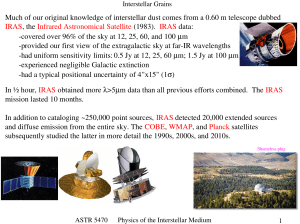
GRB 130603B: No Compelling Evidence for Neutron Star Merger
... matter are probably ejected in such events and produce narrowly collimated GRBs by inverse Compton scattering of circumstellar light. They also suggested that short GRBs may also be produced by highly relativistic jets ejected in the phase transition of compact stars, such as neutron stars, strange ...
... matter are probably ejected in such events and produce narrowly collimated GRBs by inverse Compton scattering of circumstellar light. They also suggested that short GRBs may also be produced by highly relativistic jets ejected in the phase transition of compact stars, such as neutron stars, strange ...
Undergraduate Project in Physics Boaz Jaron Advisor: Prof. Eduardo Guendelman Department of Physics
... solution to the Einstein equation describing the evolution of spacetime geometry. This solution, a possible shape of spacetime, would describe the effects of gravity outside a spherically symmetric, uncharged, nonrotating object (and would serve approximately to describe even slowly rotating objects ...
... solution to the Einstein equation describing the evolution of spacetime geometry. This solution, a possible shape of spacetime, would describe the effects of gravity outside a spherically symmetric, uncharged, nonrotating object (and would serve approximately to describe even slowly rotating objects ...
Stellar Lifetimes
... Open cluster: A few thousand loosely packed stars © 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... Open cluster: A few thousand loosely packed stars © 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
A comparison of the s- and r-process element evolution in local
... galaxies to have a more homogeneous sample with data coming from different authors and to make a more proper comparison with the predictions of the models. In LMC06a, however, we only analysed the elements Ba and Eu. We extend the analysis to Yttrium and Lanthanum, for which there is a new set of dat ...
... galaxies to have a more homogeneous sample with data coming from different authors and to make a more proper comparison with the predictions of the models. In LMC06a, however, we only analysed the elements Ba and Eu. We extend the analysis to Yttrium and Lanthanum, for which there is a new set of dat ...
Stellar populations in the intergalactic space (invited talk)
... Cosmological Hydrodynamic Simulations with Star Formation and Feedback • Studies of ICL in cosmological simulations require a model of star formation from cold gas, including cooling and feedback effects. Recent studies are by Murante+2004, Willman+2004, SommerLarsen+2005. Here we use Gadget-2 with ...
... Cosmological Hydrodynamic Simulations with Star Formation and Feedback • Studies of ICL in cosmological simulations require a model of star formation from cold gas, including cooling and feedback effects. Recent studies are by Murante+2004, Willman+2004, SommerLarsen+2005. Here we use Gadget-2 with ...
1. The Birth of a Star
... Dilation Effect of Special Relativity). The span of space between you and M42 is ENORMOUS. 14. Fortunately, the Celestia 2 is a “special” ship. It can travel faster than the speed of light. We won’t have to wait 1,177 years to make our first stop in the story of a star’s life cycle. 15. M42 is a clo ...
... Dilation Effect of Special Relativity). The span of space between you and M42 is ENORMOUS. 14. Fortunately, the Celestia 2 is a “special” ship. It can travel faster than the speed of light. We won’t have to wait 1,177 years to make our first stop in the story of a star’s life cycle. 15. M42 is a clo ...
Environment and self-regulation in galaxy formation
... We visually inspected the 48,023 objects and divided the sample in 31,521 late-type (spiral arms, clear disc-like structures) and 16,502 early-type (roundish, elliptically shaped) galaxies. Hence, 34 per cent of the objects are classified as ’early-type’. This is in good agreement with the typical v ...
... We visually inspected the 48,023 objects and divided the sample in 31,521 late-type (spiral arms, clear disc-like structures) and 16,502 early-type (roundish, elliptically shaped) galaxies. Hence, 34 per cent of the objects are classified as ’early-type’. This is in good agreement with the typical v ...
Formation and evolution of giant molecular clouds in a barred spiral
... Understanding where and how gas is converted into stars in a galaxy is important for understanding a galaxy’s formation and evolution through each epoch of the universe. Which physical processes control the star formation in a galaxy is heavily debated. We are now at a stage where it is possible to ...
