Chandra Sees the Atmosphere of a Neutron Star - Chandra X
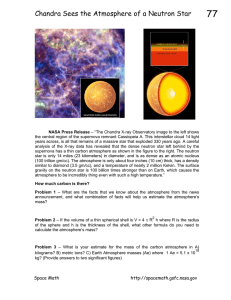
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
Earth and Stars
... certainly do better in the matter of accuracy. Yet, in spite of all these flaws, it worked fine: around 250 BC, Earth had at last a size. ...
... certainly do better in the matter of accuracy. Yet, in spite of all these flaws, it worked fine: around 250 BC, Earth had at last a size. ...
galaxies and stars
... They contain only one star but hundreds of planets. They may contain a few hundred stars in a space slightly larger than the solar system. They may contain billions of stars in a space much larger than our solar system. ...
... They contain only one star but hundreds of planets. They may contain a few hundred stars in a space slightly larger than the solar system. They may contain billions of stars in a space much larger than our solar system. ...
Section I - General Information Proposal Title: Mass and Radius of a
... these measurements we will be able to infer the mass of the pulsar with 4% precision. This, combined with the NICER measurement, will yield its radius to 10% precision. Both mass and radius are of fundamental importance in understanding the structure of neutron stars and the behavior of nuclear matt ...
... these measurements we will be able to infer the mass of the pulsar with 4% precision. This, combined with the NICER measurement, will yield its radius to 10% precision. Both mass and radius are of fundamental importance in understanding the structure of neutron stars and the behavior of nuclear matt ...
18 O
... chemical-dynamical model of Lee, Bergin, and Evans 2004 – cloud mass of 1.6 M◉ – approximate pre-collapse evolution as a series of Bonner-Ebert solutions with increasing condensation on a timescale of 1 Myr – use Shu 1977 “inside-out” collapse model – examine evolution of chemistry in the context of ...
... chemical-dynamical model of Lee, Bergin, and Evans 2004 – cloud mass of 1.6 M◉ – approximate pre-collapse evolution as a series of Bonner-Ebert solutions with increasing condensation on a timescale of 1 Myr – use Shu 1977 “inside-out” collapse model – examine evolution of chemistry in the context of ...
Lecture 18 Gamma-Ray Bursts
... and HETE-2 and coordinated searches for counterparts were carried out. The bursts were GRB 050509b (z = 0.2248, elliptical galaxy), 050709 (z = 0.161) and 050724 (z = 0.258) The bursts were either on the outskirts of galaxies or in old galaxies with low star formation rate There was no accompanying ...
... and HETE-2 and coordinated searches for counterparts were carried out. The bursts were GRB 050509b (z = 0.2248, elliptical galaxy), 050709 (z = 0.161) and 050724 (z = 0.258) The bursts were either on the outskirts of galaxies or in old galaxies with low star formation rate There was no accompanying ...
The coronal temperatures of low-mass main
... the relevant parameter, then this would indicate that temperature scales somehow with how far a star is below the saturation threshold in rotation, given that saturation happens at a single mass-independent value of RX . It would further imply that all saturated stars have similar coronal temperatur ...
... the relevant parameter, then this would indicate that temperature scales somehow with how far a star is below the saturation threshold in rotation, given that saturation happens at a single mass-independent value of RX . It would further imply that all saturated stars have similar coronal temperatur ...
Here
... protons) combine to form 1 helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). • The details are a bit complex: In the Sun, 6 hydrogen nuclei are involved in a sequence that produces two hydrogen nuclei and one helium nucleus. This is the proton-proton chain. In more massive stars, a carbon ...
... protons) combine to form 1 helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). • The details are a bit complex: In the Sun, 6 hydrogen nuclei are involved in a sequence that produces two hydrogen nuclei and one helium nucleus. This is the proton-proton chain. In more massive stars, a carbon ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... Supergiant Bright-Giant Giant Sub-Giant Main Sequence Star (dwarf) ...
... Supergiant Bright-Giant Giant Sub-Giant Main Sequence Star (dwarf) ...
Recycling strange stars to millisecond periods
... absorption of neutrons by strange matter, and their fusion with strange matter in a strong-interaction process n −→ 2d + u, followed by the weak-interaction process u + d −→ s + u. These reactions lead to an additional heat release (deconfinement heating) at the crust-strange matter interface, of so ...
... absorption of neutrons by strange matter, and their fusion with strange matter in a strong-interaction process n −→ 2d + u, followed by the weak-interaction process u + d −→ s + u. These reactions lead to an additional heat release (deconfinement heating) at the crust-strange matter interface, of so ...
