mslien~1
... Out of deep images & with the detection 20 of stars on 5 level Succeeded to detected very faint (low mass) stars ...
... Out of deep images & with the detection 20 of stars on 5 level Succeeded to detected very faint (low mass) stars ...
Supernovae Gamma-Ray Bursts and and some of their uses
... layers of the star • The star may collapse directly into a black hole: these are called hypernovae or collapsars • Hypernova may or may not produce a supernova explosion, it can emit jets of gamma rays • Mergers of neutron stars should occur occassionally but not enough to produce the number of GRBs ...
... layers of the star • The star may collapse directly into a black hole: these are called hypernovae or collapsars • Hypernova may or may not produce a supernova explosion, it can emit jets of gamma rays • Mergers of neutron stars should occur occassionally but not enough to produce the number of GRBs ...
Space Test Explanations
... bodies. They think the star exploded in a supernova. The supernova blasted material out into the universe. Some of this material pulled back together to form our solar system. Some of those bits of the solar system ended up in our bodies. 29. Describe two pieces of evidence for Big Bang theory? 1) a ...
... bodies. They think the star exploded in a supernova. The supernova blasted material out into the universe. Some of this material pulled back together to form our solar system. Some of those bits of the solar system ended up in our bodies. 29. Describe two pieces of evidence for Big Bang theory? 1) a ...
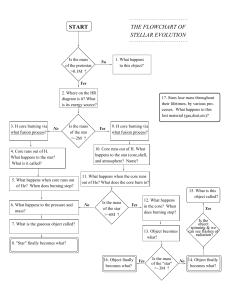
stellar evolution the flowchart of start
... 2. Where on the HR diagram is it? What is its energy source? ...
... 2. Where on the HR diagram is it? What is its energy source? ...
Presentation for perspective graduate students 2006
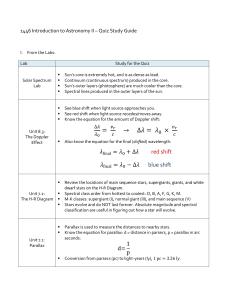
... not too hot and not too cold, many hydrogen atoms have their electron in the n = 2 orbit: hence strong absorption ...
... not too hot and not too cold, many hydrogen atoms have their electron in the n = 2 orbit: hence strong absorption ...
Astronomy 1 – Winter 2011
... not too hot and not too cold, many hydrogen atoms have their electron in the n = 2 orbit: hence strong absorption ...
... not too hot and not too cold, many hydrogen atoms have their electron in the n = 2 orbit: hence strong absorption ...
Star and Galaxies Chapter 13
... amount of energy is released) • Fusion occurs in cores of all stars. In the core of stars the temperatures are high enough to fuse atoms ...
... amount of energy is released) • Fusion occurs in cores of all stars. In the core of stars the temperatures are high enough to fuse atoms ...
Star and Galaxies Chapter 13 2013
... amount of energy is released) • Fusion occurs in cores of all stars. In the core of stars the temperatures are high enough to fuse atoms ...
... amount of energy is released) • Fusion occurs in cores of all stars. In the core of stars the temperatures are high enough to fuse atoms ...
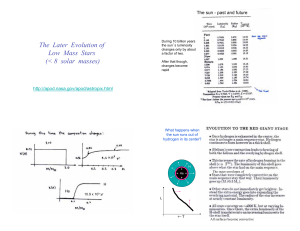
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
DYNAMICAL STABILITY OF SPHERICAL STARS
... If σ 2 < 0 then the motion is oscillatory, i.e. the star is dynamically stable. If σ 2 > 0 than there is a solution that increases exponentially, i.e. the star is dynamically unstable. Therefore, the star is dynamically unstable if γ < 4/3. We obtained this result in a crude way. The proper analysis ...
... If σ 2 < 0 then the motion is oscillatory, i.e. the star is dynamically stable. If σ 2 > 0 than there is a solution that increases exponentially, i.e. the star is dynamically unstable. Therefore, the star is dynamically unstable if γ < 4/3. We obtained this result in a crude way. The proper analysis ...
