AstronomyQuotes
... We are a spiral galaxy with many spiral arms that revolve around a bulge on a relatively flat disk, surrounded by a dimmer halo. The Halo contains about 200 globular clusters of stars. Our galaxy is abour 100,000 light years in diameter. We can use stellar orbits to measure galactic mass through Kep ...
... We are a spiral galaxy with many spiral arms that revolve around a bulge on a relatively flat disk, surrounded by a dimmer halo. The Halo contains about 200 globular clusters of stars. Our galaxy is abour 100,000 light years in diameter. We can use stellar orbits to measure galactic mass through Kep ...
Astronomy 100 Tuesday, Thursday 2:30
... of energy since the rest of the star collapses and then bounces off the neutron core • 1044-46 Joules • Annual energy generation of Sun is 1034 Joules ...
... of energy since the rest of the star collapses and then bounces off the neutron core • 1044-46 Joules • Annual energy generation of Sun is 1034 Joules ...
STEM for TY Teachers
... ! X-ray Binary Star: X-ray binary stars are a special type of binary star in which one of the stars is a compact, evolved object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. As matter is stripped from the normal star, it falls at very high speed onto the collapsed star, ...
... ! X-ray Binary Star: X-ray binary stars are a special type of binary star in which one of the stars is a compact, evolved object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. As matter is stripped from the normal star, it falls at very high speed onto the collapsed star, ...
CHAPTER 14
... 3. A typical white dwarf will have 0.8 solar masses, a diameter of 10,000 km (3/4 of Earth’s), and a density of 106 g/cm3. A teaspoon of white dwarf material would weigh two tons. 4. To get to the white dwarf stage, a low-mass star will have gone through these stages: protostar, main sequence star, ...
... 3. A typical white dwarf will have 0.8 solar masses, a diameter of 10,000 km (3/4 of Earth’s), and a density of 106 g/cm3. A teaspoon of white dwarf material would weigh two tons. 4. To get to the white dwarf stage, a low-mass star will have gone through these stages: protostar, main sequence star, ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 5 Due: 04 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1 1
... One’s first guess might be that the L ∝ M since a larger star will have proportionately more mass available for fusion reactions. However, the larger stellar mass exerts a larger pressure on the star’s core and increases its temperature. Since the luminosity depends on the the energy-generation rate ...
... One’s first guess might be that the L ∝ M since a larger star will have proportionately more mass available for fusion reactions. However, the larger stellar mass exerts a larger pressure on the star’s core and increases its temperature. Since the luminosity depends on the the energy-generation rate ...
Binary Star - Armagh Observatory
... X-ray Binary Star: X-ray binary stars are a special type of binary star in which one of the stars is a compact, evolved object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. As matter is stripped from the normal star, it falls at very high speed onto the collapsed star, producing X-rays. ...
... X-ray Binary Star: X-ray binary stars are a special type of binary star in which one of the stars is a compact, evolved object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. As matter is stripped from the normal star, it falls at very high speed onto the collapsed star, producing X-rays. ...
Stellar Lifetime - Madison Public Schools
... Stage 6: Newborn Star • 10 million years have passed • The Protostar has shrunk down to almost 1 solar radius • Its central temperature reaches 10,000,000 K • Fusion of Hydrogen begins • It is still not on the main sequence ...
... Stage 6: Newborn Star • 10 million years have passed • The Protostar has shrunk down to almost 1 solar radius • Its central temperature reaches 10,000,000 K • Fusion of Hydrogen begins • It is still not on the main sequence ...
March 2017 - Shasta Astronomy Club
... Galaxies are immense structures. Composed of gas, dust, dark matter, and billions of stars, big ones can be a hundred thousand light-years across — a million trillion kilometers — and have masses equaling trillions of Suns. Our own Milky Way fits those numbers pretty well. It formed not long after t ...
... Galaxies are immense structures. Composed of gas, dust, dark matter, and billions of stars, big ones can be a hundred thousand light-years across — a million trillion kilometers — and have masses equaling trillions of Suns. Our own Milky Way fits those numbers pretty well. It formed not long after t ...
Hubblecast72: ESO 137
... 6. Streams of murky dust are also being pulled away from ESO 137-001, visible as the dark brown tangled region around the galaxy’s centre. This image also shows other telltale signs of this process, such as the curved appearance of the galaxy’s disc — a result of the forces exerted by the heated gas ...
... 6. Streams of murky dust are also being pulled away from ESO 137-001, visible as the dark brown tangled region around the galaxy’s centre. This image also shows other telltale signs of this process, such as the curved appearance of the galaxy’s disc — a result of the forces exerted by the heated gas ...
Parallax, Event Horizon, HR diagrams equation
... by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
... by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
nuclear fusion atoms
... 2. Where do most of the stars you see exist in outer space? 3. What is a light-year? 4. What is in space besides planets and stars? 5. Describe the interstellar medium. 6. What happens inside of the interstellar medium? 7. Are there more galaxies than the Milky Way galaxy? If so, why do scientists n ...
