The Earth in Space Scientific evidence indicates the universe is
... gravitational attraction to form stars and galaxies. According to the Big Bang theory, the universe has been continually expanding at an increasing rate since its formation about 13.7 billion years ago. E5.1A Describe the position and motion of our solar system in our galaxy and the overall scale, s ...
... gravitational attraction to form stars and galaxies. According to the Big Bang theory, the universe has been continually expanding at an increasing rate since its formation about 13.7 billion years ago. E5.1A Describe the position and motion of our solar system in our galaxy and the overall scale, s ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... When nuclear fusion stops->the star’s core begins to collapse due to its own gravity->the outer layers of the star drift away->hot core is all that remains (white dwarf)->cools down, all that remains is dark, cold matter (black dwarf) For stars tens of times more massive than the sun, the outer laye ...
... When nuclear fusion stops->the star’s core begins to collapse due to its own gravity->the outer layers of the star drift away->hot core is all that remains (white dwarf)->cools down, all that remains is dark, cold matter (black dwarf) For stars tens of times more massive than the sun, the outer laye ...
PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... 11. Describe and contrast galactic clusters, globular clusters, X-ray bursters. 12. Relate the various types of variable stars to stellar evolution. 13. Provide examples of the atoms and molecules existing in the interstellar medium. 14. Sketch the life cycle of several stars. ...
... 11. Describe and contrast galactic clusters, globular clusters, X-ray bursters. 12. Relate the various types of variable stars to stellar evolution. 13. Provide examples of the atoms and molecules existing in the interstellar medium. 14. Sketch the life cycle of several stars. ...
Rachel Henning
... hydrogen burning. Our star will slowly puff into a red giant, which is a star that has exhausted it hydrogen and is burning helium fuel. It will eat all of the inner planets, even the Earth. Then the sun would burn into carbon, but it is not big enough so it will probably end up being a white dwarf. ...
... hydrogen burning. Our star will slowly puff into a red giant, which is a star that has exhausted it hydrogen and is burning helium fuel. It will eat all of the inner planets, even the Earth. Then the sun would burn into carbon, but it is not big enough so it will probably end up being a white dwarf. ...
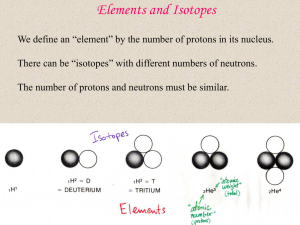
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... its luminosity with fusion. Brown dwarfs fuse at least deuterium, but then find their pressure support without heat, and fade slowly away. ...
... its luminosity with fusion. Brown dwarfs fuse at least deuterium, but then find their pressure support without heat, and fade slowly away. ...
Planetary Configurations
... fusion switches on. Leads to an explosion and ejection of mass. Repeats. • SUPERNOVAE: (Type Ia) Transfer is rapid so fusion is ongoing. Mass accumulates until Chandra limit is exceeded which leads to a catastrophic explosion. SNe can become brighter than a galaxy for a time. ...
... fusion switches on. Leads to an explosion and ejection of mass. Repeats. • SUPERNOVAE: (Type Ia) Transfer is rapid so fusion is ongoing. Mass accumulates until Chandra limit is exceeded which leads to a catastrophic explosion. SNe can become brighter than a galaxy for a time. ...
Star Formation - University of Redlands
... • Dust grains = wavelength of blue light • Dust clouds: – Opaque to blue light, UV, X-rays – Transparent to red light, IR, radio ...
... • Dust grains = wavelength of blue light • Dust clouds: – Opaque to blue light, UV, X-rays – Transparent to red light, IR, radio ...
Replenishing the ISM - Stockton University
... – Unreasonable! It would mean that nature had put the Sun at a special place where the size of the clusters was the smallest. – More reasonable: the Sun is in a typical spot. It's simply that more distant clusters have more stuff between us and the clusters so that they appear fainter (farther away) ...
... – Unreasonable! It would mean that nature had put the Sun at a special place where the size of the clusters was the smallest. – More reasonable: the Sun is in a typical spot. It's simply that more distant clusters have more stuff between us and the clusters so that they appear fainter (farther away) ...
Masers and high mass star formation Claire Chandler
... • Ionization phenomena associated with massive SF: UCHII regions • Different environments observed has led to the suggestion that different mechanisms (or modes) apply to low- and high-mass SF ...
