powerpoint
... • These methods create different atoms and/or isotopes. • However, this type of supernova does not produce all of the heaviest elements in the abundances we have on the earth (so there is something more – to be discovered later in the course). ...
... • These methods create different atoms and/or isotopes. • However, this type of supernova does not produce all of the heaviest elements in the abundances we have on the earth (so there is something more – to be discovered later in the course). ...
Sem one 2011 review KEY
... Tide- bulge in large masses of water on Earth caused by gravitational attraction towards the Moon. Perigee- Point in orbit when the moon is closest to the earth. Wane- get or appear smaller. Lunar Eclipse- Answered earlier in the packet. Gibbous Moon- between the full and quarter moon. Spring Tides- ...
... Tide- bulge in large masses of water on Earth caused by gravitational attraction towards the Moon. Perigee- Point in orbit when the moon is closest to the earth. Wane- get or appear smaller. Lunar Eclipse- Answered earlier in the packet. Gibbous Moon- between the full and quarter moon. Spring Tides- ...
galaxy.
... Shapely (Harvard): Argued that spiral nebulae were inside our galaxy for several reasons • Galaxy was huge (he didn’t know about dust). • van Maanen’s observations showed that one spiral nebula, M 101, could be observed to rotate. It it were outside our galaxy, it would have to be turning faster tha ...
... Shapely (Harvard): Argued that spiral nebulae were inside our galaxy for several reasons • Galaxy was huge (he didn’t know about dust). • van Maanen’s observations showed that one spiral nebula, M 101, could be observed to rotate. It it were outside our galaxy, it would have to be turning faster tha ...
Concept map-Rubric-final - Berkeley Center for Cosmological
... •CMB: predicted by Gamow; relic from 380,000yrs after Big Bang; when universe cooled, neutral atoms formed and the universe became transparent; matches black body spectrum from hot early universe •Ratios of elements (nucleosynthesis): predictions of ratios from nuclear physics match observed ratios ...
... •CMB: predicted by Gamow; relic from 380,000yrs after Big Bang; when universe cooled, neutral atoms formed and the universe became transparent; matches black body spectrum from hot early universe •Ratios of elements (nucleosynthesis): predictions of ratios from nuclear physics match observed ratios ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
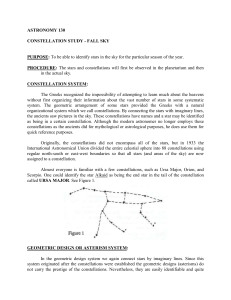
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
The Milky Way The Milky Way`s Neighbourhood
... unwind and break suddenly, and the matter and energy that had been contained rushes outward from the Sun. Solar flares can be many thousands of miles long, and they can contain far more energy than all of the energy consumption of all of human history on Earth. What Is A Supernova? A supernova is a ...
... unwind and break suddenly, and the matter and energy that had been contained rushes outward from the Sun. Solar flares can be many thousands of miles long, and they can contain far more energy than all of the energy consumption of all of human history on Earth. What Is A Supernova? A supernova is a ...
chap17_f04_probs
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64 times greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is ...
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64 times greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is ...
Constellations
... • Stars have a north-south position called the declination which is similar to the idea of latitude • Polaris has a declination of 90º N. • Stars over the Equator have a declination of 0º. ...
... • Stars have a north-south position called the declination which is similar to the idea of latitude • Polaris has a declination of 90º N. • Stars over the Equator have a declination of 0º. ...
Geography
... find the Big Dipper. Draw a straight line between the two stars of the Big Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... find the Big Dipper. Draw a straight line between the two stars of the Big Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
ν - Luleå tekniska universitet
... nebulous envelope around the nucleus of a comet Halley’s comet ...
... nebulous envelope around the nucleus of a comet Halley’s comet ...
M - ASTRONOMY GROUP – University of St Andrews
... 1948: Gamov predicts background radiation from Big Bang 1965: Penzias & Wilson discover Cosmic Microwave Background BIG BANG THEORY ADOPTED 1975: Computers: Big-Bang Nucleosynthesis ( 75% H, 25% He ) 1985: Observations confirm BBN predictions 1992… CMB observatories: COBE, WMAP, Planck ...
... 1948: Gamov predicts background radiation from Big Bang 1965: Penzias & Wilson discover Cosmic Microwave Background BIG BANG THEORY ADOPTED 1975: Computers: Big-Bang Nucleosynthesis ( 75% H, 25% He ) 1985: Observations confirm BBN predictions 1992… CMB observatories: COBE, WMAP, Planck ...
Chapter 19. Mapping the Universe from Herschel to Sloan
... While Cepheids are useful for getting distances to nearby galaxies it is also a painfully slow process because you need to get many images of a galaxy spread out over more than a year and discover all the Cepheids, measure their brightnesses as a function of time, etc. Fortunately, a second discover ...
