The Spectra of Stars
... • Color of a star depends on its Temperature Color of a star depends on its Temperature – Red Stars are Cooler – Blue Stars are Hotter ...
... • Color of a star depends on its Temperature Color of a star depends on its Temperature – Red Stars are Cooler – Blue Stars are Hotter ...
Planisphere Exercise
... In what direction does the celestial equator appear to “rise” and “set” as the night progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. Look at the ecliptic, the path of the Sun among the background of stars over the course of a year. As the night progresses, does the ecli ...
... In what direction does the celestial equator appear to “rise” and “set” as the night progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. Look at the ecliptic, the path of the Sun among the background of stars over the course of a year. As the night progresses, does the ecli ...
Light Energy, Dark Energy 1. Another View of Olber's Paradox
... The universe is filled with stars like the Sun, each one of them putting out way more light energy than it absorbs. Since this light has nowhere to go, it can only build up with time. Technicality: You might ask, what about planets and gas and dust – can't they absorb the light?. Indeed they can, bu ...
... The universe is filled with stars like the Sun, each one of them putting out way more light energy than it absorbs. Since this light has nowhere to go, it can only build up with time. Technicality: You might ask, what about planets and gas and dust – can't they absorb the light?. Indeed they can, bu ...
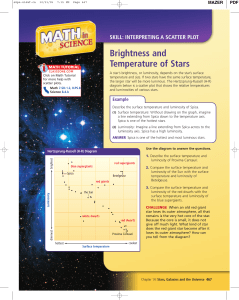
Brightness and Temperature of Stars
... A star’s brightness, or luminosity, depends on the star’s surface temperature and size. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star will be more luminous. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram below is a scatter plot that shows the relative temperatures and luminosities of variou ...
... A star’s brightness, or luminosity, depends on the star’s surface temperature and size. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star will be more luminous. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram below is a scatter plot that shows the relative temperatures and luminosities of variou ...
Black Holes S.Chandrasekhar (1910-1995) March 27
... because nothing can go faster than light. No escape means there is no more contact with something that falls in. It increases the hole mass, changes the spin or charge, but otherwise loses its identity. ...
... because nothing can go faster than light. No escape means there is no more contact with something that falls in. It increases the hole mass, changes the spin or charge, but otherwise loses its identity. ...
The quest for cradles of life: using the fundamental metallicity
... local Universe to answer the question “Which type of galaxy is most habitable in terms of complex life in the Universe?” We draw on the progress made by SHZ and GHZ studies to isolate the primary physical ingredients required to model habitability: planets form in stellar vicinities with a metallici ...
... local Universe to answer the question “Which type of galaxy is most habitable in terms of complex life in the Universe?” We draw on the progress made by SHZ and GHZ studies to isolate the primary physical ingredients required to model habitability: planets form in stellar vicinities with a metallici ...
How Big is the Solar System?
... that scientists have no way of detecting any objects. Astronomers believe that the Oort Cloud – the source of long period comets – extends out to a distance of 50,000 AU, and maybe even 100,000 AU. Once again, though, the Oort Cloud has never been seen directly. We just guess that it exists because ...
... that scientists have no way of detecting any objects. Astronomers believe that the Oort Cloud – the source of long period comets – extends out to a distance of 50,000 AU, and maybe even 100,000 AU. Once again, though, the Oort Cloud has never been seen directly. We just guess that it exists because ...
stars-notes
... • When a chemical element emits light, only some colors in the spectrum show up. The colors that appear are called emission lines. • Every element has a unique set of emission lines that act like a fingerprint for that element. ...
... • When a chemical element emits light, only some colors in the spectrum show up. The colors that appear are called emission lines. • Every element has a unique set of emission lines that act like a fingerprint for that element. ...
Is the Sun a Star? - Classroom Websites
... draw what a distant planetary system might look like based on actual scientists' reports may help students recognize that each planetary system has a central starjust as our own solar system has one star, sometimes called by its Roman name, Sol. In some systems there are two (or even more stars) at ...
... draw what a distant planetary system might look like based on actual scientists' reports may help students recognize that each planetary system has a central starjust as our own solar system has one star, sometimes called by its Roman name, Sol. In some systems there are two (or even more stars) at ...
THE PHYSICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE STARS 1
... As often as possible it is necessary to look for reddening-free indicators, like the intensity of certain spectral lines or bands (Hβ line, TiO molecular bands, for instance), IR indices, etc. Or, either derive the interstellar absorption independently and correct the pseudo-continuum color indices. ...