... • Ionization phenomena associated with massive SF: UCHII regions • Different environments observed has led to the suggestion that different mechanisms (or modes) apply to low- and high-mass SF ...
Stellar Birth - Chabot College
... 1. Shock creates fragments & “blobs” 2. Gravity creates clusters of star “seeds” 3. Individual blobs heat up and glow as protostars 4. Protostars start fusion in cores 5. ♫ A star is born! ♫ ...
... 1. Shock creates fragments & “blobs” 2. Gravity creates clusters of star “seeds” 3. Individual blobs heat up and glow as protostars 4. Protostars start fusion in cores 5. ♫ A star is born! ♫ ...
Chapter 12
... – This theory says the Universe goes through a series of bangs and crunches in an ongoing cycle – Currently still expanding from the most recent ...
... – This theory says the Universe goes through a series of bangs and crunches in an ongoing cycle – Currently still expanding from the most recent ...
Chapter 30
... seen in the sky during different seasons of the year? A. Stellar motion around Polaris B. Earth’s rotation on its axis C. Earth’s revolution around the sun D. Position north or south of the equator ...
... seen in the sky during different seasons of the year? A. Stellar motion around Polaris B. Earth’s rotation on its axis C. Earth’s revolution around the sun D. Position north or south of the equator ...
Stars are classified according to their color
... between the stars. • Distance that light travels in one year. Its about 9.5 million million kilometers. That is not a typo! ...
... between the stars. • Distance that light travels in one year. Its about 9.5 million million kilometers. That is not a typo! ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... (given an appropriate graph) and combine this with its apparent magnitude and the distance-magnitude equation to determine how far it is from Earth. 7. Briefly describe the conditions necessary for mass transfer to occur in a binary star system. 1. Prototstars become pre-main-sequence stars when the ...
... (given an appropriate graph) and combine this with its apparent magnitude and the distance-magnitude equation to determine how far it is from Earth. 7. Briefly describe the conditions necessary for mass transfer to occur in a binary star system. 1. Prototstars become pre-main-sequence stars when the ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High School
... • As particles fall to the core they lose kinetic & potential energy and more HEAT results • This heat triggers nuclear fusion in the outer layers, and the resulting explosion is the supernova. • The energy released can fuse iron and other heavier elements, up to uranium. ...
... • As particles fall to the core they lose kinetic & potential energy and more HEAT results • This heat triggers nuclear fusion in the outer layers, and the resulting explosion is the supernova. • The energy released can fuse iron and other heavier elements, up to uranium. ...
1.1 Stars in the Broader Context of Modern Astro
... burst is thought to mark the end of a massive and rapidly rotating star, when its core collapses directly into a black hole and two extremely energetic jets of plasma are emitted from its rotational poles at nearly the speed of light (see Figure 1.2). The massive star that produced GRB 090429B at z ...
... burst is thought to mark the end of a massive and rapidly rotating star, when its core collapses directly into a black hole and two extremely energetic jets of plasma are emitted from its rotational poles at nearly the speed of light (see Figure 1.2). The massive star that produced GRB 090429B at z ...
9. Lectures on Star Formation.
... -Disks appear dark, because are viewed against the bright background of Orion Nebula. Reddish glowing object in the middle is a proto-star: Star hasn’t yet reached the main sequence, no nuclear reactions at center, still contracting. These stars are only about 150,000 years old. ...
... -Disks appear dark, because are viewed against the bright background of Orion Nebula. Reddish glowing object in the middle is a proto-star: Star hasn’t yet reached the main sequence, no nuclear reactions at center, still contracting. These stars are only about 150,000 years old. ...
Groups of Stars
... nebula • This means they formed at about the same time and they are all about the same distance from Earth ...
... nebula • This means they formed at about the same time and they are all about the same distance from Earth ...
Our Galaxy and the Universe
... • The Doppler Effect - used to determine whether an object in space are moving away from or toward Earth. • When applied to light (EMS), the Doppler Effect shows: Red Shift when the source is moving away from an observer. (wavelengths are stretched) Blue Shift when the source is moving towards an ob ...
... • The Doppler Effect - used to determine whether an object in space are moving away from or toward Earth. • When applied to light (EMS), the Doppler Effect shows: Red Shift when the source is moving away from an observer. (wavelengths are stretched) Blue Shift when the source is moving towards an ob ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.