Ch. 21
... 21.4 The Formation of the Elements The last nucleus in the alpha-particle chain is nickel-56, which is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 and then to iron-56. Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays. However, within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron captu ...
... 21.4 The Formation of the Elements The last nucleus in the alpha-particle chain is nickel-56, which is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 and then to iron-56. Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays. However, within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron captu ...
A high-power liquid-lithium target for production of keV
... for production of keV-energy neutrons Research workshop on Nuclear Structure and Astrophysics with Radioactive Beams ...
... for production of keV-energy neutrons Research workshop on Nuclear Structure and Astrophysics with Radioactive Beams ...
Stellar Explosions
... The Formation of the Elements The last nucleus in the alpha-particle chain is nickel-56, which is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 and then to iron-56. Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays. However, within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron capture ca ...
... The Formation of the Elements The last nucleus in the alpha-particle chain is nickel-56, which is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 and then to iron-56. Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays. However, within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron capture ca ...
An Alternative Cosmology to the Big Bang–Dispersive Extinction
... But there are flaws in such argument. In order for the raisin-pudding model to work, three necessary conditions must be satisfied: 1) Hubble law must be strictly linear; 2) Classical Galileo velocity transformation must apply; 3) The positions and the velocities of the galaxies in the universe must ...
... But there are flaws in such argument. In order for the raisin-pudding model to work, three necessary conditions must be satisfied: 1) Hubble law must be strictly linear; 2) Classical Galileo velocity transformation must apply; 3) The positions and the velocities of the galaxies in the universe must ...
Some FAQs and Answers for the Big Bang, Dark Matter, and Dark
... At the moment, we don’t know whether the Universe is finite or infinite but the consensus is that it is effectively infinite due to cosmic inflation. Inflation is a process believed to have occurred at the energy density just beyond where our physics begins to break down. Driven by a supercooled qua ...
... At the moment, we don’t know whether the Universe is finite or infinite but the consensus is that it is effectively infinite due to cosmic inflation. Inflation is a process believed to have occurred at the energy density just beyond where our physics begins to break down. Driven by a supercooled qua ...
Blackholes - Indiana University Astronomy
... • The process by which elements (nuclei) are created (synthesized) is called nucleosynthesis • Nucleosynthesis has occurred since the creation of the universe and will essentially go on forever • The elements created come together to form everything material we know, including us ...
... • The process by which elements (nuclei) are created (synthesized) is called nucleosynthesis • Nucleosynthesis has occurred since the creation of the universe and will essentially go on forever • The elements created come together to form everything material we know, including us ...
Nucleosynthesis, the r-Process, Abundances and Jim Truran
... Cameron & Truran (1977) The Supernova Trigger for the Formation of the Solar System Truran, Cowan & Cameron (1978) The Helium Driven rProcess in Supernovae Truran (1981) A New Interpretation of the Heavy Element Abundances in Metal-deficient Stars Cowan, Thielemann & Truran (1991) The r-Process and ...
... Cameron & Truran (1977) The Supernova Trigger for the Formation of the Solar System Truran, Cowan & Cameron (1978) The Helium Driven rProcess in Supernovae Truran (1981) A New Interpretation of the Heavy Element Abundances in Metal-deficient Stars Cowan, Thielemann & Truran (1991) The r-Process and ...
observable Universe - faculty.ucmerced.edu
... has a finite range, typically operating on nuclear scales, ∼ 10−15 meters. There are other types of nuclear decay, for example beta decay, where beta particles (electrons) are emitted. One example of a system undergoing beta decay is a free neutron. Outside the nucleus a neutron is not stable, but d ...
... has a finite range, typically operating on nuclear scales, ∼ 10−15 meters. There are other types of nuclear decay, for example beta decay, where beta particles (electrons) are emitted. One example of a system undergoing beta decay is a free neutron. Outside the nucleus a neutron is not stable, but d ...
Article #1- How the Big Bang Theory Works
... Because of the limitations of the laws of science, we can't make any guesses about the instant the universe came into being. Instead, we can look at the period immediately following the creation of the universe. Right now, the earliest moment scientists talk about occurs at t = 1 x 10-43 seconds (th ...
