The Life Cycle of a Star
... Lowmass stars (red dwarfs) consume hydrogen at a very slow rate (~ 100 billion years). During this time, they lose significant mass, and eventually evaporate. The result is a very faint white dwarf. ...
... Lowmass stars (red dwarfs) consume hydrogen at a very slow rate (~ 100 billion years). During this time, they lose significant mass, and eventually evaporate. The result is a very faint white dwarf. ...
Pathways to Habitability: from disks to active stars, planets and life
... In the past, the Sun was too faint ...
... In the past, the Sun was too faint ...
PH109 Exploring the Universe, Test 3, Fall 2001 Please indicate the
... a) Fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium atoms., b) Collapse of an interstellar cloud. c) Formation of a photosphere., d) Instability in an interstellar cloud. 9. The final core element for a massive star is a) carbon, b) oxygen, c) silicon, d) iron 10. What is a planetary nebula? a) A planet surroun ...
... a) Fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium atoms., b) Collapse of an interstellar cloud. c) Formation of a photosphere., d) Instability in an interstellar cloud. 9. The final core element for a massive star is a) carbon, b) oxygen, c) silicon, d) iron 10. What is a planetary nebula? a) A planet surroun ...
The Planet with Three Suns
... The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not entirel ...
... The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not entirel ...
Clase-06_Star_Formation - Departamento de Astronomía
... gas in Giant Molecular Clouds (molecular and atomic gas, with some dust, and 106-107 M) may be eventually compressed by shock fronts fragmentation and gravitational collapse take place, against some combination of resisting turbulent and magnetic energies (as the ionization level of material, g ...
... gas in Giant Molecular Clouds (molecular and atomic gas, with some dust, and 106-107 M) may be eventually compressed by shock fronts fragmentation and gravitational collapse take place, against some combination of resisting turbulent and magnetic energies (as the ionization level of material, g ...
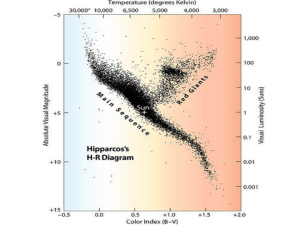
Stars from Afar
... An HR diagram shows the two most important characteristics of stars, which are temperature and absolute magnitude (brightness) and/or luminosity. ...
... An HR diagram shows the two most important characteristics of stars, which are temperature and absolute magnitude (brightness) and/or luminosity. ...
Week 9 Concept Summary - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... intrinsic luminosity and the mass: L ∝ M 4 , and the main sequence lifetime goes as t ∝ M −3 . Knowing the color of a main sequence star tells you the temperature, and uminosity, which in turn tells you the radius of the star and how far away it is. 3. Stellar Birth: Stars form out of giant gas clou ...
... intrinsic luminosity and the mass: L ∝ M 4 , and the main sequence lifetime goes as t ∝ M −3 . Knowing the color of a main sequence star tells you the temperature, and uminosity, which in turn tells you the radius of the star and how far away it is. 3. Stellar Birth: Stars form out of giant gas clou ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... • As particles fall to the core they lose kinetic & potential energy and more HEAT results • This heat triggers nuclear fusion in the outer layers, and the resulting explosion is the supernova. • The energy released can fuse iron and other heavier elements, up to uranium. ...
... • As particles fall to the core they lose kinetic & potential energy and more HEAT results • This heat triggers nuclear fusion in the outer layers, and the resulting explosion is the supernova. • The energy released can fuse iron and other heavier elements, up to uranium. ...
Stars and Deep Time
... (brightness) of stars against their color (temperature), and revealed patterns • Most stars fell into a band from the upper left to lower right—the Main Sequence • Some grouped in the upper right—Red ...
... (brightness) of stars against their color (temperature), and revealed patterns • Most stars fell into a band from the upper left to lower right—the Main Sequence • Some grouped in the upper right—Red ...
JSchreiberTalk3 - FSU High Energy Physics
... enhancements either grew or dispersed. Smaller, more dense density enhancements first to collapse. These first “lumps” that broke free contained some H and He, but mostly dark matter. ...
... enhancements either grew or dispersed. Smaller, more dense density enhancements first to collapse. These first “lumps” that broke free contained some H and He, but mostly dark matter. ...
The_Birth_of_a_Star
... • If the star is very large, it burns through the hydrogen quickly; helium fuses to make carbon, and as the helium is exhausted the collapse of the core generates enough energy to fuse the carbon forming iron. • Eventually the star collapses, as the electrons are trapped inside the core, forming ne ...
... • If the star is very large, it burns through the hydrogen quickly; helium fuses to make carbon, and as the helium is exhausted the collapse of the core generates enough energy to fuse the carbon forming iron. • Eventually the star collapses, as the electrons are trapped inside the core, forming ne ...
Stages in the Life of a Star
... Giant Molecular Cloud • Giant Molecular Cloud--large dense gas cloud (with dust) that is cold! • 100,000's to few million solar masses of material • Has fragments of 10's to 100's solar masses that start collapsing • Reason(s) - shock waves, cool enough for gravity to take over, etc.. ...
... Giant Molecular Cloud • Giant Molecular Cloud--large dense gas cloud (with dust) that is cold! • 100,000's to few million solar masses of material • Has fragments of 10's to 100's solar masses that start collapsing • Reason(s) - shock waves, cool enough for gravity to take over, etc.. ...
Chapter #10 Question #27: (c) Four individual protons. During
... The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have released iron into the surrounding space which was used up by our solar system during its formatio ...
... The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have released iron into the surrounding space which was used up by our solar system during its formatio ...
“Contact” Movie Notes
... Just before Ellie is dropped out of the machine, she sees a group of shiny lights shooting across the sky. What do you think this could be? _________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Just before Ellie is dropped out of the machine, she sees a group of shiny lights shooting across the sky. What do you think this could be? _________________________________________________________________________ ...
Stars - HMXEarthScience
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
a star is born reading
... quickly than red ones. They are also brighter. They are like the spotlights in the dark auditorium. Yellow stars have a shorter life span than red ones, only ten billion years or so. Our Sun is about five billion years old. Toward the end of its life, it will become much larger. It will swallow up t ...
... quickly than red ones. They are also brighter. They are like the spotlights in the dark auditorium. Yellow stars have a shorter life span than red ones, only ten billion years or so. Our Sun is about five billion years old. Toward the end of its life, it will become much larger. It will swallow up t ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.