Studying Variable stars using Small Telescopes Observational
... In addition to the short-term variation due to rotational modulation of stellar brightness in rotating variables, it is believed that there should also exist a systematic long-term variations. These long-term variations or Stellar Activity Cycles are very similar to the solar 11-year sunspot cycle o ...
... In addition to the short-term variation due to rotational modulation of stellar brightness in rotating variables, it is believed that there should also exist a systematic long-term variations. These long-term variations or Stellar Activity Cycles are very similar to the solar 11-year sunspot cycle o ...
P1a_Revision_lesson
... as a fuel. During its main sequence a star will release energy by combining hydrogen and helium nuclei (light elements) into _________ elements. Any element in space that is heavier than helium is thought to have been made in a star. Words – heavier, balanced, hydrogen, nuclear, temperatures ...
... as a fuel. During its main sequence a star will release energy by combining hydrogen and helium nuclei (light elements) into _________ elements. Any element in space that is heavier than helium is thought to have been made in a star. Words – heavier, balanced, hydrogen, nuclear, temperatures ...
How Bright is that Star?
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
Lecture9
... mass and the collapsed core will have mass larger than the neutron star maximum mass limit ~ 3M☉ So, if the remnant collapsed mass is larger than ~3M☉, the core keeps collapsing to singularity, and hence becomes a black hole. Note: Though nothing can come out of a black hole itself, the gas around t ...
... mass and the collapsed core will have mass larger than the neutron star maximum mass limit ~ 3M☉ So, if the remnant collapsed mass is larger than ~3M☉, the core keeps collapsing to singularity, and hence becomes a black hole. Note: Though nothing can come out of a black hole itself, the gas around t ...
Searching for Baby Planets in a Star`s Dusty Rings
... occur at different distances from the star because of large radial temperature gradients in the disk. Alternatively, they could arise from the concentration of millimeter-sized particles in regions of gas where the turbulence is low or the pressure is high. The work by Isella et al. [1] makes a cons ...
... occur at different distances from the star because of large radial temperature gradients in the disk. Alternatively, they could arise from the concentration of millimeter-sized particles in regions of gas where the turbulence is low or the pressure is high. The work by Isella et al. [1] makes a cons ...
GALEX UV Light-curves of M-Dwarf Flare Stars: THE FLARING UV
... form of electrons that gyrate down the field lines towards the star’s surface • When the electrons encounter the denser material in the stellar chromosphere they release impulsive energy (in the form of hard X-rays) and the collisions ionize and heat the chromospheric gas ...
... form of electrons that gyrate down the field lines towards the star’s surface • When the electrons encounter the denser material in the stellar chromosphere they release impulsive energy (in the form of hard X-rays) and the collisions ionize and heat the chromospheric gas ...
Dynamics of nuclear burning during type-I X-ray bursts 1. 2. 3.
... •Conduction: too slow (100 cm/s) •Convection: convective speed 5x106cm/s 1) Front width = scaleheight; ...
... •Conduction: too slow (100 cm/s) •Convection: convective speed 5x106cm/s 1) Front width = scaleheight; ...
Lecture 11
... – Observations of these pulses were the first evidence for neutron stars • What can happen to a neutron star in a close binary system? – The accretion disk around a neutron star gets hot enough to produce X-rays, making the system an X-ray binary – Sudden fusion events periodically occur on a th ...
... – Observations of these pulses were the first evidence for neutron stars • What can happen to a neutron star in a close binary system? – The accretion disk around a neutron star gets hot enough to produce X-rays, making the system an X-ray binary – Sudden fusion events periodically occur on a th ...
Abs-Apar Mag
... – Brightest stars = 1st class, then 2nd, 3rd… – 6th magnitude are faintest stars seen at night – Result: lower number = brighter “There is no other rule for classing the stars but the estimation of the observer; and hence it is that some astronomers reckon those stars of the first magnitude which ot ...
... – Brightest stars = 1st class, then 2nd, 3rd… – 6th magnitude are faintest stars seen at night – Result: lower number = brighter “There is no other rule for classing the stars but the estimation of the observer; and hence it is that some astronomers reckon those stars of the first magnitude which ot ...
Modified Newtonian Mechanics
... with the oldest stars pointing to the very beginning of the formation of stars. This age does not correspond with the destruction of the number of stars required in order to produce such a large amount of non-luminous matter. If the universe had a great deal of hydrogen in it there would be other pr ...
... with the oldest stars pointing to the very beginning of the formation of stars. This age does not correspond with the destruction of the number of stars required in order to produce such a large amount of non-luminous matter. If the universe had a great deal of hydrogen in it there would be other pr ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.