When radiation ruled
... stars – Hydrogen is primordial – Helium is too abundant to have been made in stars. – Helium was made at 3min. ...
... stars – Hydrogen is primordial – Helium is too abundant to have been made in stars. – Helium was made at 3min. ...
Document
... • As the protostar heats up, enough thermal energy is radiated away from surface to allow collapse to continue. – energy is transported to surface first via convection – as core gets even hotter, transport via radiation takes over ...
... • As the protostar heats up, enough thermal energy is radiated away from surface to allow collapse to continue. – energy is transported to surface first via convection – as core gets even hotter, transport via radiation takes over ...
Extracting science from surveys of our Galaxy
... ¤CDM does not currently predict the structure of the MW Key observables (,¹) are far removed from quantities of physical interest Errors in s corrupt estimates of all physical quantities Inversion of data to physical model ill-advised Should fit model to data in (>6d) space of observables To do thi ...
... ¤CDM does not currently predict the structure of the MW Key observables (,¹) are far removed from quantities of physical interest Errors in s corrupt estimates of all physical quantities Inversion of data to physical model ill-advised Should fit model to data in (>6d) space of observables To do thi ...
English Summary
... Another important energetic contribution in a galaxy may come from the formation and evolution of stars. Star formation in the center of the galaxy may be triggered for example, by a collision or a close encounter with another galaxy. Many of these newly formed stars are very massive and very bright ...
... Another important energetic contribution in a galaxy may come from the formation and evolution of stars. Star formation in the center of the galaxy may be triggered for example, by a collision or a close encounter with another galaxy. Many of these newly formed stars are very massive and very bright ...
H-R Diagrams
... If we plot a graph of luminosity against temperature for lots of stars we get a graph like this… ...
... If we plot a graph of luminosity against temperature for lots of stars we get a graph like this… ...
View/Open - NuSpace Home - National University of Science and
... started by the collapse of a MC in which process when the MC collapses, it contracts causing portions thereof to also further collapse and this causes the cloud to fragment into smaller parcels of matter (cores) and these collapse further to form stars. This collapse process is generally believed to ...
... started by the collapse of a MC in which process when the MC collapses, it contracts causing portions thereof to also further collapse and this causes the cloud to fragment into smaller parcels of matter (cores) and these collapse further to form stars. This collapse process is generally believed to ...
Solar Magnetism in Little Ice Age, Orbits in Solar Ecliptic
... supernovae compare with redshift, the Hubble constant, studies of cosmic largescale structure, and the flat topology of space – all point the same way.” Support for the article – After examining recent measurements by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, NASA declared "We now know that the univ ...
... supernovae compare with redshift, the Hubble constant, studies of cosmic largescale structure, and the flat topology of space – all point the same way.” Support for the article – After examining recent measurements by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, NASA declared "We now know that the univ ...
hst/stis spectroscopy of the environment in the starburst core of m82
... • c1: two possible broadening mechanisms (gravitationally induced virial motions and the stirring effects of wide-scale, intense star-formation on the ambient ISM) in ...
... • c1: two possible broadening mechanisms (gravitationally induced virial motions and the stirring effects of wide-scale, intense star-formation on the ambient ISM) in ...
ASTR2100 - Saint Mary's University | Astronomy & Physics
... the distance to the Andromeda Nebula using Cepheid variables. Somewhat less well-known is Lindblad’s 1926 development of a mathematical model for Galactic rotation. Lindblad’s model was developed further in 1927-28 by Oort, who demonstrated its applicability to the radial velocity data for stars. Fi ...
... the distance to the Andromeda Nebula using Cepheid variables. Somewhat less well-known is Lindblad’s 1926 development of a mathematical model for Galactic rotation. Lindblad’s model was developed further in 1927-28 by Oort, who demonstrated its applicability to the radial velocity data for stars. Fi ...
PoS(HTRA-IV)044 - Proceeding of science
... to waste some of them. On the figure are also shown two K-band magnitude limits, that ensure stars above to be smaller than FS at 40 a.u and a wavelength of 550 nm. One is set in the situation where we take all populations from the sample, the other one in the situation where the red giant stars hav ...
... to waste some of them. On the figure are also shown two K-band magnitude limits, that ensure stars above to be smaller than FS at 40 a.u and a wavelength of 550 nm. One is set in the situation where we take all populations from the sample, the other one in the situation where the red giant stars hav ...
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
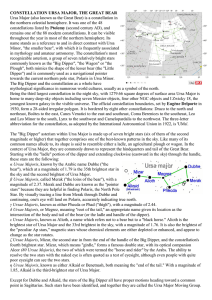
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
Surveying the Stars
... • How hot are stars? • The surface temperatures of the hottest stars exceed 40,000 K and those of the coolest stars are less than 3,000 K. We measure a star’s surface temperature from its color or spectrum, and we classify spectra according to the sequence of spectral types ...
... • How hot are stars? • The surface temperatures of the hottest stars exceed 40,000 K and those of the coolest stars are less than 3,000 K. We measure a star’s surface temperature from its color or spectrum, and we classify spectra according to the sequence of spectral types ...
Star
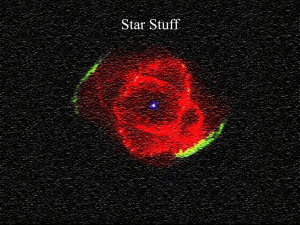
... • According to this theory, the entire universe was at one time confined in a dense, hot, super massive concentration. • About 20 billion years ago, a cataclysmic explosion hurled this material in all directions, creating all matter and space. • Eventually the ejected masses of gas cooled and conden ...
... • According to this theory, the entire universe was at one time confined in a dense, hot, super massive concentration. • About 20 billion years ago, a cataclysmic explosion hurled this material in all directions, creating all matter and space. • Eventually the ejected masses of gas cooled and conden ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.