The Nature of Light II
... Luminosity of a Star q Luminosity is the total amount of energy radiated into space each second from a star’s surface. q It is the rate of energy emission - not just the energy of visible light, but also the energy of any type of EM radiation, from radio waves to gamma-rays. q It does not dep ...
... Luminosity of a Star q Luminosity is the total amount of energy radiated into space each second from a star’s surface. q It is the rate of energy emission - not just the energy of visible light, but also the energy of any type of EM radiation, from radio waves to gamma-rays. q It does not dep ...
About SDSS - Astro Projects
... SDSS mainly imaged the area around the North Galactic Pole (RA = 193 deg, Dec = 27 deg). This is a point directly 'above' our position in the Milky Way Galaxy. Because of this the survey includes hardly any supernova remnants or planetary nebulae. This is because these objects are remnants of dead s ...
... SDSS mainly imaged the area around the North Galactic Pole (RA = 193 deg, Dec = 27 deg). This is a point directly 'above' our position in the Milky Way Galaxy. Because of this the survey includes hardly any supernova remnants or planetary nebulae. This is because these objects are remnants of dead s ...
2020 Vision: An Overview of New Worlds, New Horizons in
... known to exist at the centers of most galaxies. Precision measurements of primordial radiation left from the big bang have enabled astronomers to determine the age and structure of the universe. Other astronomical observations have revealed that most of the matter in the universe is invisible (i.e., ...
... known to exist at the centers of most galaxies. Precision measurements of primordial radiation left from the big bang have enabled astronomers to determine the age and structure of the universe. Other astronomical observations have revealed that most of the matter in the universe is invisible (i.e., ...
Introduction This book will teach you all you need to know about the
... A black dwarf is when a white dwarf cools off over millions of years and it no longer emits light so it is simple now just a black floating object in space. We are now moving onto the life cycle of a high mass star. Just like the low mass star the high mass star starts out as a nebula. The nebula co ...
... A black dwarf is when a white dwarf cools off over millions of years and it no longer emits light so it is simple now just a black floating object in space. We are now moving onto the life cycle of a high mass star. Just like the low mass star the high mass star starts out as a nebula. The nebula co ...
Deriving the Isoradius Lines (optional, mathematical
... Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating – alternately growing bigger and smaller – ...
... Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating – alternately growing bigger and smaller – ...
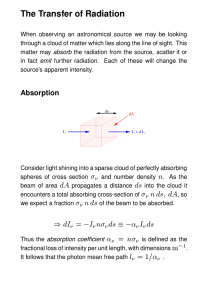
The Transfer of Radiation вб дже диз дж ¡ бгабдиз ¡ бдиз
... photons from a protostar through a dusty cloud, both involve scattering. Scattering can be described by a new emission coefficient, but this is dependent on the incident radiation field; this makes it impossible to integrate the equation of transfer directly. In general, scattering is very complicat ...
... photons from a protostar through a dusty cloud, both involve scattering. Scattering can be described by a new emission coefficient, but this is dependent on the incident radiation field; this makes it impossible to integrate the equation of transfer directly. In general, scattering is very complicat ...
Sizing Up The Universe
... distant galaxies, the angular size of the galaxy. Hubble then measured the radial velocities of these galaxies using the redshifts he found in their spectral lines. Galaxies showing a redshift are moving away from us. On average, Hubble found, the larger their distance, the larger their redshift. So ...
... distant galaxies, the angular size of the galaxy. Hubble then measured the radial velocities of these galaxies using the redshifts he found in their spectral lines. Galaxies showing a redshift are moving away from us. On average, Hubble found, the larger their distance, the larger their redshift. So ...
the 82nd arthur h. compton lecture series
... polarization) and measuring how it’s intensity evolves over time (light curves). ➢ Type Ia SNe come from explosions of white dwarfs in binary systems and do not show signs of He, but strong Si absorption. ➢ Type II SNe show H in the spectra. Subtypes are IIP, IIn, IIL. ➢ Type Ib/c SNe have lost thei ...
... polarization) and measuring how it’s intensity evolves over time (light curves). ➢ Type Ia SNe come from explosions of white dwarfs in binary systems and do not show signs of He, but strong Si absorption. ➢ Type II SNe show H in the spectra. Subtypes are IIP, IIn, IIL. ➢ Type Ib/c SNe have lost thei ...
TWO NEW VARIABLE STARS OBSERVED IN THE FIELD OF THE
... precise identity of the system, and we considered here two plausible alternatives. The object could be a short-period non eclipsing binary system showing the properties typical of an ellipsoidal variable (ELL variable star according the GCVS classification). In this case, the small changes in the lu ...
