Sternentstehung - Star Formation
... - End of protostellar/beginning or pre-main sequence evolution à birthline. - Pre-main sequence evolution in the Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) diagram. - Connection of HR diagram with protostellar and pre-main sequence classes. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
... - End of protostellar/beginning or pre-main sequence evolution à birthline. - Pre-main sequence evolution in the Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) diagram. - Connection of HR diagram with protostellar and pre-main sequence classes. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
The Sun . . .
... H-R Diagram: Diagram that classifies stars according to their luminosity/absolute magnitude, and spectral class based on color and surface temperature. Luminosity: The brightness of a star compared to the Sun. Absolute Magnitude: Compares the brightness of stars from a standard distance ...
... H-R Diagram: Diagram that classifies stars according to their luminosity/absolute magnitude, and spectral class based on color and surface temperature. Luminosity: The brightness of a star compared to the Sun. Absolute Magnitude: Compares the brightness of stars from a standard distance ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud of gas in which stars are currently forming. To the astronomer this nebula is known as Messier 42 or M42 ...
... Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud of gas in which stars are currently forming. To the astronomer this nebula is known as Messier 42 or M42 ...
wdm_shanghai_Mayinzhe
... For m_X > 5keV, star formation efficiency is degenerated with WDM For low mass, the two are not degenerated. This is observable by the high-redshift measurement such as square kilometer array (2020). ...
... For m_X > 5keV, star formation efficiency is degenerated with WDM For low mass, the two are not degenerated. This is observable by the high-redshift measurement such as square kilometer array (2020). ...
Chapter 27.1
... Spectrometers attached to optical telescopes separate light into lines of different colors, called a spectrum. Each chemical element has a characteristic dark-line spectrum. The same elements found on earth can be found in stars, but hydrogen and helium are the two most common elements. ...
... Spectrometers attached to optical telescopes separate light into lines of different colors, called a spectrum. Each chemical element has a characteristic dark-line spectrum. The same elements found on earth can be found in stars, but hydrogen and helium are the two most common elements. ...
Alien Worlds Discovered
... Orion Nebula Referred to as a “Stellar Nursery” Large (25 light years in size) cloud of dust and gas about 1270 light years away About 700 stars being formed ...
... Orion Nebula Referred to as a “Stellar Nursery” Large (25 light years in size) cloud of dust and gas about 1270 light years away About 700 stars being formed ...
30.4 Gravitational collapse & early protostellar evolution I (HB)
... the protostar can be described by its entropy profile s(Mr), reflecting the changing conditions at the accretion shock. - Since s represents heat content of each added mass shell, an increase of s(MR) causes a swelling of the protostar. - In the absence of nuclear burning, an increasing s(Mr) arises ...
... the protostar can be described by its entropy profile s(Mr), reflecting the changing conditions at the accretion shock. - Since s represents heat content of each added mass shell, an increase of s(MR) causes a swelling of the protostar. - In the absence of nuclear burning, an increasing s(Mr) arises ...
The Lives of Stars
... moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
... moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
30-1 Directed Reading
... _______________________________________________________________ 15. What is the temperature range of most stars? _______________________________________________________________ 16. What color are the coolest stars? _______________________________________________________________ 17. What color are th ...
... _______________________________________________________________ 15. What is the temperature range of most stars? _______________________________________________________________ 16. What color are the coolest stars? _______________________________________________________________ 17. What color are th ...
Directed Reading Section: Characteristics of Stars
... _______________________________________________________________ 15. What is the temperature range of most stars? _______________________________________________________________ 16. What color are the coolest stars? _______________________________________________________________ 17. What color are th ...
... _______________________________________________________________ 15. What is the temperature range of most stars? _______________________________________________________________ 16. What color are the coolest stars? _______________________________________________________________ 17. What color are th ...
Lecture 12
... There is an upper limit to the mass of a white dwarf - we do not see WDs with masses > 1.4 M We will see in next lectures what the implications of this are for other phenomena in the Universe. It actually led to the discovery of dark energy! The collapse of massive stars produces two types of remna ...
