Notes (PowerPoint)
... o Many purely rational arguments have been shown to be wrong – e.g. Aristotle o Experiments keep science correct and reliable ...
... o Many purely rational arguments have been shown to be wrong – e.g. Aristotle o Experiments keep science correct and reliable ...
Sun, Stars and Planets Part 1: The Sun: its structure and energy
... Because of the high T in stars all but the most tightly bound electrons are separated from the atoms. This allows a greater compression of stellar material without deviation from the perfect gas law because a nuclear dimension is 10 -15 m compared with a typical atomic dimension of 10-10 m, and so t ...
... Because of the high T in stars all but the most tightly bound electrons are separated from the atoms. This allows a greater compression of stellar material without deviation from the perfect gas law because a nuclear dimension is 10 -15 m compared with a typical atomic dimension of 10-10 m, and so t ...
Resume
... TIFR 100 cm FIR Balloon-borne Telescope TIFR 100 cm Far-Infrared Balloon-borne Telescope was mostly observed in the sky chopped mode. However, more sensitive observations can be done in the fast spectral scan mode where sky chopping is not done. I developed a wavelet based signal processing step for ...
... TIFR 100 cm FIR Balloon-borne Telescope TIFR 100 cm Far-Infrared Balloon-borne Telescope was mostly observed in the sky chopped mode. However, more sensitive observations can be done in the fast spectral scan mode where sky chopping is not done. I developed a wavelet based signal processing step for ...
Early-type stars in the core of the young open cluster Westerlund 2
... therefore adopt an A0 III spectral type. Our photometric data yield V = 14.13 ± 0.03 and B − V = 0.34 ± 0.04. If the intrinsic colours and absolute magnitudes of MSP 218 are those of a typical A0 III star (Schmidt-Kaler 1982), then AV ∼ 1.15 and the star must be located at a distance of about 4.0 kp ...
... therefore adopt an A0 III spectral type. Our photometric data yield V = 14.13 ± 0.03 and B − V = 0.34 ± 0.04. If the intrinsic colours and absolute magnitudes of MSP 218 are those of a typical A0 III star (Schmidt-Kaler 1982), then AV ∼ 1.15 and the star must be located at a distance of about 4.0 kp ...
X-ray emission from supernova shock waves Tanja Kramer Nymark Department of Astronomy
... interaction with a circumstellar medium. In particular the reverse shock created by the interaction is investigated. In most Type IIL and Type IIn supernovae this shock is radiative, and due to the high temperature most of the radiation comes out as X-rays. A numerical model is presented which calcu ...
... interaction with a circumstellar medium. In particular the reverse shock created by the interaction is investigated. In most Type IIL and Type IIn supernovae this shock is radiative, and due to the high temperature most of the radiation comes out as X-rays. A numerical model is presented which calcu ...
Figueira, Pont, Mordasini, Alibert, Georgy, Benz
... The discovery by radial velocity surveys of close-in planets in the 4-20 Earth-mass range (e.g. Lovis et al. 2004, Udry et al. 2007, Mayor et al. 2008) has motivated the development of several sets of structure models of these planets (Valencia et al. 2007; Fortney et al. 2007; Seager et al. 2007). ...
... The discovery by radial velocity surveys of close-in planets in the 4-20 Earth-mass range (e.g. Lovis et al. 2004, Udry et al. 2007, Mayor et al. 2008) has motivated the development of several sets of structure models of these planets (Valencia et al. 2007; Fortney et al. 2007; Seager et al. 2007). ...
Conference Abstract Booklet here.
... White dwarfs represent the end point of stellar evolution for the majority of stars. As such, they are excellent astrophysical laboratories. They are structurally simple, with electron degenerate cores surrounded by thin surface layers of helium and/or hydrogen. The g-mode pulsations provide a windo ...
... White dwarfs represent the end point of stellar evolution for the majority of stars. As such, they are excellent astrophysical laboratories. They are structurally simple, with electron degenerate cores surrounded by thin surface layers of helium and/or hydrogen. The g-mode pulsations provide a windo ...
The Homo Neanderthalis and the Dravidians–A
... hypothesis, the cosmic dust magnetotactic bacteria play a role in the formation of the intergalactic magnetic field. A magnetic field equal in strength to about one millionth part of the magnetic field of earth exists throughout much of our galaxy. The magnetic files can be used to trace the spiral ...
... hypothesis, the cosmic dust magnetotactic bacteria play a role in the formation of the intergalactic magnetic field. A magnetic field equal in strength to about one millionth part of the magnetic field of earth exists throughout much of our galaxy. The magnetic files can be used to trace the spiral ...