... Because of the limitations of the laws of science, we can't make any guesses about the instant the universe came into being. Instead, we can look at the period immediately following the creation of the universe. Right now, the earliest moment scientists talk about occurs at t = 1 x 10-43 seconds (th ...
here - The Planetary Chemistry Laboratory
... ISM/molecular cloud composition 4.6 billion years ago proto-solar abundances Li, D, short-lived radioactive nuclides: 26Al, 129I long-lived (still present) radioactive nuclides: 87Rb, 235U, 238U, 232Th ...
... ISM/molecular cloud composition 4.6 billion years ago proto-solar abundances Li, D, short-lived radioactive nuclides: 26Al, 129I long-lived (still present) radioactive nuclides: 87Rb, 235U, 238U, 232Th ...
a brief history of time
... Light rays too must follow geodesics in space-time... this means that light from a distant star that happened to pass near the sun would be deflected through a small angel, causing the star to appear in a different position to an observer on the earth. The Expanding Universe The nearest star, called ...
... Light rays too must follow geodesics in space-time... this means that light from a distant star that happened to pass near the sun would be deflected through a small angel, causing the star to appear in a different position to an observer on the earth. The Expanding Universe The nearest star, called ...
Genesis of the Heaviest Elements in the Milky Way Galaxy
... elements are the most tightly bound of all, and the direct fusion of these nuclei is endothermic, requiring extra energy input to loosen the nuclear bonds (2). Instead, almost all isotopes of ...
... elements are the most tightly bound of all, and the direct fusion of these nuclei is endothermic, requiring extra energy input to loosen the nuclear bonds (2). Instead, almost all isotopes of ...
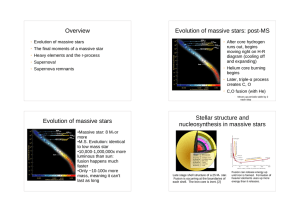
Overview Evolution of massive stars Evolution of massive stars
... Core rapidly collapses until neutron degeneracy pressure suddenly kicks in Material from outside core is falling inward; it hasn't 'gotten the message' that the core is supported. Material bounces off of core. ...
... Core rapidly collapses until neutron degeneracy pressure suddenly kicks in Material from outside core is falling inward; it hasn't 'gotten the message' that the core is supported. Material bounces off of core. ...
Slide 1
... - but not representative for composition of entire Earth Earth is also not representative for solar system composition Chemical and physical fractionations during (1) formation of planetesimals from molecular cloud material processed in the protoplanetary accretion disk (solar nebula) (2) differenti ...
... - but not representative for composition of entire Earth Earth is also not representative for solar system composition Chemical and physical fractionations during (1) formation of planetesimals from molecular cloud material processed in the protoplanetary accretion disk (solar nebula) (2) differenti ...
Lesson 55 – The Structure of the Universe - science
... The brightness of the star varied in a particular way (see Figure 3) and in 1912 Miss Henrietta Leavitt of Harvard College observatory discovered an important connection between the period and brightness. This is now known as the period-luminosity relationship. Many other stars were found to vary in ...
... The brightness of the star varied in a particular way (see Figure 3) and in 1912 Miss Henrietta Leavitt of Harvard College observatory discovered an important connection between the period and brightness. This is now known as the period-luminosity relationship. Many other stars were found to vary in ...
Galaxy map hints at fractal universe
... pattern up to a scale of about 100 million light years. And they say if the universe does become homogeneous at some point, it has to be on a scale larger than a staggering 300 million light years across. That's because even at that scale, they still observe large fluctuations – a cluster here, a vo ...
... pattern up to a scale of about 100 million light years. And they say if the universe does become homogeneous at some point, it has to be on a scale larger than a staggering 300 million light years across. That's because even at that scale, they still observe large fluctuations – a cluster here, a vo ...
Search for Life in the Universe
... • Distance to Galactic Center: 2.5 x 104 light years • Distance to the nearest big galaxy, Andromeda (M31): 2 x 106 light years ...
... • Distance to Galactic Center: 2.5 x 104 light years • Distance to the nearest big galaxy, Andromeda (M31): 2 x 106 light years ...
pptx
... The Tully-Fisher Relation The rotation speed of a galaxy depends on its mass (as we found when discussing dark matter). Galaxies with higher masses generally have higher luminosities. So the luminosities and rotation speeds of galaxies are correlated, which is know as the Tully-Fisher relation. So ...
