Pop Goes the Universe
... (pink at right) requires very special starting conditions and thus seems implausible. This down the other hill. But then you notice analogy with two ski hills offers an idea of why the second class of models—the kind of something about the stranger. She has no inflation that has not been ruled out by ...
... (pink at right) requires very special starting conditions and thus seems implausible. This down the other hill. But then you notice analogy with two ski hills offers an idea of why the second class of models—the kind of something about the stranger. She has no inflation that has not been ruled out by ...
Lab 15 How Many Galaxies Are There in the
... final section of this lab, we now want to explore the implications of this calculation by making an estimate of the matter density of the Universe. In your lecture sections, and some of the earlier labs (like the Terrestrial Planet lab, esp. Table 4.2) you have probably encountered the concept of de ...
... final section of this lab, we now want to explore the implications of this calculation by making an estimate of the matter density of the Universe. In your lecture sections, and some of the earlier labs (like the Terrestrial Planet lab, esp. Table 4.2) you have probably encountered the concept of de ...
Inflation - Caltech Astronomy
... interact with each other at a very large distance. Weak and strong interactions are mediated by similar particles. For example, weak interactions are mediated by particles called W and Z. However, whereas photons are massless particles, the particles W and Z are extremely heavy; it is very difficult ...
... interact with each other at a very large distance. Weak and strong interactions are mediated by similar particles. For example, weak interactions are mediated by particles called W and Z. However, whereas photons are massless particles, the particles W and Z are extremely heavy; it is very difficult ...
Classical Probability, Shakespearean Sonnets, and
... use the proportion from Penrose,3 where πi = 1 in 10(10^123). (Penrose calculated the probability for generating a universe similar to the observed universe with the following considerations: the universe has 1080 baryons with maximum entropy in a big crunch of 1043 photons per baryon while the entr ...
... use the proportion from Penrose,3 where πi = 1 in 10(10^123). (Penrose calculated the probability for generating a universe similar to the observed universe with the following considerations: the universe has 1080 baryons with maximum entropy in a big crunch of 1043 photons per baryon while the entr ...
Nuclear reactions and stellar processes
... processes. The nuclear reactions occur deep in the core of the star, but the freshly formed nuclei are eventually transported by sequences of convective dredge-up processes from the burning zones to the stellar atmosphere followed by mass loss due to radiation-pressure-driven winds. This scenario of ...
... processes. The nuclear reactions occur deep in the core of the star, but the freshly formed nuclei are eventually transported by sequences of convective dredge-up processes from the burning zones to the stellar atmosphere followed by mass loss due to radiation-pressure-driven winds. This scenario of ...
The Big Bang and Stellar Evolution
... or a planet, or anything else. Since both hydrogen and helium are gases, they are good at spreading out, but not at clumping together. 2 - Careful analysis has revealed that there is not enough matter in gas clouds to produce stars. 3 - There would not be enough time for the gas to reach the current ...
... or a planet, or anything else. Since both hydrogen and helium are gases, they are good at spreading out, but not at clumping together. 2 - Careful analysis has revealed that there is not enough matter in gas clouds to produce stars. 3 - There would not be enough time for the gas to reach the current ...
FIRST DETECTION OF KRYPTON AND XENON IN A WHITE DWARF
... discussed that these overabundances might be ascribed to diffusion processes and to s-process nucleosynthesis in the AGB phase of the previous evolution. They also pointed out that this phenomenon is obviously restricted to DO WDs. This can be understood when considering that their immediate progeni ...
... discussed that these overabundances might be ascribed to diffusion processes and to s-process nucleosynthesis in the AGB phase of the previous evolution. They also pointed out that this phenomenon is obviously restricted to DO WDs. This can be understood when considering that their immediate progeni ...
Priestly Contributions to Modern Science: The
... writings of cosmic rays…Cosmic rays are the birth cries of the universe still lingering ...
... writings of cosmic rays…Cosmic rays are the birth cries of the universe still lingering ...
Structure of the Universe
... What makes up the universe? • A galaxy is a large collection of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. • Small galaxies, called dwarf galaxies, may contain a few billion stars. Giant galaxies may contain more than 1 trillion stars. • Our solar system is located in the Milky Way galaxy. The M ...
... What makes up the universe? • A galaxy is a large collection of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. • Small galaxies, called dwarf galaxies, may contain a few billion stars. Giant galaxies may contain more than 1 trillion stars. • Our solar system is located in the Milky Way galaxy. The M ...
