Habitibility of Earth, in our Solar System, and Beyond
... Most stars are double, triple or more. Some have planets! (HD88753) Planet orbits are stable only near a star or far from them all. A multiple star system is as bad for life as its worst star. And … multiple stars have more restricted habitable zones, and more variable planetary environments. Imagin ...
... Most stars are double, triple or more. Some have planets! (HD88753) Planet orbits are stable only near a star or far from them all. A multiple star system is as bad for life as its worst star. And … multiple stars have more restricted habitable zones, and more variable planetary environments. Imagin ...
Pluto(2274km)- Pluto is a dwarf planet, and was classified as such in
... Saturn is a gas giant. It has amazing rings that are made of mostly ice chunks and some rocks. The rings range in size from that of a fingernail to that of a car. The mean temperature on the surface of the clouds is -290°F and it is composed of mostly hydrogen and helium gas. Jupiter(1.4x10^5km)Jup ...
... Saturn is a gas giant. It has amazing rings that are made of mostly ice chunks and some rocks. The rings range in size from that of a fingernail to that of a car. The mean temperature on the surface of the clouds is -290°F and it is composed of mostly hydrogen and helium gas. Jupiter(1.4x10^5km)Jup ...
Apparent versus Event Horizon
... up by a star and the core collapses. How far it collapses, into what kind of object, and at what rate, is determined by the star's final mass and the remaining outward pressure that the burnt-up nuclear residue (largely iron) can muster. If the star is sufficiently massive or compressible, it may co ...
... up by a star and the core collapses. How far it collapses, into what kind of object, and at what rate, is determined by the star's final mass and the remaining outward pressure that the burnt-up nuclear residue (largely iron) can muster. If the star is sufficiently massive or compressible, it may co ...
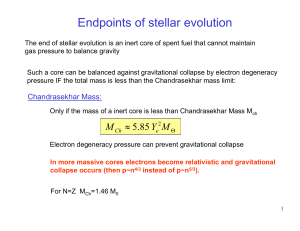
Endpoints of stellar evolution
... Electron degeneracy pressure can prevent gravitational collapse In more massive cores electrons become relativistic and gravitational collapse occurs (then p~n4/3 instead of p~n5/3). For N=Z MCh=1.46 M0 ...
... Electron degeneracy pressure can prevent gravitational collapse In more massive cores electrons become relativistic and gravitational collapse occurs (then p~n4/3 instead of p~n5/3). For N=Z MCh=1.46 M0 ...
Properties of Stars
... same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, mediummass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, mediummass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
Chapter 20 Stellar Evolution (20.1-20.3)
... This graphic shows the entire evolution of a Sun-like star. Use it as a review device. Try to describe each of the phases shown. Low mass stars like the sun never become hot enough for fusion past carbon to take place. ...
... This graphic shows the entire evolution of a Sun-like star. Use it as a review device. Try to describe each of the phases shown. Low mass stars like the sun never become hot enough for fusion past carbon to take place. ...
10. The Lives of the Stars
... • After core helium fusion stops, He fuses into carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer. ...
... • After core helium fusion stops, He fuses into carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer. ...
Unit 9 Day 9 Notes
... scientific concepts related to the , of the universe. Key concepts include a. ...
... scientific concepts related to the , of the universe. Key concepts include a. ...
TEK 8 Test Review 1. List the three subatomic particles and give
... 1. List the three subatomic particles and give each of their masses. 2. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the most common element in the Universe. 3. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the second most common element in the ...
... 1. List the three subatomic particles and give each of their masses. 2. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the most common element in the Universe. 3. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the second most common element in the ...
The galaxies that host powerful radio sources
... • Optically faint (R>25). • Faint at radio and IR wavelengths. These facts suggest they are distant and dusty. ...
... • Optically faint (R>25). • Faint at radio and IR wavelengths. These facts suggest they are distant and dusty. ...
–1– Solutions to PH6820 Midterm 1. Define the following: molecular
... 1. Define the following: molecular cloud, molecular core, protostar. Include typical properties when necessary. A molecular cloud is a distinct, self-gravitating cloud comprised primarily of H2 and He. The sizes range from 10 M⊙ (for a dark globule) to 106 M⊙ for the most massive giant molecular clo ...
... 1. Define the following: molecular cloud, molecular core, protostar. Include typical properties when necessary. A molecular cloud is a distinct, self-gravitating cloud comprised primarily of H2 and He. The sizes range from 10 M⊙ (for a dark globule) to 106 M⊙ for the most massive giant molecular clo ...
Our Universe
... •Our Sun has around 5 Billion years remaining. It is predicted to only exist for 10 Billion total years. ...
... •Our Sun has around 5 Billion years remaining. It is predicted to only exist for 10 Billion total years. ...
Coords
... The French philosopher and mathematician Rene Descartes invented a system for locating objects in three-dimensional space. Called the Cartesian Coordinate System, it requires a starting point and three axes (called X, Y, and Z) for horizontal, vertical, and radial distance respectively. Any object c ...
... The French philosopher and mathematician Rene Descartes invented a system for locating objects in three-dimensional space. Called the Cartesian Coordinate System, it requires a starting point and three axes (called X, Y, and Z) for horizontal, vertical, and radial distance respectively. Any object c ...
Stars off the Main Sequence - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... T-Tauri Stars Star's formation and evolution right before it becomes a main sequence star Occurs at the end of the protostar phase Gravitational pressure holding the star together is the source of all its energy ...
... T-Tauri Stars Star's formation and evolution right before it becomes a main sequence star Occurs at the end of the protostar phase Gravitational pressure holding the star together is the source of all its energy ...
Formation of Globular Clusters: In and Out of Dwarf
... Globular clusters can form in giant molecular clouds within the disks of high-redshift galaxies, resolved by hydrodynamical simulations: same microphysics as for young clusters in interacting galaxies model explains observed ages, sizes, masses metallicities correspond to blue/metal-poor clust ...
... Globular clusters can form in giant molecular clouds within the disks of high-redshift galaxies, resolved by hydrodynamical simulations: same microphysics as for young clusters in interacting galaxies model explains observed ages, sizes, masses metallicities correspond to blue/metal-poor clust ...
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
Lecture20 - University of Waterloo
... • By comparing the distance of the supernova to their redshift (recession velocity) we can measure not only the velocity of this expansion, but how it has changed over time (i.e. acceleration of deceleration). ...
... • By comparing the distance of the supernova to their redshift (recession velocity) we can measure not only the velocity of this expansion, but how it has changed over time (i.e. acceleration of deceleration). ...
The Sky Above
... solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. One hundred and nine Earths would be required to fit across the Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and has a tem ...
... solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. One hundred and nine Earths would be required to fit across the Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and has a tem ...
File
... 21. Which letter correctly identifies where our sun would be found? D 22. Which letter correctly identifies where a Red Super giant would be found? B 23. What would be the temperature range over which you would find a white dwarf? 15,000K-40,000 K ...
... 21. Which letter correctly identifies where our sun would be found? D 22. Which letter correctly identifies where a Red Super giant would be found? B 23. What would be the temperature range over which you would find a white dwarf? 15,000K-40,000 K ...
Slides
... There was most likely a disturbance caused by a supernova (an exploding star), and the resulting waves compressed the cloud causing gravity to pull the gas and dust together, thus forming a solar nebula. This caused the entire cloud to start spinning: the center having the highest angular veloci ...
... There was most likely a disturbance caused by a supernova (an exploding star), and the resulting waves compressed the cloud causing gravity to pull the gas and dust together, thus forming a solar nebula. This caused the entire cloud to start spinning: the center having the highest angular veloci ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.