... The Tully-Fisher Relation The rotation speed of a galaxy depends on its mass (as we found when discussing dark matter). Galaxies with higher masses generally have higher luminosities. So the luminosities and rotation speeds of galaxies are correlated, which is know as the Tully-Fisher relation. So ...
viz05 - KICP Workshops
... 9. Closing thoughts The physics of the early Universe can be cast in terms which are bizarrely familiar, allowing us access to what must surely be one of the most remote but important of times. ...
... 9. Closing thoughts The physics of the early Universe can be cast in terms which are bizarrely familiar, allowing us access to what must surely be one of the most remote but important of times. ...
Rare isotopes in the cosmos - National Superconducting Cyclotron
... nature’s chemical elements out of the hydrogen and helium left over from the Big Bang. Fusion reactions in stars drive the formation of elements with atomic numbers up to about that of iron. But fusion does not produce heavier elements; the nuclear binding energy per nucleon is maximal for nuclei ar ...
... nature’s chemical elements out of the hydrogen and helium left over from the Big Bang. Fusion reactions in stars drive the formation of elements with atomic numbers up to about that of iron. But fusion does not produce heavier elements; the nuclear binding energy per nucleon is maximal for nuclei ar ...
Space Science Chapter 10.1 textbook
... in the night sky. However, it would be impossible for you to develop any sense of the world beyond what you could see with your naked eye. Your knowledge would grow only when you had better ways of leaving your island and exploring new areas. Earth is like an island in the universe, and humans are c ...
... in the night sky. However, it would be impossible for you to develop any sense of the world beyond what you could see with your naked eye. Your knowledge would grow only when you had better ways of leaving your island and exploring new areas. Earth is like an island in the universe, and humans are c ...
PDF file - Memorie della SAIt
... a fossil record of the nucleosynthesis that occurred several Gyr ago in halo AGB stars. They are dwarfs or giants, whose surface composition was polluted by the wind of an AGB companion. Then, the C and s-element enhancements are ashes of the nucleosynthesis occurred in the He-rich inter-shell of a ...
... a fossil record of the nucleosynthesis that occurred several Gyr ago in halo AGB stars. They are dwarfs or giants, whose surface composition was polluted by the wind of an AGB companion. Then, the C and s-element enhancements are ashes of the nucleosynthesis occurred in the He-rich inter-shell of a ...
The Chemical Composition of the Local Interstellar Dust
... Sun: + star that can be studied best + independent abundances from different indicators - 4.56 Gyr old, representative for present-day ISM? F&G stars: + differential abundances relative to Sun + increased number statistics - difficult age determination - non-LTE & 3D-corrections (convection) not con ...
... Sun: + star that can be studied best + independent abundances from different indicators - 4.56 Gyr old, representative for present-day ISM? F&G stars: + differential abundances relative to Sun + increased number statistics - difficult age determination - non-LTE & 3D-corrections (convection) not con ...
Checklist for Geo- vs. Heliocentric Model of Universe
... the other atomic abundances The Big Bang expansion would perhaps have pulled apart baby galaxies before they could grow; nevertheless, galaxies did evolve, but no one could explain how Young galaxies existed in the early universe and should therefore be observable only at great distances, which effe ...
... the other atomic abundances The Big Bang expansion would perhaps have pulled apart baby galaxies before they could grow; nevertheless, galaxies did evolve, but no one could explain how Young galaxies existed in the early universe and should therefore be observable only at great distances, which effe ...
1 December 2014 An Update on the Universe Professor Ian Morison
... Predictions of a “Hot” Big Bang and hence the presence of radiation within the Universe Two American scientists, George Gamow and Richard Dicke independently predicted that very high temperatures must have existed at the time of the Big Bang − both for somewhat the wrong reasons. Gamov wanted the te ...
... Predictions of a “Hot” Big Bang and hence the presence of radiation within the Universe Two American scientists, George Gamow and Richard Dicke independently predicted that very high temperatures must have existed at the time of the Big Bang − both for somewhat the wrong reasons. Gamov wanted the te ...