Astronomy Test Objective 1: Origins of the Universe Multiple Choice
... Astronomers are concluding that monstrous black holes were not born that big, as once believed, but instead grew on a diet of gas and stars controlled by their host galaxies in the beginning years of the universe. An initial look at 30 galaxies indicates that black holes do not precede a galaxy’s bi ...
... Astronomers are concluding that monstrous black holes were not born that big, as once believed, but instead grew on a diet of gas and stars controlled by their host galaxies in the beginning years of the universe. An initial look at 30 galaxies indicates that black holes do not precede a galaxy’s bi ...
Introducing the Stars
... field of view is about 20 degrees across. This is a double star that sharp eyes can pick out in the real sky at night – try it! Search for the ‘Milky Way Centre’ (which is best seen from the southern hemisphere) and zoom in until the field is about 1 degree across. Note how dense and rich this field ...
... field of view is about 20 degrees across. This is a double star that sharp eyes can pick out in the real sky at night – try it! Search for the ‘Milky Way Centre’ (which is best seen from the southern hemisphere) and zoom in until the field is about 1 degree across. Note how dense and rich this field ...
Slide 1
... If you try to squeeze a lot of electrons in a small volume, they are forced into a smaller range of space-type quantum coordinates. This makes them be in higher and higher quantum energy levels, so they will tend to move at higher and higher “velocities.” This has nothing to do with temperature: eve ...
... If you try to squeeze a lot of electrons in a small volume, they are forced into a smaller range of space-type quantum coordinates. This makes them be in higher and higher quantum energy levels, so they will tend to move at higher and higher “velocities.” This has nothing to do with temperature: eve ...
Stars Part Two
... How do we know all this? By observing Globular clusters… 1. Globular clusters are thousands of stars that all formed at more or less the same time. 2. Globular clusters are much smaller than galaxies. 3. Galaxies create stars in an on-going process. 4. The stars in a globular cluster accrete sudde ...
... How do we know all this? By observing Globular clusters… 1. Globular clusters are thousands of stars that all formed at more or less the same time. 2. Globular clusters are much smaller than galaxies. 3. Galaxies create stars in an on-going process. 4. The stars in a globular cluster accrete sudde ...
Galaxies
... concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
... concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
Spectral-Type Trends: Absorption
... The winds of massive stars deposit chemically enriched matter as well as momentum and energy into their galactic environment (wind-blown bubble XXX at left). The X-rays are produced very close to the stars, however, necessitating the use of spectroscopy of the unresolved central stars in order to u ...
... The winds of massive stars deposit chemically enriched matter as well as momentum and energy into their galactic environment (wind-blown bubble XXX at left). The X-rays are produced very close to the stars, however, necessitating the use of spectroscopy of the unresolved central stars in order to u ...
X Ray Astronomy
... for example, or the emission from an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN), this is useful to show the orbital period of the source (or part of it). ...
... for example, or the emission from an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN), this is useful to show the orbital period of the source (or part of it). ...
pals_20160211_howpla.. - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 4.6Gyr ago gas+dust cloud collapsed by own gravity Triggering mechanism could be: - shock wave from a Supernova explosion - little gravity fluctuation in cloud of gas ...
... 4.6Gyr ago gas+dust cloud collapsed by own gravity Triggering mechanism could be: - shock wave from a Supernova explosion - little gravity fluctuation in cloud of gas ...
2 - Lnk2Lrn
... Stars Stars are formed by interstellar dust coming together through mutual gravitational attraction. The loss of potential energy is responsible for the initial high temperature necessary for fusion. The fusion process releases so much energy that the pressure created prevents the star from c ...
... Stars Stars are formed by interstellar dust coming together through mutual gravitational attraction. The loss of potential energy is responsible for the initial high temperature necessary for fusion. The fusion process releases so much energy that the pressure created prevents the star from c ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.