A Reservoir of Ionized Gas in the Galactic Halo to Sustain Star
... The timescale for gas consumption via star formation in spiral galaxies is far shorter than a Hubble time (13.8 billion years), requiring an on-going replenishment of the gaseous fuel in the disks of galaxies for continued star formation. Analytical models and hydrodynamical simulations have emphasi ...
... The timescale for gas consumption via star formation in spiral galaxies is far shorter than a Hubble time (13.8 billion years), requiring an on-going replenishment of the gaseous fuel in the disks of galaxies for continued star formation. Analytical models and hydrodynamical simulations have emphasi ...
Chapter 12
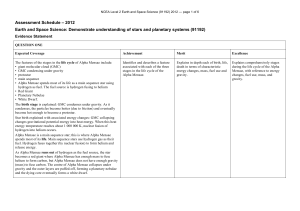
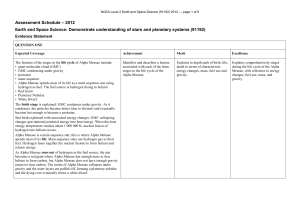
... 2. Apparent magnitude is a measure of the amount of light received from a celestial object. Hipparchus assigned an apparent magnitude of 1 for the brightest stars and 6 for the dimmest. 3. The modern magnitude scale is set up so that a 5-magnitude difference corresponds to a ratio of 100 in the amou ...
... 2. Apparent magnitude is a measure of the amount of light received from a celestial object. Hipparchus assigned an apparent magnitude of 1 for the brightest stars and 6 for the dimmest. 3. The modern magnitude scale is set up so that a 5-magnitude difference corresponds to a ratio of 100 in the amou ...
What`s in the Night Sky?
... tudents know that when they look at the night sky they can see stars and the moon. They may not know that sometimes they can also see planets, meteorites, and comets. On a clear dark night, away from city lights, it is possible to see about 2,000 stars. With the help of a telescope, many thousands m ...
... tudents know that when they look at the night sky they can see stars and the moon. They may not know that sometimes they can also see planets, meteorites, and comets. On a clear dark night, away from city lights, it is possible to see about 2,000 stars. With the help of a telescope, many thousands m ...
IR Spectroscopy
... F(l) : observed flux density from the galaxy 1st term : arises from the narrowing of the filter passband in the restframe of the galaxy by a factor (1+z) 2nd term : allows for the fact that radiation seen by the observer at ...
... F(l) : observed flux density from the galaxy 1st term : arises from the narrowing of the filter passband in the restframe of the galaxy by a factor (1+z) 2nd term : allows for the fact that radiation seen by the observer at ...
Slides from Dr. Frank`s Lecture17
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
Fig. 16-7, p.363
... • There are two types of planets in our solar system, Earth-like and Jupiter-like, results of a process we think we understand • Almost 200 planets have now been found around other stars, but those planetary systems often have “hot Jupiters” - is our solar system weird, or are those systems weird ? ...
... • There are two types of planets in our solar system, Earth-like and Jupiter-like, results of a process we think we understand • Almost 200 planets have now been found around other stars, but those planetary systems often have “hot Jupiters” - is our solar system weird, or are those systems weird ? ...
Chapter 6 Stars
... from the life cycle of a low-mass or medium-mass star. High-mass stars quickly evolve into brilliant supergiants. When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly. Within hours, the star blazes millions of times brighter. The explosion is called a supernova. After a supernova, some of th ...
... from the life cycle of a low-mass or medium-mass star. High-mass stars quickly evolve into brilliant supergiants. When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly. Within hours, the star blazes millions of times brighter. The explosion is called a supernova. After a supernova, some of th ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... Review EM radiation How far away are stars? What can starlight tell us? ...
... Review EM radiation How far away are stars? What can starlight tell us? ...
Are turbulent spheres suitable initial conditions for star
... We show the column density plots of the six clouds 5 Myr after the first star is formed in Fig. 2 (except for Early A). In the galactic simulation, Early A evolves into Cloud A after 10 Myr. Therefore, in Fig. 2 we show Early A at 15 Myr, to compare it with Cloud A at 5 Myr. All clouds show a comple ...
