Which property of a star would not change if we could observe it
... • It works the same with stars! • If we know the total energy output of a star (luminosity), and we can count the number of photons we receive from that star (brightness), we can calculate its distance ...
... • It works the same with stars! • If we know the total energy output of a star (luminosity), and we can count the number of photons we receive from that star (brightness), we can calculate its distance ...
Lecture 6: Properties of Stars The Constellations The Constellations
... o Greek astronomer Hipparchos made first known catalogue of stars in ~130-160 BC, which was added to by Ptolomy in ~150 AD. o Hipparcus grouped stars into six magnitude groups, with 1st magnitude being brightest and 6th the faintest. o In 19th century, it was shown that stars of a given magnitude ...
... o Greek astronomer Hipparchos made first known catalogue of stars in ~130-160 BC, which was added to by Ptolomy in ~150 AD. o Hipparcus grouped stars into six magnitude groups, with 1st magnitude being brightest and 6th the faintest. o In 19th century, it was shown that stars of a given magnitude ...
The HR Diagram Interpreted (PowerPoint version)
... temperatures. [This montage starts with the moon and planets, the visible colours of which are determined by reflected sunlight: they are so cool that they ‘glow’ in the infrared. The beautiful blue planet Earth is not at a temperature of 20,000 K!] ...
... temperatures. [This montage starts with the moon and planets, the visible colours of which are determined by reflected sunlight: they are so cool that they ‘glow’ in the infrared. The beautiful blue planet Earth is not at a temperature of 20,000 K!] ...
The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars
... temperatures. [This montage starts with the moon and planets, the visible colours of which are determined by reflected sunlight: they are so cool that they ‘glow’ in the infrared. The beautiful blue planet Earth is not at a temperature of 20,000 K!] ...
... temperatures. [This montage starts with the moon and planets, the visible colours of which are determined by reflected sunlight: they are so cool that they ‘glow’ in the infrared. The beautiful blue planet Earth is not at a temperature of 20,000 K!] ...
The Formation of Massive Star Systems by Accretion
... radiation pressure produced no noticeable effects. After ~20,000 years, the disk became gravitationally unstable and developed a pronounced twoarmed spiral that transported angular momentum efficiently (Fig. 1B) (24). Accretion onto the protostar continued smoothly. Accretion, unimpeded by radiation ...
... radiation pressure produced no noticeable effects. After ~20,000 years, the disk became gravitationally unstable and developed a pronounced twoarmed spiral that transported angular momentum efficiently (Fig. 1B) (24). Accretion onto the protostar continued smoothly. Accretion, unimpeded by radiation ...
Patterns in the Sky - Plano Independent School District
... There are many stars being formed in this cloud. ...
... There are many stars being formed in this cloud. ...
Chapter 12. Basic Equations of Stellar Structure
... and then how they evolve. Prior to 1905, it was not understood how a star could power itself. That is, the luminosity of the Sun is so large that it could not last for more than about 20 million years on the basis of the gravitational potential energy that it gained by contracting to its present siz ...
... and then how they evolve. Prior to 1905, it was not understood how a star could power itself. That is, the luminosity of the Sun is so large that it could not last for more than about 20 million years on the basis of the gravitational potential energy that it gained by contracting to its present siz ...
An introduction to the HR diagram File
... Red giants are “using helium and later heavier atoms as fuels. Stars here are reaching the end of their lives White dwarf stars White dwarf stars are “remnants” They are essentially the central cores of what were main sequence stars like the Sun ...
... Red giants are “using helium and later heavier atoms as fuels. Stars here are reaching the end of their lives White dwarf stars White dwarf stars are “remnants” They are essentially the central cores of what were main sequence stars like the Sun ...
The Dramatic Lives of Stars
... Given the position of young stars in the HR diagram, which of the following is true? A 0.5 solar mass star mostly: ...
... Given the position of young stars in the HR diagram, which of the following is true? A 0.5 solar mass star mostly: ...
matthewchristianstarprodject
... becomes sufficiently cool to no longer emit significant heat or light. Since the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than the current age of the universe of 13.7 billion years, no black dwarfs are expected to exist in the universe yet, and the temperature ...
... becomes sufficiently cool to no longer emit significant heat or light. Since the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than the current age of the universe of 13.7 billion years, no black dwarfs are expected to exist in the universe yet, and the temperature ...
FRIENDS OF THE PLANETARIUM NEWSLETTER April2002
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
Star Types - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... Planetary Nebula At the center of the nebula there is the dying star. Destiny of stars with roughly M ...
... Planetary Nebula At the center of the nebula there is the dying star. Destiny of stars with roughly M ...
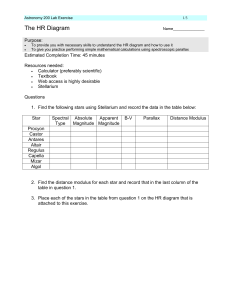
labex7
... magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitude-brightness rule to convert this into a brightness factor or luminosity. See Chp 2.1 in the online notes to do this. You will find that Polaris is 2513 times more luminous than the Sun.) Record this information in the following table: Star ...
... magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitude-brightness rule to convert this into a brightness factor or luminosity. See Chp 2.1 in the online notes to do this. You will find that Polaris is 2513 times more luminous than the Sun.) Record this information in the following table: Star ...
neutron star - The University of Chicago
... ➢ Multi-dimensional supercomputer simulations key to understanding core-collapse SNe. ➢ Neutrinos are emitted en-masse during core-collapse and play an important role in reviving the SN shock BUT even small changes in the neutrino heating can halt the explosion. ➢ Proper 3D initial conditions play a ...
... ➢ Multi-dimensional supercomputer simulations key to understanding core-collapse SNe. ➢ Neutrinos are emitted en-masse during core-collapse and play an important role in reviving the SN shock BUT even small changes in the neutrino heating can halt the explosion. ➢ Proper 3D initial conditions play a ...
SALT Science – UW Madison
... These line profiles were observed for the recurrent nova T Pyx a year and a half after the outburst. Nebular [O III] lines at 5007 Å were still very strong and confirmed a bipolar mass ejection. There seem to be two distincts region of emission, both asymmetric. The He II emission line at 4686 Å, mu ...
... These line profiles were observed for the recurrent nova T Pyx a year and a half after the outburst. Nebular [O III] lines at 5007 Å were still very strong and confirmed a bipolar mass ejection. There seem to be two distincts region of emission, both asymmetric. The He II emission line at 4686 Å, mu ...
South Pasadena • Chemistry Name 8 • Nuclear Chemistry Period
... 5. The hydrogen nucleus is the most stable nucleus in nature. 6. Elements heavier than iron can only be formed in the first few seconds after a supernova’s collapse. 7. The type of elements produced by a star depends on the temperature and pressure of its core. 8. There are no radioactive isotopes o ...
... 5. The hydrogen nucleus is the most stable nucleus in nature. 6. Elements heavier than iron can only be formed in the first few seconds after a supernova’s collapse. 7. The type of elements produced by a star depends on the temperature and pressure of its core. 8. There are no radioactive isotopes o ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.