Weighing Ultracompact Dwarf Galaxies in the Fornax Cluster
... are consistent with those expected for pure stellar populations. No dark matter contribution is needed. Thus, these UCDs seem to be the result of star-cluster formation processes within galaxies, rather than being compact dwarf galaxies formed in dark-matter halos. Dwarf galaxies have only been exte ...
... are consistent with those expected for pure stellar populations. No dark matter contribution is needed. Thus, these UCDs seem to be the result of star-cluster formation processes within galaxies, rather than being compact dwarf galaxies formed in dark-matter halos. Dwarf galaxies have only been exte ...
Star Formation in Isolated Disk Galaxies. I. Models and
... results). However, in these simulations, gravitational collapse and star formation are either not resolved, or are followed with empirical recipes tuned to reproduce the observations a priori. The mechanisms that produce the empirical star formation laws have remained uncertain. Recent cosmological ...
... results). However, in these simulations, gravitational collapse and star formation are either not resolved, or are followed with empirical recipes tuned to reproduce the observations a priori. The mechanisms that produce the empirical star formation laws have remained uncertain. Recent cosmological ...
A SUMMARY OF SELF
... 2. Experimental cross sections are often available for reactions related to explosive burning. What is the reason for this? 3. The possibilities to study p-, s- and r-process nuclei in the laboratory are very different. For which of the processes are most (least) experimental data available. What do ...
... 2. Experimental cross sections are often available for reactions related to explosive burning. What is the reason for this? 3. The possibilities to study p-, s- and r-process nuclei in the laboratory are very different. For which of the processes are most (least) experimental data available. What do ...
Celebrating the centennial of a celestial yardstick
... had abundant volcanic activity (and may have some ongoing activity today), which is involved in concentrating such elements. Yet the amounts of these elements, their distribution, and many other factors are completely unknown. The MESSENGER spacecraft is studying Mercury’s composition from orbit, bu ...
... had abundant volcanic activity (and may have some ongoing activity today), which is involved in concentrating such elements. Yet the amounts of these elements, their distribution, and many other factors are completely unknown. The MESSENGER spacecraft is studying Mercury’s composition from orbit, bu ...
Object A
... Luminosity: amount of light leaving a source. The amount and type of light leaving a source changes as an object heats up or cools down. The hotter an object is, the more luminous it is. The hotter an object is, the bluer it is. ...
... Luminosity: amount of light leaving a source. The amount and type of light leaving a source changes as an object heats up or cools down. The hotter an object is, the more luminous it is. The hotter an object is, the bluer it is. ...
Document
... Venn & Lambert (2008) have argued that this may not be the case. Peculiar stars such as post AGB stars and l Boo stars have iron abundances as low as [Fe/H] ~ –5. These are thought to be due to the separation of gas and dust beyond the stellar surface followed by an accretion of the dust-depleted g ...
... Venn & Lambert (2008) have argued that this may not be the case. Peculiar stars such as post AGB stars and l Boo stars have iron abundances as low as [Fe/H] ~ –5. These are thought to be due to the separation of gas and dust beyond the stellar surface followed by an accretion of the dust-depleted g ...
Chapter 30 Review
... 1. recording radio waves 2. observing RR Lyrae variables 3. measuring infrared radiation 4. observing hydrogen emission spectra ...
... 1. recording radio waves 2. observing RR Lyrae variables 3. measuring infrared radiation 4. observing hydrogen emission spectra ...
PPT
... • probes correlations with optical galaxy morphology, dynamical mass, IR flux, and variations with redshift ...
... • probes correlations with optical galaxy morphology, dynamical mass, IR flux, and variations with redshift ...
Document
... • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use spectroscopy! ...
... • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use spectroscopy! ...
Molecular cloud regulated star formation in galaxies
... halo. The haloes in turn form from the non-linear collapse of initially small density perturbations that were imprinted by quantum fluctuations before inflation. When the virial temperature of the halo is high enough, the gas can cool radiatively (Rees & Ostriker 1977; White & Rees 1978) and may bec ...
... halo. The haloes in turn form from the non-linear collapse of initially small density perturbations that were imprinted by quantum fluctuations before inflation. When the virial temperature of the halo is high enough, the gas can cool radiatively (Rees & Ostriker 1977; White & Rees 1978) and may bec ...
The Origin of Our Solar System
... • Proposes that the planets, including Earth, formed in a rotating disk of gas and dust that surrounded the sun as it, the sun, formed. Laplace’s nebular hypothesis included a disk but depended on rings of matter left behind by disk contraction. He did not take into account how gas and dust behave i ...
