Lecture 2-10: Complex Sounds in the Auditory Periphery
... which cover some range of frequencies by varying their centre frequencies across the range. You have come across this idea before when we discussed the construction of spectrograms; you may also be familiar with graphic equalisers which are based upon a filterbank. Filterbanks are a good way of thin ...
... which cover some range of frequencies by varying their centre frequencies across the range. You have come across this idea before when we discussed the construction of spectrograms; you may also be familiar with graphic equalisers which are based upon a filterbank. Filterbanks are a good way of thin ...
Logging
... Effects of Noise Exposure Daily Allowable Exposure Times to Noise The table below shows noise levels and how long a person can be exposed without hearing protection before there is damage to the ear. Noise Level ...
... Effects of Noise Exposure Daily Allowable Exposure Times to Noise The table below shows noise levels and how long a person can be exposed without hearing protection before there is damage to the ear. Noise Level ...
Risk Factors for Dual Sensory Impairments
... Total loss of vision will be present if anophthalmos (absence of the eyeball) occurs ...
... Total loss of vision will be present if anophthalmos (absence of the eyeball) occurs ...
A.1.3.2HearMeNowLoggerPro
... Conclusion Questions 1. Patients with Tinnitus experience the constant perception of sound in the ear, often in the form of high pitched whining, buzzing, hissing, ringing, or whooshing sounds. The Speechin-Noise Test you just performed uses a constant whooshing sound to simulate environmental noise ...
... Conclusion Questions 1. Patients with Tinnitus experience the constant perception of sound in the ear, often in the form of high pitched whining, buzzing, hissing, ringing, or whooshing sounds. The Speechin-Noise Test you just performed uses a constant whooshing sound to simulate environmental noise ...
Review Unit 4 Sen_ Perception 2014-2015
... to dif. sound frequencies based on where they are located on membrane • Frequency theory=entire cochlea vibrates at particular frequency of a tone sending signals to brain ...
... to dif. sound frequencies based on where they are located on membrane • Frequency theory=entire cochlea vibrates at particular frequency of a tone sending signals to brain ...
THE HUMAN EAR (LIVE) 20 MAY 2015 Section A
... Sensorineural hearing loss: This refers to insensitivity of the cochlea due to abnormalities of the hair cells of the organs of Corti. It may also be due to a lack of function of the auditory nerve system. Noise-induced hearing loss: Hearing loss that is as a result of excessive noise levels (3 000 ...
... Sensorineural hearing loss: This refers to insensitivity of the cochlea due to abnormalities of the hair cells of the organs of Corti. It may also be due to a lack of function of the auditory nerve system. Noise-induced hearing loss: Hearing loss that is as a result of excessive noise levels (3 000 ...
SoundBites Audiogram Stu`s News
... detection and correction felt in our closest relationships—like can make a significant with our spouses, or our children and difference for anyone to successfully grandchildren. We don’t like to hear transition into wearing hearing aids. the subtle (and often not-so-subtle) suggestion that we might ...
... detection and correction felt in our closest relationships—like can make a significant with our spouses, or our children and difference for anyone to successfully grandchildren. We don’t like to hear transition into wearing hearing aids. the subtle (and often not-so-subtle) suggestion that we might ...
File
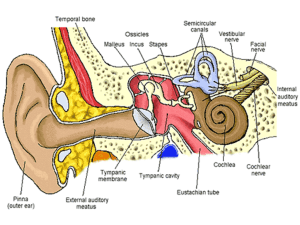
... the sound wave Ear-ossicles- magnify the sound vibrations and make the oval window vibrate at the same frequency ...
... the sound wave Ear-ossicles- magnify the sound vibrations and make the oval window vibrate at the same frequency ...
Document
... age 6 Prevalence is highest during the first two years of life 50% of all kids with one episode before their first birthday will have 6 or more bouts within two years Most episodes occur in winter and spring Risk factors ...
... age 6 Prevalence is highest during the first two years of life 50% of all kids with one episode before their first birthday will have 6 or more bouts within two years Most episodes occur in winter and spring Risk factors ...
2015 Regional Presentation â Programme Updates
... ABR testing or on an unaided test. • Children with limited aided speech information above 2 kHz (as seen on speech-mapping). Children with a severe reverse sloping hearing loss or worse whose speech and language is not progressing adequately. • Children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder who ...
... ABR testing or on an unaided test. • Children with limited aided speech information above 2 kHz (as seen on speech-mapping). Children with a severe reverse sloping hearing loss or worse whose speech and language is not progressing adequately. • Children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder who ...
Hearing Loss - Eastern Shore ENT
... hearing loss that only affects the high frequencies would be described as a highfrequency loss. Its configuration would show good hearing in the low frequencies and poor hearing in the high frequencies. On the other hand, if only the low frequencies are affected, the configuration would show poorer ...
... hearing loss that only affects the high frequencies would be described as a highfrequency loss. Its configuration would show good hearing in the low frequencies and poor hearing in the high frequencies. On the other hand, if only the low frequencies are affected, the configuration would show poorer ...
Print this article - Nepal Journals Online
... affecting nearly 250 million people in the world, and 75% of sufferers live in developing countries (2). Study by Little et al (3) showed around 16.6% of total population in Nepal, had hearing impairment. This study was conducted to see type of hearing loss with pattern and severity of hearing loss ...
... affecting nearly 250 million people in the world, and 75% of sufferers live in developing countries (2). Study by Little et al (3) showed around 16.6% of total population in Nepal, had hearing impairment. This study was conducted to see type of hearing loss with pattern and severity of hearing loss ...
Sensorineural hearing loss

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss, or deafness, in which the root cause lies in the inner ear (cochlear), vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), or central processing centers of the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total.The great majority of human sensorineural hearing loss is caused by abnormal structure or function of the hair cells of the organ of Corti in the cochlea. There are also very unusual sensorineural hearing impairments that involve the eighth cranial nerve (the vestibulocochlear nerve) or the auditory portions of the brain. In the rarest of these sorts of hearing loss, only the auditory centers of the brain are affected. In this situation, cortical deafness, sounds may be heard at normal thresholds, but the quality of the sound perceived is so poor that speech cannot be understood.Sensory hearing loss is due to poor hair cell function. The hair cells may be abnormal at birth, or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, like noise trauma and infection, and intrinsic abnormalities, like deafness genes.Neural hearing loss occurs because of damage to the cochlear nerve (CVIII). This damage may affect the initiation of the nerve impulse in the cochlear nerve or the transmission of the nerve impulse along the nerve. Hearing loss that results from abnormalities of the central auditory system in the brain is called central hearing impairment. Since the auditory pathways cross back and forth on both sides of the brain, deafness from a central cause is unusual.Sensory hearing loss can also be caused by prolonged exposure to very loud noise, for example, being in a loud workplace without wearing protection, or having headphones set to high volumes for a long period. Exposure to a very loud noise such as a bomb blast can cause noise-induced hearing loss.