... precise identity of the system, and we considered here two plausible alternatives. The object could be a short-period non eclipsing binary system showing the properties typical of an ellipsoidal variable (ELL variable star according the GCVS classification). In this case, the small changes in the lu ...
Measuring Stars
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
sachkov_2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... High – resolution, high signal-to-noise, high time-resolution Spectroscopy. New heights in asteroseismology: “Until recently the idea of using 8- to 10-m telescope to observe some of the brightest stars in the sky was anathema” (D.Kurtz, ...
... High – resolution, high signal-to-noise, high time-resolution Spectroscopy. New heights in asteroseismology: “Until recently the idea of using 8- to 10-m telescope to observe some of the brightest stars in the sky was anathema” (D.Kurtz, ...
PDF file - Memorie della SAIt
... a Z=5 × 10−5 low mass (M=1.5 M ) AGB stellar model. A full network including all the relevant isotopes up to the end point of the s-process path has been used. After a few weak thermal pulses, the convective region generated by the He burning engulfs protons from the overlying H-rich envelope into ...
... a Z=5 × 10−5 low mass (M=1.5 M ) AGB stellar model. A full network including all the relevant isotopes up to the end point of the s-process path has been used. After a few weak thermal pulses, the convective region generated by the He burning engulfs protons from the overlying H-rich envelope into ...
solutions 3
... A star like the Sun is essentially a box of hydrogen, held together by gravity. After 10 billion years or so, the core of the star contains enough helium and other fusion products that the fusion processes slow down and the star begins to cool and contract. Eventually, as the star cools, the effects ...
... A star like the Sun is essentially a box of hydrogen, held together by gravity. After 10 billion years or so, the core of the star contains enough helium and other fusion products that the fusion processes slow down and the star begins to cool and contract. Eventually, as the star cools, the effects ...
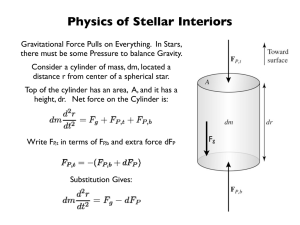
Lecture notes 11
... For very low mass stars, the central temperature will diminish to the point where no nuclear fusion occurs. For a star with Solar compositions this is 0.072 M⊙. For very high mass stars, (>90 M⊙), the radiation pressure can create thermal oscillations that produce variations in their luminosity on 8 ...
... For very low mass stars, the central temperature will diminish to the point where no nuclear fusion occurs. For a star with Solar compositions this is 0.072 M⊙. For very high mass stars, (>90 M⊙), the radiation pressure can create thermal oscillations that produce variations in their luminosity on 8 ...
GALAXY FORMATION AND CLUSTER FORMATION Richard B
... disk, violent instability occurs when Q < 1; limited growth of spiral density perturbations occurs for 1 < Q < ^2 (Larson 1984); and stability occurs for Q > ^ 2 . Numerical simulations of disks containing gas (e.g. Sellwood and Carlberg 1984) show that, while dissipation tends to reduce Q and make ...
... disk, violent instability occurs when Q < 1; limited growth of spiral density perturbations occurs for 1 < Q < ^2 (Larson 1984); and stability occurs for Q > ^ 2 . Numerical simulations of disks containing gas (e.g. Sellwood and Carlberg 1984) show that, while dissipation tends to reduce Q and make ...
project.generative.interactive.music
... features protruding from monstrous columns of cold gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula (also called M16). The columns protrude from the wall of a vast cloud of molecular hydrogen, like stalagmites rising above the floor of a cavern. Inside the gaseous towers, which are light-years long, the interstella ...
... features protruding from monstrous columns of cold gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula (also called M16). The columns protrude from the wall of a vast cloud of molecular hydrogen, like stalagmites rising above the floor of a cavern. Inside the gaseous towers, which are light-years long, the interstella ...
Explore the Galaxy - Museum of Science
... Black Hole- A region of sp ace w here m ass is so highly concentrated that the gravitational p u ll becom es incred ibly strong. Within a certain d istance from the black hole, called the event horizon, nothing, not even light, is fast enou gh to escap e the gravitational p u ll. Stellar black holes ...
... Black Hole- A region of sp ace w here m ass is so highly concentrated that the gravitational p u ll becom es incred ibly strong. Within a certain d istance from the black hole, called the event horizon, nothing, not even light, is fast enou gh to escap e the gravitational p u ll. Stellar black holes ...
8-12 февраля 2010 г., ИКИ РАН
... manifestations, observations and models which are well investigated. We will mark unclear and questionable details, as well as the points of obvious disagreement with the current wisdom. The last is probably most important for the further steps in theory and observations. ...
... manifestations, observations and models which are well investigated. We will mark unclear and questionable details, as well as the points of obvious disagreement with the current wisdom. The last is probably most important for the further steps in theory and observations. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.