... While Cepheids are useful for getting distances to nearby galaxies it is also a painfully slow process because you need to get many images of a galaxy spread out over more than a year and discover all the Cepheids, measure their brightnesses as a function of time, etc. Fortunately, a second discover ...
What keeps stars shining? What holds them up? Lecture 14. The
... correspond nicely to this stage. Duration of stage, 20% of Main Sequence lifetime. For sun, (in about 5 billion years) Radius -> 1 AU (incinerating Mercury, Venus, and Earth) Surface Temp -> 3500 K (very red) Why is the star adjusting in this way? There are at least three things happening simultaneo ...
... correspond nicely to this stage. Duration of stage, 20% of Main Sequence lifetime. For sun, (in about 5 billion years) Radius -> 1 AU (incinerating Mercury, Venus, and Earth) Surface Temp -> 3500 K (very red) Why is the star adjusting in this way? There are at least three things happening simultaneo ...
Name
... Stars are born, grow, and die in a certain pattern. This page will show you some images of each of these steps. Skip down to Step a.) of the page (where you see the pictures). 3. List the steps of stellar evolution in order, according to the left hand side of the page. Examine the pictures. 1st ____ ...
... Stars are born, grow, and die in a certain pattern. This page will show you some images of each of these steps. Skip down to Step a.) of the page (where you see the pictures). 3. List the steps of stellar evolution in order, according to the left hand side of the page. Examine the pictures. 1st ____ ...
CVs
... accretes matter onto the WD through Lagrangian point • Turbulence and friction cause the stream of matter to spread into a disc (sometimes) • How does the system maintain this mass transfer? ...
... accretes matter onto the WD through Lagrangian point • Turbulence and friction cause the stream of matter to spread into a disc (sometimes) • How does the system maintain this mass transfer? ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • A light year (ly) is the distance light travels in a year – About 1016 m (~6 trillion miles) • Speed of light is 3 108 m/sec or 186,000 mi/sec ...
... • A light year (ly) is the distance light travels in a year – About 1016 m (~6 trillion miles) • Speed of light is 3 108 m/sec or 186,000 mi/sec ...
Using AO to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Massive Galaxies
... The age and metallicity distributions of stars in bulges and disks are sensitive indicators of galaxy formation physics. Resolved stellar populations can be used to measure the entire star formation and chemical enrichment histories of galaxies. Spatial resolution is the most critical capability nee ...
... The age and metallicity distributions of stars in bulges and disks are sensitive indicators of galaxy formation physics. Resolved stellar populations can be used to measure the entire star formation and chemical enrichment histories of galaxies. Spatial resolution is the most critical capability nee ...
P1 The Earth in the Universe
... This theory states that the universe has always existed as it does now and hasn’t changed. The trouble is that the night sky would be completely lit up because of the billions of stars, but it’s not, so… The “Big Bang” theory This theory states that the universe started off with an explosion and eve ...
... This theory states that the universe has always existed as it does now and hasn’t changed. The trouble is that the night sky would be completely lit up because of the billions of stars, but it’s not, so… The “Big Bang” theory This theory states that the universe started off with an explosion and eve ...
SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF A NEWLY DISCOVERED HgMn STAR
... age ~100Myr) open cluster, using low and high-resolution (R~7500, R~25000) spectra stretching from 4500-5840 Å. The data were obtained with the multi-fiber spectrograph GIRAFFE with MEDUSA, mounted at UT2 (Kueyen), the 8 meter class VLT telescope, in Chile. The atmospheric parameters of the star wer ...
... age ~100Myr) open cluster, using low and high-resolution (R~7500, R~25000) spectra stretching from 4500-5840 Å. The data were obtained with the multi-fiber spectrograph GIRAFFE with MEDUSA, mounted at UT2 (Kueyen), the 8 meter class VLT telescope, in Chile. The atmospheric parameters of the star wer ...
Exoplanet
... (silicates) and ices (solid H2O, CH4, NH3) – Mostly H and He (these two elements make up about 98% of our Solar System) ...
... (silicates) and ices (solid H2O, CH4, NH3) – Mostly H and He (these two elements make up about 98% of our Solar System) ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (b) The region on the H-R diagram where, once they are formed. new stars rest for most of their lives. (c) The sequence of events a star follows from its formation to supernova. (d) The region on the H-R diagram where protostars first appear. 50. Define hydrogen burning. (a) The formation of a hydro ...
... (b) The region on the H-R diagram where, once they are formed. new stars rest for most of their lives. (c) The sequence of events a star follows from its formation to supernova. (d) The region on the H-R diagram where protostars first appear. 50. Define hydrogen burning. (a) The formation of a hydro ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.