to very loud noise, for example, being in a loud workplace without wearing protection, or having headphones set to high volumes for a long period. Exposure to a very loud noise such as a bomb blast can cause noise-induced hearing loss.