... Understanding where and how gas is converted into stars in a galaxy is important for understanding a galaxy’s formation and evolution through each epoch of the universe. Which physical processes control the star formation in a galaxy is heavily debated. We are now at a stage where it is possible to ...
Dynamical properties of a large young disk galaxy at z=2.03⋆
... with the local stellar mass TFR. F257 is then a nearly (∼ 75%) maximum disk. The dynamical properties of F257 are more like those of local galaxies than those of any other galaxy at similar redshift observed to date. However, the gas-to-stellar mass ratio is unusally large: 2.5. Key words. Galaxies: ...
... with the local stellar mass TFR. F257 is then a nearly (∼ 75%) maximum disk. The dynamical properties of F257 are more like those of local galaxies than those of any other galaxy at similar redshift observed to date. However, the gas-to-stellar mass ratio is unusally large: 2.5. Key words. Galaxies: ...
No Slide Title
... galaxy (not a lot of O and B-type Main Sequence Stars in the HR Diagram of the closest stars). • Stars spend most of their time on the Main Sequence (not a lot of supergiants and giants in the HR Diagram of the closest stars). ...
... galaxy (not a lot of O and B-type Main Sequence Stars in the HR Diagram of the closest stars). • Stars spend most of their time on the Main Sequence (not a lot of supergiants and giants in the HR Diagram of the closest stars). ...
Atoms and Stars IST 3360 and IST 1990
... Built great observatories on his island Fights, duels, possibly died from being drunk, but also careful astronomical measurements • Convinced astronomy needed good measurements ...
... Built great observatories on his island Fights, duels, possibly died from being drunk, but also careful astronomical measurements • Convinced astronomy needed good measurements ...
Chapter 31
... • In 1929, Edwin Hubble, by measuring the redshifts and distances of many galaxies, found that the farther away from Earth a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away. • The universe is expanding. • In a medium that is uniformly expanding, all points are moving away from all other points, and no point ...
... • In 1929, Edwin Hubble, by measuring the redshifts and distances of many galaxies, found that the farther away from Earth a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away. • The universe is expanding. • In a medium that is uniformly expanding, all points are moving away from all other points, and no point ...
Determination of the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy using variable stars U
... position of each variable star. The scaling factor at the position of each variable star was obtained from the comparison with the DIA photometry of each PSF. For similar PSFs, the scaling factor can be obtained with an error of 0.3% or less. This process provided instrumental magnitudes for all the ...
... position of each variable star. The scaling factor at the position of each variable star was obtained from the comparison with the DIA photometry of each PSF. For similar PSFs, the scaling factor can be obtained with an error of 0.3% or less. This process provided instrumental magnitudes for all the ...
P1 topic 3 - WordPress.com
... Not all electromagnetic radiation coming from space reaches the Earth's surface. The diagram shows how far radiation from each part of the electromagnetic spectrum travels down through the atmosphere. ...
... Not all electromagnetic radiation coming from space reaches the Earth's surface. The diagram shows how far radiation from each part of the electromagnetic spectrum travels down through the atmosphere. ...
Lecture 2. Thermal evolution and surface emission of neutron stars
... In both studies only upper limits were derived. Still, the zero result can be just due to unfavorable orientations (at long periods NSs have very narrow beams). It is necessary to increase statistics. ...
... In both studies only upper limits were derived. Still, the zero result can be just due to unfavorable orientations (at long periods NSs have very narrow beams). It is necessary to increase statistics. ...
Ch 33) Astrophysics and Cosmology
... In addition to stars both within and outside the Milky Way, we can see by telescope many faint cloudy patches in the sky which were all referred to once as “nebulae” (Latin for “clouds”). A few of these, such as those in the constellations Andromeda and Orion, can actually be discerned with the nake ...
... In addition to stars both within and outside the Milky Way, we can see by telescope many faint cloudy patches in the sky which were all referred to once as “nebulae” (Latin for “clouds”). A few of these, such as those in the constellations Andromeda and Orion, can actually be discerned with the nake ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.