Managing Low-Frequency Hearing Loss
... one of the more difficult-to-fit audiomet- & Abbas3 compared the speech recognition ric configurations. Although many ability of 3 subjects who were identified researchers1,2 have proposed solutions to with a low frequency dead region and 5 manage this hearing loss configuration, normal-hearing indi ...
... one of the more difficult-to-fit audiomet- & Abbas3 compared the speech recognition ric configurations. Although many ability of 3 subjects who were identified researchers1,2 have proposed solutions to with a low frequency dead region and 5 manage this hearing loss configuration, normal-hearing indi ...
Otitis Media with Effusion in Down`s Syndrome
... anomalies include a flat occiput, oblique palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds, speckled irides, a protruding tongue, prominent malformed ears, and a flat nasal bridge. Hearing impairment and otological problems including otitis media are still found in 38-90% of children with Down syndrome compared ...
... anomalies include a flat occiput, oblique palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds, speckled irides, a protruding tongue, prominent malformed ears, and a flat nasal bridge. Hearing impairment and otological problems including otitis media are still found in 38-90% of children with Down syndrome compared ...
Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing
... successfully. The fourth type of hearing loss is an auditory processing difficulty, which means that the individual can “hear” the sounds, but has problems understanding them Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. ...
... successfully. The fourth type of hearing loss is an auditory processing difficulty, which means that the individual can “hear” the sounds, but has problems understanding them Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. ...
AAC and Multiple Disabilities, Del Monte/Conatser
... has difficulty hearing faint or distant speech. A person with this degree of hearing impairment may use a hearing aid to amplify sounds. If the hearing loss is severe, the person may not be able to distinguish any sounds. There are four types of hearing loss: Conductive: caused by diseases or obst ...
... has difficulty hearing faint or distant speech. A person with this degree of hearing impairment may use a hearing aid to amplify sounds. If the hearing loss is severe, the person may not be able to distinguish any sounds. There are four types of hearing loss: Conductive: caused by diseases or obst ...
Sound - Townley Grammar School
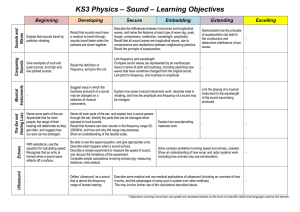
... Link the playing of a musical instrument to the wavelength of the sound wave being produced. ...
... Link the playing of a musical instrument to the wavelength of the sound wave being produced. ...
Rachela Greenman 23
... begun to lose their hearing at earlier ages than ever before, and more young children and teenagers have begun to suffer from hearing loss than in years past. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has found that 30 million Americans are exposed daily to unsafe levels of n ...
... begun to lose their hearing at earlier ages than ever before, and more young children and teenagers have begun to suffer from hearing loss than in years past. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has found that 30 million Americans are exposed daily to unsafe levels of n ...
Hearing and Auditory Processing Basics
... joined bones (malleus, incus and stapes). When sound enters the ear, it causes the TM to vibrate and the lever action of the ossicles act as an impedance matching device moving the sound through the bones to the inner ear. The Eustachian tube also feeds into the ear from the nose and throat and is r ...
... joined bones (malleus, incus and stapes). When sound enters the ear, it causes the TM to vibrate and the lever action of the ossicles act as an impedance matching device moving the sound through the bones to the inner ear. The Eustachian tube also feeds into the ear from the nose and throat and is r ...
Overcoming the Challenge of Rehabilitating Older Adults with Combined Vision and Hearing Loss Walter Wittich, PhD FAAO CLVT
... • Average hearing detection thresholds (dB HL 35) measured at four audiometric frequencies (i.e., 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 Hz) in the better ear, without assistive technology. • Children under the age of 12 years, if sufficient to be a potential threat to language development. • Youth between 12-18 ...
... • Average hearing detection thresholds (dB HL 35) measured at four audiometric frequencies (i.e., 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 Hz) in the better ear, without assistive technology. • Children under the age of 12 years, if sufficient to be a potential threat to language development. • Youth between 12-18 ...
