CHAPTER @2- Solar Sun and Earth
... Our Sun is a typical yellow-dwarf thermonuclear (fusion) star. How does the Sun produce such tremendous quantities of energy? The solar mass of gas produces tremendous pressure and high temperatures deep in its dense interior region. Under these conditions, pairs of hydrogen nuclei, the lightest of ...
... Our Sun is a typical yellow-dwarf thermonuclear (fusion) star. How does the Sun produce such tremendous quantities of energy? The solar mass of gas produces tremendous pressure and high temperatures deep in its dense interior region. Under these conditions, pairs of hydrogen nuclei, the lightest of ...
Figures from Lectures 2+3 - University of Texas Astronomy
... Building blocks of matter: protons, electron, neutrons, and atoms Stars Brown Dwarfs, Planets, and Moons Death of Stars: Planetary Nebulae, White Dwarfs, Supernovae remnants Why is human life `star stuff’?’ Different Type of Nebulae: Star-forming nebulae vs Planetary nebulae Galaxies and the Milky W ...
... Building blocks of matter: protons, electron, neutrons, and atoms Stars Brown Dwarfs, Planets, and Moons Death of Stars: Planetary Nebulae, White Dwarfs, Supernovae remnants Why is human life `star stuff’?’ Different Type of Nebulae: Star-forming nebulae vs Planetary nebulae Galaxies and the Milky W ...
Слайд 1 - University of Wrocław
... 1. Equation of state (EOS) determines the pressure of the matter, P. 2. The neutron star matter is so dense that P is almost independen t of the temperatu re T and is determined by the mass density and the compositio n of the matter; one usually w rites P P ( ). 3. The mass density is defined ...
... 1. Equation of state (EOS) determines the pressure of the matter, P. 2. The neutron star matter is so dense that P is almost independen t of the temperatu re T and is determined by the mass density and the compositio n of the matter; one usually w rites P P ( ). 3. The mass density is defined ...
Day-13
... the idea of “uniform circular motion.” • Objects moved in perfect circles at uniform speeds. ...
... the idea of “uniform circular motion.” • Objects moved in perfect circles at uniform speeds. ...
Lecture 9 - Angular Momentum Transport
... Particles lost from the star also carry away angular momentum. Given an initial mass, rotation rate, and radius, we can thus calculate the rate of AM loss. ...
... Particles lost from the star also carry away angular momentum. Given an initial mass, rotation rate, and radius, we can thus calculate the rate of AM loss. ...
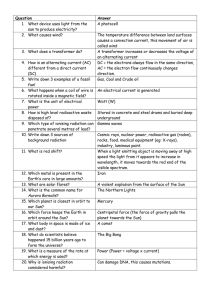
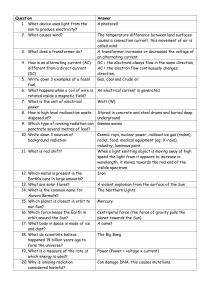
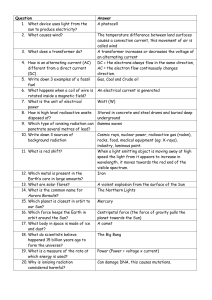
P2 revision quiz
... The Northern Lights Centripetal force (the force of gravity pulls the planet towards the Sun) The Big Bang Can damage DNA, this causes mutations. There are 20 questions (1 per student). Every student has a full table to complete with every answer. Each student also receives one answer. All answers m ...
... The Northern Lights Centripetal force (the force of gravity pulls the planet towards the Sun) The Big Bang Can damage DNA, this causes mutations. There are 20 questions (1 per student). Every student has a full table to complete with every answer. Each student also receives one answer. All answers m ...
COSMOLOGY 1 An Introduction to the Universe
... wave propels this material out into space. The material that is exploded away from the star is now known as a supernova remnant. The hot material, the radioactive isotopes, as well as the leftover core of the exploded star, produce X-rays and gamma-rays. February 19, 2004: The brightest supernova ex ...
... wave propels this material out into space. The material that is exploded away from the star is now known as a supernova remnant. The hot material, the radioactive isotopes, as well as the leftover core of the exploded star, produce X-rays and gamma-rays. February 19, 2004: The brightest supernova ex ...