... 2. Where do most of the stars you see exist in outer space? 3. What is a light-year? 4. What is in space besides planets and stars? 5. Describe the interstellar medium. 6. What happens inside of the interstellar medium? 7. Are there more galaxies than the Milky Way galaxy? If so, why do scientists n ...
Ch_16-18_Example_Exam
... a. a planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas b. the disk of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a star system c. the ejected envelope of a giant star surrounding the remnant of a star d. a type of young, medium-mass star e. leftover gas from a supernova explosion ...
... a. a planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas b. the disk of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a star system c. the ejected envelope of a giant star surrounding the remnant of a star d. a type of young, medium-mass star e. leftover gas from a supernova explosion ...
temperature - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... trails off at long wavelengths this is called the “Rayleigh-Jeans tail” (i.e. cooler temperatures, lower energies than the peak) ...
... trails off at long wavelengths this is called the “Rayleigh-Jeans tail” (i.e. cooler temperatures, lower energies than the peak) ...
Molecular Gas in Nearby Dwarf Galaxies:
... “…Extreme properties are often sought for in Astronomy as one way to sharpen our understanding of fundamental concepts…” ...
... “…Extreme properties are often sought for in Astronomy as one way to sharpen our understanding of fundamental concepts…” ...
Observational Overview
... This is an exciting “new” waveband. The youngest galaxies, producing their first generation of stars, will be brightest in the far-IR (light is red-shifted into this region). The successor to the Hubble Space Telescope will focus on the IR part of the spectrum and study the time “when galaxies were ...
... This is an exciting “new” waveband. The youngest galaxies, producing their first generation of stars, will be brightest in the far-IR (light is red-shifted into this region). The successor to the Hubble Space Telescope will focus on the IR part of the spectrum and study the time “when galaxies were ...
My Presentation
... electromagnetic radiation (electric and magnetic energy). This energy causes the star to erupt into a supernova. Most supernovae reach maximum brightness a few days after they occur and shine intensely for several weeks. Some fade within months. Others fade over a period of years. Supernovae also di ...
... electromagnetic radiation (electric and magnetic energy). This energy causes the star to erupt into a supernova. Most supernovae reach maximum brightness a few days after they occur and shine intensely for several weeks. Some fade within months. Others fade over a period of years. Supernovae also di ...
Review for Midterm Exam 2
... Suppose the atoms in a receding gas cloud have two energy levels separated by an energy corresponding to a wavelength of 486.3 nm. The observer will see a spectrum with absorption at a wavelength A. Less than 483.3 nm. B. Equal to 486.3 nm. C. Greater than 486.3 nm. D. It depends on the temperature ...
... Suppose the atoms in a receding gas cloud have two energy levels separated by an energy corresponding to a wavelength of 486.3 nm. The observer will see a spectrum with absorption at a wavelength A. Less than 483.3 nm. B. Equal to 486.3 nm. C. Greater than 486.3 nm. D. It depends on the temperature ...
Slide 1
... layers drift off into space and we’re left with a tiny, white-hot core of carbon just sitting there. This is a “white dwarf”. All the stuff that puffs off into space forms a planetary nebula. But what about the big stars? ...
... layers drift off into space and we’re left with a tiny, white-hot core of carbon just sitting there. This is a “white dwarf”. All the stuff that puffs off into space forms a planetary nebula. But what about the big stars? ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Molecular Cloud, and it is a vast reservoir of cold molecular gas and interstellar dust. Although the Orion Nebula is the only molecular cloud visible to the naked eye, similar clouds are numerously scattered throughout the Milky Way and some of them are close enough to Earth, so that they can be st ...
... Molecular Cloud, and it is a vast reservoir of cold molecular gas and interstellar dust. Although the Orion Nebula is the only molecular cloud visible to the naked eye, similar clouds are numerously scattered throughout the Milky Way and some of them are close enough to Earth, so that they can be st ...
Stars - Mrs. Tosh`s class
... When the fuel runs out, gravity collapses the core even more. The iron core absorbs energy instead of releasing it…. ...
... When the fuel runs out, gravity collapses the core even more. The iron core absorbs energy instead of releasing it…. ...
What is a galaxy?
... Stars formed at the time the Galaxy formed are called Population II stars. They are almost entirely hydrogen and helium with few heavier elements, because the matter in them had not previously been in another star. They lie in all parts of the galaxy, the halo (globular clusters), disk, and bulge. Y ...
... Stars formed at the time the Galaxy formed are called Population II stars. They are almost entirely hydrogen and helium with few heavier elements, because the matter in them had not previously been in another star. They lie in all parts of the galaxy, the halo (globular clusters), disk, and bulge. Y ...
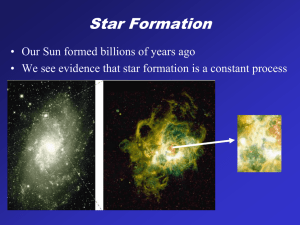
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.