... We show the column density plots of the six clouds 5 Myr after the first star is formed in Fig. 2 (except for Early A). In the galactic simulation, Early A evolves into Cloud A after 10 Myr. Therefore, in Fig. 2 we show Early A at 15 Myr, to compare it with Cloud A at 5 Myr. All clouds show a comple ...
Phase Analysis of RV Tauri and Semi-regular Variables Abstract
... RV Tauri variable stars, related classes of pulsating variable stars. The ultimate objective for our research is to determine whether the stars stellar properties such as temperature, radius, and luminosity correlate with their pulsation cycles. In order to determine this, we need to closely examine ...
... RV Tauri variable stars, related classes of pulsating variable stars. The ultimate objective for our research is to determine whether the stars stellar properties such as temperature, radius, and luminosity correlate with their pulsation cycles. In order to determine this, we need to closely examine ...
PowerPoint - Physics and Astronomy
... The rapid variation of brightness of quasars indicates a) the source of energy is very small. b) energy is coming from matter and antimatter. c) the energy source is rotating rapidly. d) a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. e) there are many separate sources of energy in the core. Explanation: ...
... The rapid variation of brightness of quasars indicates a) the source of energy is very small. b) energy is coming from matter and antimatter. c) the energy source is rotating rapidly. d) a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. e) there are many separate sources of energy in the core. Explanation: ...
The star
... I have told no one yet, but the truth cannot be concealed. The facts are there for all to read, recorded on the countless miles of magnetic tape and the thousands of photographs we are carrying back to Earth. Other scientists can interpret them as easily as I can, and I am not one who would condone ...
... I have told no one yet, but the truth cannot be concealed. The facts are there for all to read, recorded on the countless miles of magnetic tape and the thousands of photographs we are carrying back to Earth. Other scientists can interpret them as easily as I can, and I am not one who would condone ...
58KB - NZQA
... • Planetary Nebulae • White Dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Star birth explained with associated energy changes: GMC collapsing changes gravitation ...
... • Planetary Nebulae • White Dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Star birth explained with associated energy changes: GMC collapsing changes gravitation ...
powerpoint file
... It may stabilize as a neutron star or it may become a black hole. But the next layers out that crash onto it are still nuclear fuel; they get superheated and explode as a supernova. ...
... It may stabilize as a neutron star or it may become a black hole. But the next layers out that crash onto it are still nuclear fuel; they get superheated and explode as a supernova. ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... • If a small galaxy has a central collision with a larger spiral galaxy, the gravitational pulse can compress gas/dust and make a star formation burst in a ring. • Collision energy added to the central bulge can stretch it out into a very non-spherica ...
... • If a small galaxy has a central collision with a larger spiral galaxy, the gravitational pulse can compress gas/dust and make a star formation burst in a ring. • Collision energy added to the central bulge can stretch it out into a very non-spherica ...
the ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM / WAVE PROPERTIES
... • Any object that is above absolute zero emits electromagnetic waves • The entire group of waves with these properties is called the “Electromagnetic Spectrum” ...
... • Any object that is above absolute zero emits electromagnetic waves • The entire group of waves with these properties is called the “Electromagnetic Spectrum” ...
Mass determinations of PMS stars with the
... F.Cusano, E.W.Guenther, M.Esposito, B.Stecklum TLS-Tautenburg, Germany ...
... F.Cusano, E.W.Guenther, M.Esposito, B.Stecklum TLS-Tautenburg, Germany ...
Our Solar System, Our Galaxy, then the Universe
... of this are referred to as the Kuiper belt, Scattered Objects, and the Oort Cloud. The furthest portion, the Oort Cloud, may reach half way to the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, about 4.2 light ...
... of this are referred to as the Kuiper belt, Scattered Objects, and the Oort Cloud. The furthest portion, the Oort Cloud, may reach half way to the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, about 4.2 light ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.