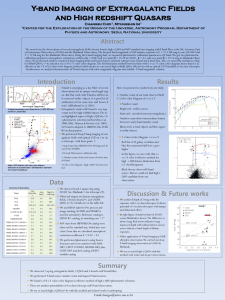
Y-band Imaging of Extragalatic Fields and High redshift
... h redshift QSO (z > 6) selection via i-z VS z-Y color-color diagram. The discrimination method between them with i-z va z-Y color-color diagram shows that it is as effective as the i-Y vsY-J color-color diagram method which means we can search high redshift QSOs effectively with an optical CCD insta ...
... h redshift QSO (z > 6) selection via i-z VS z-Y color-color diagram. The discrimination method between them with i-z va z-Y color-color diagram shows that it is as effective as the i-Y vsY-J color-color diagram method which means we can search high redshift QSOs effectively with an optical CCD insta ...
Rotating Disk-Jet System of the NGC 1333 IRAS 4A2 Protostar
... Astrophysical jets play important roles in many interesting astronomical phenomena, such as star formation and active galactic nuclei. The jets are thought to be driven by rotating disks through magneto-centrifugal processes. However, quantitative understanding of the jet-driving mechanism has been ...
... Astrophysical jets play important roles in many interesting astronomical phenomena, such as star formation and active galactic nuclei. The jets are thought to be driven by rotating disks through magneto-centrifugal processes. However, quantitative understanding of the jet-driving mechanism has been ...
Lecture01-ASTA01 - University of Toronto
... Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 ly from Earth. • In other words, light from Proxima Centauri takes 4.2 years to reach us. 4.3 ly from us is a companion Alpha Cen B. An Earth-mass planet was discovered 1yr ago around it! ...
... Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 ly from Earth. • In other words, light from Proxima Centauri takes 4.2 years to reach us. 4.3 ly from us is a companion Alpha Cen B. An Earth-mass planet was discovered 1yr ago around it! ...
Discovery of the optical counterpart to the X
... about 8 were bright enough in Hα to call our attention. The position of each one of these potential candidates with respect to the satellites error circle was then checked. Of these relatively strong Hα emitters only one lied inside the WFC BeppoSAX satellite position uncertainty circles (Fig.1). As ...
... about 8 were bright enough in Hα to call our attention. The position of each one of these potential candidates with respect to the satellites error circle was then checked. Of these relatively strong Hα emitters only one lied inside the WFC BeppoSAX satellite position uncertainty circles (Fig.1). As ...
Stellar death - Department of Astronomy
... Teaspoon of white dwarf stuff weighs as much as SUV! A114: Lecture 20—28 Mar 2007 ...
... Teaspoon of white dwarf stuff weighs as much as SUV! A114: Lecture 20—28 Mar 2007 ...
A Star`s Color, Temperature, and Brightness are Related!
... • What is the peak wavelength of our sun, with a T = 5750 K? 2.9 x 106 = 504 nm (yellowish-green) 5750 K • What is the peak wavelength of a star with a surface temperature of 3500 K? 2.9 x 106 = 829 nm (this star emits the 3500 K majority of its light as infrared, IR). ...
... • What is the peak wavelength of our sun, with a T = 5750 K? 2.9 x 106 = 504 nm (yellowish-green) 5750 K • What is the peak wavelength of a star with a surface temperature of 3500 K? 2.9 x 106 = 829 nm (this star emits the 3500 K majority of its light as infrared, IR). ...
How are a star`s temperature, color, and brightness related?
... • What is the peak wavelength of our sun, with a T = 5778 K? 2.9 x 106 = 502 nm (yellowish-green) 5778 K • What is the peak wavelength of a star with a surface temperature of 3500 K? 2.9 x 106 = 829 nm (this star emits the 3500 K majority of its light as infrared, IR). ...
... • What is the peak wavelength of our sun, with a T = 5778 K? 2.9 x 106 = 502 nm (yellowish-green) 5778 K • What is the peak wavelength of a star with a surface temperature of 3500 K? 2.9 x 106 = 829 nm (this star emits the 3500 K majority of its light as infrared, IR). ...
High-precision abundances of elements in solar twin stars: Trends
... (EWs) of spectral lines by Gaussian fitting relative to pseudocontinuum regions lying within 3 Å from the line measured. These regions do not necessarily represent the true continuum, but care was taken to use the same continuum windows in all stars, so that differences in EW between stars are preci ...
... (EWs) of spectral lines by Gaussian fitting relative to pseudocontinuum regions lying within 3 Å from the line measured. These regions do not necessarily represent the true continuum, but care was taken to use the same continuum windows in all stars, so that differences in EW between stars are preci ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.