Semester 1 Earth Science Gallery Review
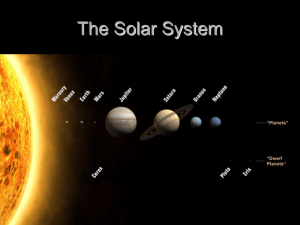
... i. Where is most of the mass found in the solar system? ...
... i. Where is most of the mass found in the solar system? ...
Our Sun Produces Bizarre Radiation Bursts—Now NASA Knows Why
... Closer to home, solar flares can also produce gamma rays. Flares happen when active regions on the sun suddenly release explosions of magnetic energy. That accelerates particles to incredibly high speeds and creates intense bursts of light that can briefly outshine the sun itself. (Also see “How Su ...
... Closer to home, solar flares can also produce gamma rays. Flares happen when active regions on the sun suddenly release explosions of magnetic energy. That accelerates particles to incredibly high speeds and creates intense bursts of light that can briefly outshine the sun itself. (Also see “How Su ...
Worksheet
... 2. What holds the Solar System together? a. Sun’s gravity 3. How old do cosmologists believe the Solar System is? b. 4.5 billion years 4. What force pulls an apple to the ground? c. Gravity 5. Without gravity, what would happen to the Solar System? a. Planets would fly away from the Sun 6. Bigger ob ...
... 2. What holds the Solar System together? a. Sun’s gravity 3. How old do cosmologists believe the Solar System is? b. 4.5 billion years 4. What force pulls an apple to the ground? c. Gravity 5. Without gravity, what would happen to the Solar System? a. Planets would fly away from the Sun 6. Bigger ob ...
Solar SyStem - Lorenz Educational Press
... exploding nuclear bomb. It is the center of our Solar System. It provides us with heat and light. The Sun has been spinning on its axis and exploding for about 5 billion years. The Sun is an average-size star, but seems larger because it is the star nearest to us—only 93,000,000 miles (150,000,000 k ...
... exploding nuclear bomb. It is the center of our Solar System. It provides us with heat and light. The Sun has been spinning on its axis and exploding for about 5 billion years. The Sun is an average-size star, but seems larger because it is the star nearest to us—only 93,000,000 miles (150,000,000 k ...
Sixth Grade NGSS
... (i.e., from sunlight) to occur. In this reaction, carbon dioxide and water combine to form carbon-based organic molecules and release oxygen. (secondary to MS-LS1-6) Cellular respiration in plants and animals involve chemical reactions with oxygen that release stored energy. In these processes, comp ...
... (i.e., from sunlight) to occur. In this reaction, carbon dioxide and water combine to form carbon-based organic molecules and release oxygen. (secondary to MS-LS1-6) Cellular respiration in plants and animals involve chemical reactions with oxygen that release stored energy. In these processes, comp ...
Chapter 29, Section 2
... What are the similarities and differences between Ptolemy’s and Copernicus’ models of the universe? What are Kepler’s 3 laws of planetary motion and what do they say? ...
... What are the similarities and differences between Ptolemy’s and Copernicus’ models of the universe? What are Kepler’s 3 laws of planetary motion and what do they say? ...
Stars and Galaxies PP 2013
... High mass supergiants may undergo a supernova, where the core suddenly collapses and explodes. A neutron star is what remains after the supernova. It is composed mainly of neutrons and is very dense. If it spins and releases radiation it is called a pulsar. ...
... High mass supergiants may undergo a supernova, where the core suddenly collapses and explodes. A neutron star is what remains after the supernova. It is composed mainly of neutrons and is very dense. If it spins and releases radiation it is called a pulsar. ...
Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System”
... assume that everything formed in the same place at the same time, about 4.5 billion years ago. ...
... assume that everything formed in the same place at the same time, about 4.5 billion years ago. ...
THE SUN - rgreenbergscience
... All of the Sun is gas 70% Hydrogen, 20% helium and 2% heavier elements Sun is a madhouse of electromagnetic activity On the Sun, almost everything is electrically conductive because there aren’t very many intact neutral atoms Overwhelming thermal and radiation energies excite electrons to the point ...
... All of the Sun is gas 70% Hydrogen, 20% helium and 2% heavier elements Sun is a madhouse of electromagnetic activity On the Sun, almost everything is electrically conductive because there aren’t very many intact neutral atoms Overwhelming thermal and radiation energies excite electrons to the point ...