File
... Pinna – Cochlea – Ceruminous Glands – Eustachion tube – Ossicles – Oval Window – Tympanic membrane – Auditory Canal – Organ of Corti – Round Window – Semicircular Canals – High – Low – Temporal – Basilar The outer ear is composed of the following parts: 1. ______________ These are flaps of skin & ca ...
... Pinna – Cochlea – Ceruminous Glands – Eustachion tube – Ossicles – Oval Window – Tympanic membrane – Auditory Canal – Organ of Corti – Round Window – Semicircular Canals – High – Low – Temporal – Basilar The outer ear is composed of the following parts: 1. ______________ These are flaps of skin & ca ...
Treatment Controversies in Meniere’s Disease
... Possible Meniere's disease Episodic vertigo of the Meniere's type without documented hearing loss, or Sensorineural hearing loss, fluctuating or fixed, with dysequilibrium but without definitive episodes Other causes excluded ...
... Possible Meniere's disease Episodic vertigo of the Meniere's type without documented hearing loss, or Sensorineural hearing loss, fluctuating or fixed, with dysequilibrium but without definitive episodes Other causes excluded ...
Training New Screener Spring 2015
... • Many babies who do not pass the screen will turn out to have normal hearing; there are several possible causes of a refer result, other than hearing loss. • Stress the importance of following through with subsequent appointments. • Offer appropriate written information, and a contact number for th ...
... • Many babies who do not pass the screen will turn out to have normal hearing; there are several possible causes of a refer result, other than hearing loss. • Stress the importance of following through with subsequent appointments. • Offer appropriate written information, and a contact number for th ...
the efficacy of early identification and - Paediatrie
... It was not until later that theories came together on the exact time line for the development of auditory perceptions and of language. Scientists are now aided by new technologies that permit access to brain activity. Chugani, [3] a pediatric neurobiologist at Wayne State University, uses positron-e ...
... It was not until later that theories came together on the exact time line for the development of auditory perceptions and of language. Scientists are now aided by new technologies that permit access to brain activity. Chugani, [3] a pediatric neurobiologist at Wayne State University, uses positron-e ...
Cochlear and Auditory Brainstem Implants
... Hybrid Cochlear Implant Request is for an approved hybrid cochlear implant (for example, Nucleus® Hybrid™ L24 Cochlear Implant System) (If checked, mark all of the following conditions that apply) Individual is 18 years of age or older with bilateral severe-to-profound high-frequency sensorineural h ...
... Hybrid Cochlear Implant Request is for an approved hybrid cochlear implant (for example, Nucleus® Hybrid™ L24 Cochlear Implant System) (If checked, mark all of the following conditions that apply) Individual is 18 years of age or older with bilateral severe-to-profound high-frequency sensorineural h ...
Sensorineural hearing loss

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss, or deafness, in which the root cause lies in the inner ear (cochlear), vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), or central processing centers of the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total.The great majority of human sensorineural hearing loss is caused by abnormal structure or function of the hair cells of the organ of Corti in the cochlea. There are also very unusual sensorineural hearing impairments that involve the eighth cranial nerve (the vestibulocochlear nerve) or the auditory portions of the brain. In the rarest of these sorts of hearing loss, only the auditory centers of the brain are affected. In this situation, cortical deafness, sounds may be heard at normal thresholds, but the quality of the sound perceived is so poor that speech cannot be understood.Sensory hearing loss is due to poor hair cell function. The hair cells may be abnormal at birth, or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, like noise trauma and infection, and intrinsic abnormalities, like deafness genes.Neural hearing loss occurs because of damage to the cochlear nerve (CVIII). This damage may affect the initiation of the nerve impulse in the cochlear nerve or the transmission of the nerve impulse along the nerve. Hearing loss that results from abnormalities of the central auditory system in the brain is called central hearing impairment. Since the auditory pathways cross back and forth on both sides of the brain, deafness from a central cause is unusual.Sensory hearing loss can also be caused by prolonged exposure to very loud noise, for example, being in a loud workplace without wearing protection, or having headphones set to high volumes for a long period. Exposure to a very loud noise such as a bomb blast can cause noise-induced hearing loss.