... There is an upper limit to the mass of a white dwarf - we do not see WDs with masses > 1.4 M We will see in next lectures what the implications of this are for other phenomena in the Universe. It actually led to the discovery of dark energy! The collapse of massive stars produces two types of remna ...
GRAVITY FIELD IN EXTERNAL PARTS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... move in the interstellar medium, but remain deep within the incidence of the Sun. According to (Oort, 1950) exist cloud around the Sun of comet nuclei, called the Oort cloud. This cloud is not available observations. But if it exists, the comet nucleus moving near the outskirts of the solar system. ...
... move in the interstellar medium, but remain deep within the incidence of the Sun. According to (Oort, 1950) exist cloud around the Sun of comet nuclei, called the Oort cloud. This cloud is not available observations. But if it exists, the comet nucleus moving near the outskirts of the solar system. ...
The Sun and Stars The Sun is a typical star with a mass of about 2
... 4 11 H + 20−1 e →42 He + ∆mc2 . For the fusion reaction to occur very high temperatures are needed, on the order of 107 K, which are achieved in the core of the star. The sun’s luminosity of L = 3.8 × 1026 Watts is produced by transforming 4.5 × 109 kilograms of mass into energy each second due to t ...
... 4 11 H + 20−1 e →42 He + ∆mc2 . For the fusion reaction to occur very high temperatures are needed, on the order of 107 K, which are achieved in the core of the star. The sun’s luminosity of L = 3.8 × 1026 Watts is produced by transforming 4.5 × 109 kilograms of mass into energy each second due to t ...
poster
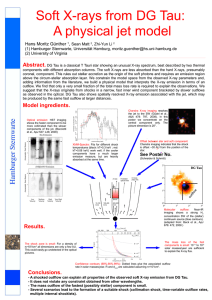
... kT=0.08 keV) work well, if the cooler components have a much larger emission measure, but are heavily absorbed at the same time. ...
... kT=0.08 keV) work well, if the cooler components have a much larger emission measure, but are heavily absorbed at the same time. ...
What do “yellowballs” have to do with the birth of new stars?
... wind moves at velocities of several hundred kilometers/second. ...
... wind moves at velocities of several hundred kilometers/second. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brigh ...
... imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brigh ...
Lecture - Ann Arbor Earth Science
... Stars vary greatly in their masses, size, and densities. We cannot observe a star’s mass directly. We can only calculate it based on other observations. It can be determined either by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational influence on other bodies. The larger the mass, the stro ...
... Stars vary greatly in their masses, size, and densities. We cannot observe a star’s mass directly. We can only calculate it based on other observations. It can be determined either by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational influence on other bodies. The larger the mass, the stro ...
Document
... Stars vary greatly in their masses, size, and densities. We cannot observe a star’s mass directly. We can only calculate it based on other observations. It can be determined either by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational influence on other bodies. The larger the mass, the stro ...
... Stars vary greatly in their masses, size, and densities. We cannot observe a star’s mass directly. We can only calculate it based on other observations. It can be determined either by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational influence on other bodies. The larger the mass, the stro ...
(HR) diagram - Cloudfront.net
... Stars vary greatly in their masses, size, and densities. We cannot observe a star’s mass directly. We can only calculate it based on other observations. It can be determined either by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational influence on other bodies. The larger the mass, the stro ...
... Stars vary greatly in their masses, size, and densities. We cannot observe a star’s mass directly. We can only calculate it based on other observations. It can be determined either by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational influence on other bodies. The larger the mass, the stro ...
STARS: how they are born, live and die
... about the size of Earth. Its weight supported against further collapse by electron degeneracy pressure, it will do nothing but sit there and cool off, for eternity. ...
... about the size of Earth. Its weight supported against further collapse by electron degeneracy pressure, it will do nothing but sit there and cool off, for eternity. ...
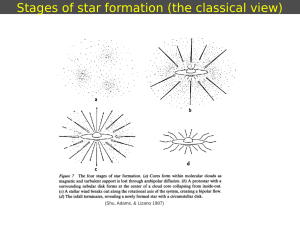
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.