... As often as possible it is necessary to look for reddening-free indicators, like the intensity of certain spectral lines or bands (Hβ line, TiO molecular bands, for instance), IR indices, etc. Or, either derive the interstellar absorption independently and correct the pseudo-continuum color indices. ...
Astronomy Exam #2 for the 10
... The two neutrinos are sub-atomic particles with almost no mass that travel near light-speed and only weakly interact with matter. They are created with the two neutrons as a by-product of the fusion of hydrogen into helium. The gamma rays are very high energy photons with no mass and travel at light ...
... The two neutrinos are sub-atomic particles with almost no mass that travel near light-speed and only weakly interact with matter. They are created with the two neutrons as a by-product of the fusion of hydrogen into helium. The gamma rays are very high energy photons with no mass and travel at light ...
Lecture Note
... • Reminder: Stefan-Boltzmann law states that a blackbody radiates electromagnetic waves with a total energy flux F directly proportional to the fourth power of the Kelvin temperature T of the object: ...
... • Reminder: Stefan-Boltzmann law states that a blackbody radiates electromagnetic waves with a total energy flux F directly proportional to the fourth power of the Kelvin temperature T of the object: ...
ppt - A century of cosmology
... candidate faint Ly emitters at z~8-10 with SFR <1 M yr-1 - a population which may contribute significantly to reionization. • Exhaustive spectroscopic and imaging follow-up supports hypothesis that many of lensed Lya emitters are at z~10 but additional follow-up still required. Final confirmation ...
... candidate faint Ly emitters at z~8-10 with SFR <1 M yr-1 - a population which may contribute significantly to reionization. • Exhaustive spectroscopic and imaging follow-up supports hypothesis that many of lensed Lya emitters are at z~10 but additional follow-up still required. Final confirmation ...
Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Characterization of the
... – A good knowledge of the properties of the stars hosting exoplanets is fundamental to improve the accuracy of exoplanet measurements – Accurate determination of stellar masses and radii are required to derive masses and radii of the planets detected with the Doppler and transit methods, respectiv ...
... – A good knowledge of the properties of the stars hosting exoplanets is fundamental to improve the accuracy of exoplanet measurements – Accurate determination of stellar masses and radii are required to derive masses and radii of the planets detected with the Doppler and transit methods, respectiv ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Search data set for interesting individual objects that represent rare classes of objects. ...
... Search data set for interesting individual objects that represent rare classes of objects. ...
Today in Astronomy 102: electron degeneracy pressure and white
... They orbit each other with a period of about 50 years. Sirius A is vastly brighter than Sirius B at visible wavelengths; the contrast is smaller in this X-ray image. Astronomy 102 ...
... They orbit each other with a period of about 50 years. Sirius A is vastly brighter than Sirius B at visible wavelengths; the contrast is smaller in this X-ray image. Astronomy 102 ...
Document
... • Electrons accelerate down the magnetic field lines toward the lower atmosphere, producing microwave emission • Electrons collide with ions, producing hard x-rays, white light emission from chromosphere • Chromospheric plasma heated to coronal temperatures, hot plasma flows up into the corona • Sho ...
... • Electrons accelerate down the magnetic field lines toward the lower atmosphere, producing microwave emission • Electrons collide with ions, producing hard x-rays, white light emission from chromosphere • Chromospheric plasma heated to coronal temperatures, hot plasma flows up into the corona • Sho ...
The Evolution of Stars - a More Detailed Picture (Chapter 8
... Potential Energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which gets thermalised, so the temperature goes up. This phase lasts a relatively short time. When the cloud is hot enough, the gas is ionised and OPACITY sets in. When that is the case, the gas finds it harder to lose energy, and becomes hotter e ...
... Potential Energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which gets thermalised, so the temperature goes up. This phase lasts a relatively short time. When the cloud is hot enough, the gas is ionised and OPACITY sets in. When that is the case, the gas finds it harder to lose energy, and becomes hotter e ...
PSC101-lecture12
... • Comets - composed of ice and rock • Asteroids - composed of rock and/or metal • There is also dust in space which can be seen in meteor showers ...
... • Comets - composed of ice and rock • Asteroids - composed of rock and/or metal • There is also dust in space which can be seen in meteor showers ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.