... • Proposes that the planets, including Earth, formed in a rotating disk of gas and dust that surrounded the sun as it, the sun, formed. Laplace’s nebular hypothesis included a disk but depended on rings of matter left behind by disk contraction. He did not take into account how gas and dust behave i ...
Contents
... PH4.5 – Application to Orbits in the Solar System and the Wider Universe. This section of the specification contains traditional kinematics and application of Newton’s Laws of Motion. Much the theory is covered in A level text books. The section on mutual orbits is an exception. The applications to ...
... PH4.5 – Application to Orbits in the Solar System and the Wider Universe. This section of the specification contains traditional kinematics and application of Newton’s Laws of Motion. Much the theory is covered in A level text books. The section on mutual orbits is an exception. The applications to ...
11 Solar Masses
... Original model due to Miyaji et al (1980). Studied many times since. A similar evolution may occur for accreting Ne-O white dwarfs (or very rapidly accreting CO-white dwarfs) in binary systems - an alternate outcome to Type Ia supernovae. This phenomena in a binary is generally referred to as “Accr ...
... Original model due to Miyaji et al (1980). Studied many times since. A similar evolution may occur for accreting Ne-O white dwarfs (or very rapidly accreting CO-white dwarfs) in binary systems - an alternate outcome to Type Ia supernovae. This phenomena in a binary is generally referred to as “Accr ...
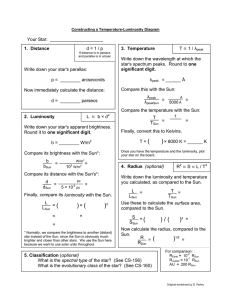
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... Winter Stars – The brightest and most spectacular stars in the sky belong to the winter. Betelgeuse, the ridiculously huge supergiant mentioned in lecture; Meissa, a rare superhot O star in Orion's belt; and dog star Sirius: the brightest of all stars are all winter stars. These stars are already vi ...
... Winter Stars – The brightest and most spectacular stars in the sky belong to the winter. Betelgeuse, the ridiculously huge supergiant mentioned in lecture; Meissa, a rare superhot O star in Orion's belt; and dog star Sirius: the brightest of all stars are all winter stars. These stars are already vi ...
The Galaxy Luminosity Function
... 2) M31 (MB = -20.3) is a 0.5L* galaxy, & the combined Local Group ~ 1 L*. 3) cD galaxies, which are 5 – 10 L*, do not fit into the Schechter function scheme. ...
... 2) M31 (MB = -20.3) is a 0.5L* galaxy, & the combined Local Group ~ 1 L*. 3) cD galaxies, which are 5 – 10 L*, do not fit into the Schechter function scheme. ...
Observational properties of stars
... steady. In some cases the peak of brightness may not even occur immediately after the core collapse. SN1987A had its peak brightness occur 80 days after the initial collapse! As the supernova cools, the outer ejected material will form into molecules and dust as they cool. This material will also b ...
... steady. In some cases the peak of brightness may not even occur immediately after the core collapse. SN1987A had its peak brightness occur 80 days after the initial collapse! As the supernova cools, the outer ejected material will form into molecules and dust as they cool. This material will also b ...
Chapter 13 32)Which method could detect a planet in an orbit that is
... 29)Which of these group of particles has the greatest mass? a) 4 protons. A helium nucleus (4.003 amu) is composed of two protons and two neutrons, but is created from the fusion of 4 protons (4.029 amu). When a helium nucleus is created energy is release which comes from the conversion of mass, so ...
... 29)Which of these group of particles has the greatest mass? a) 4 protons. A helium nucleus (4.003 amu) is composed of two protons and two neutrons, but is created from the fusion of 4 protons (4.029 amu). When a helium nucleus is created energy is release which comes from the conversion of mass, so ...
ISOLATED, MASSIVE SUPERGIANTS NEAR THE GALACTIC
... star formation can be accounted for by the three massive star clusters mentioned above, but this implies that the sites of formation for the other half of the young stars in the central 300 pc have not yet been identified. One possibility is that star clusters less massive than the Arches and Quintu ...
... star formation can be accounted for by the three massive star clusters mentioned above, but this implies that the sites of formation for the other half of the young stars in the central 300 pc have not yet been identified. One possibility is that star clusters less massive than the Arches and Quintu ...
poster
... Most models of jet launching rely on a magnetic field in either the central source, the accretion disk or both. However, the well-studied nearby young Herbig Ae star HD 163296 has a measured weak stellar magnetic field (main-sequence A stars do not have magnetic fields at all), and even indications ...
... Most models of jet launching rely on a magnetic field in either the central source, the accretion disk or both. However, the well-studied nearby young Herbig Ae star HD 163296 has a measured weak stellar magnetic field (main-sequence A stars do not have magnetic fields at all), and even indications ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.