RobinCollins_CPiS_Ca..
... Plot of the intensity of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) versus the baryon to photon ratio. CMB/CMB0 represents the intensity of the CMB in the alternative universe compared to our universe, and ηbγ/ηbγ0 represents the baryon to photon ratio in the alternative universe compared to th ...
... Plot of the intensity of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) versus the baryon to photon ratio. CMB/CMB0 represents the intensity of the CMB in the alternative universe compared to our universe, and ηbγ/ηbγ0 represents the baryon to photon ratio in the alternative universe compared to th ...
The First Stars in the Universe - Scientific American
... have been almost 1,000 times larger. In molecular clouds in the nearby part of the Milky Way, the Jeans mass is roughly equal to the mass of the sun, and the masses of the prestellar clumps observed in these clouds are about the same. If we scale up by a factor of almost 1,000, we can estimate that ...
... have been almost 1,000 times larger. In molecular clouds in the nearby part of the Milky Way, the Jeans mass is roughly equal to the mass of the sun, and the masses of the prestellar clumps observed in these clouds are about the same. If we scale up by a factor of almost 1,000, we can estimate that ...
... have been made for 8 nebulae, and several others are in progress. The results are given in Table 3, and are compared to abundances in the sun, B stars, an interstellar cloud and the Orion nebula (references are given in Pottasch & Beintema 1999). The accuracy of the values is difficult to estimate. ...
Nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars
... in case of initial solar-like metallicity, but it could as low as 2 M¯ for zero initial metallicity ([7]. The HBB is very sensitive to mass loss by stellar wind which can reduce the mass of the envelope so that the HBB will be shut off. The temperature required for HBB is at least 107 K, which means ...
... in case of initial solar-like metallicity, but it could as low as 2 M¯ for zero initial metallicity ([7]. The HBB is very sensitive to mass loss by stellar wind which can reduce the mass of the envelope so that the HBB will be shut off. The temperature required for HBB is at least 107 K, which means ...
universe
... decay on a massive scale . This allows for free electrons and protons to combine with other particles . At this period of time , the radiation is so dense (1014g/cm3) that no light is visible . Photons , neutrinos , electrons and quarks began to form as the Universe expands and cooled . After the un ...
... decay on a massive scale . This allows for free electrons and protons to combine with other particles . At this period of time , the radiation is so dense (1014g/cm3) that no light is visible . Photons , neutrinos , electrons and quarks began to form as the Universe expands and cooled . After the un ...
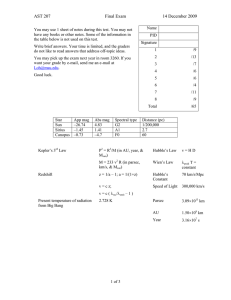
AST 207 Final Exam 14 December 2009
... a. (2 pts.) Explain why the sun moves with respect to the stars. b. (2 pts.) Explain why the planets sometimes moves east to west with respect to the stars, which is opposite the way the sun moves. c. (2 pts.) Explain why Mars moves east to west with respect to the horizon. d. (3 pts.) Copernicus’s ...
... a. (2 pts.) Explain why the sun moves with respect to the stars. b. (2 pts.) Explain why the planets sometimes moves east to west with respect to the stars, which is opposite the way the sun moves. c. (2 pts.) Explain why Mars moves east to west with respect to the horizon. d. (3 pts.) Copernicus’s ...
Dr. Amanda Karakas and Prof. John Lattanzio
... Evolution after core H-burning • After core H-burning has ceased, the envelope expands and the core begins to contract • A hydrogen-shell burning is established in a shell around the contracting He-core • This provides most of the surface luminosity • At this point (owing to L = 4πσR2Teff 4), T ...
... Evolution after core H-burning • After core H-burning has ceased, the envelope expands and the core begins to contract • A hydrogen-shell burning is established in a shell around the contracting He-core • This provides most of the surface luminosity • At this point (owing to L = 4πσR2Teff 4), T ...
APS Slide Presentation
... holes, and inflation have only begun to impact physics in general and cosmology in particular. Dark energy generally has not been factored into all universe formation models, but when considered, it changes everything. The function of dark energy is to push the universe apart, separating each super ...
... holes, and inflation have only begun to impact physics in general and cosmology in particular. Dark energy generally has not been factored into all universe formation models, but when considered, it changes everything. The function of dark energy is to push the universe apart, separating each super ...
Three Minutes After The Big Bang
... • A great deal of the understanding can be described WITHOUT the math – Eg, You can enjoy music without being a musician or a composer • As future leaders you should be able to go out into ...
... • A great deal of the understanding can be described WITHOUT the math – Eg, You can enjoy music without being a musician or a composer • As future leaders you should be able to go out into ...
Axiom Cosmology: A New Direction
... rem in general relativity demonstrated—sixty years after its discovery—that Einstein’s theory was consistent and stable [5] [6]. Most modern, accepted theories of cosmology are based on general relativity and, more specifically, the predicted Big Bang [7] [8]. In the universe, the axiom field repres ...
... rem in general relativity demonstrated—sixty years after its discovery—that Einstein’s theory was consistent and stable [5] [6]. Most modern, accepted theories of cosmology are based on general relativity and, more specifically, the predicted Big Bang [7] [8]. In the universe, the axiom field repres ...
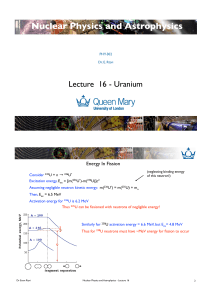
Lecture 16 - QMUL physics
... Note: 235U produces on average 2.5 fast (~1 MeV) neutrons per fission Need to slow neutrons down to thermal energies (0.025 eV) ...
... Note: 235U produces on average 2.5 fast (~1 MeV) neutrons per fission Need to slow neutrons down to thermal energies (0.025 eV) ...
element - Batesville Community Schools
... Earth’s atmosphere is about 80% nitrogen (N). Most of the rest of the atmosphere is oxygen (O) ...
... Earth’s atmosphere is about 80% nitrogen (N). Most of the rest of the atmosphere is oxygen (O) ...
Constraining planet structure from stellar chemistry: the cases of
... The abundances of magnesium (Mg) and silicon (Si) were derived for the three stars following the same methodology as in our previous works (e.g., Adibekyan et al. 2012a, 2015). We used a LTE analysis relative to the Sun with the 2014 version of the code MOOG (Sneden 1973) and a grid of Kurucz ATLAS9 ...
... The abundances of magnesium (Mg) and silicon (Si) were derived for the three stars following the same methodology as in our previous works (e.g., Adibekyan et al. 2012a, 2015). We used a LTE analysis relative to the Sun with the 2014 version of the code MOOG (Sneden 1973) and a grid of Kurucz ATLAS9 ...
Dark Matter and Dark Energy - Trans
... of particles. As the universe cooled, WIMPs decreased in density, and when the ambient temperature became low enough, WIMP creation all but ceased [12]. These particles, how- ...
... of particles. As the universe cooled, WIMPs decreased in density, and when the ambient temperature became low enough, WIMP creation all but ceased [12]. These particles, how- ...
Cosmology with objects from the Hamburg Quasar Surveys
... 2.2 The primordial Deuterium abundance D/H from HS 0105+1619 The theory of big bang nucleosynthesis predicts that the primordial D/H ratio depends sensitively on the cosmological baryon to photon ratio nb/nr ( e.g. Kolb & Turner, 1990; Schramm & Turner, 1998). A precise measurement of the primordial ...
... 2.2 The primordial Deuterium abundance D/H from HS 0105+1619 The theory of big bang nucleosynthesis predicts that the primordial D/H ratio depends sensitively on the cosmological baryon to photon ratio nb/nr ( e.g. Kolb & Turner, 1990; Schramm & Turner, 1998). A precise measurement of the primordial ...
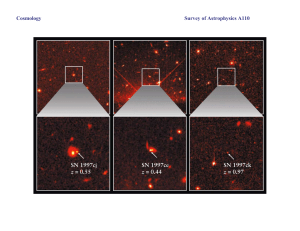
Survey of Astrophysics A110 Cosmology
... we are looking further and further into the past this implies that the Universe is not constant --- it evolves with time. • Attempts (sometimes very elaborate) to modify the Steady State Theory to account for the observed evolution do not provide a convincing explanation of the Universe. The Big Ban ...
... we are looking further and further into the past this implies that the Universe is not constant --- it evolves with time. • Attempts (sometimes very elaborate) to modify the Steady State Theory to account for the observed evolution do not provide a convincing explanation of the Universe. The Big Ban ...