Highligh in Physics 2005
... The paradigm of accretion has had a major impact on a variety of phenomena in astrophysics; in particular, it has often been applied to the context of proto-stellar disks. We have studied the role of the disk self-gravity on the properties of accretion disks and found that this role may help explain ...
... The paradigm of accretion has had a major impact on a variety of phenomena in astrophysics; in particular, it has often been applied to the context of proto-stellar disks. We have studied the role of the disk self-gravity on the properties of accretion disks and found that this role may help explain ...
Chapter 27 Quasars, Active Galaxies, and Gamma
... If we could see the last few seconds of the collapse of a star to form a black hole, we would see the star grow steadily redder. Why? 1. The star moves away from us at an increasing speed. 2. The star grows steadily cooler. 3. The star's gravitational redshift increases. 4. The star becomes obscure ...
... If we could see the last few seconds of the collapse of a star to form a black hole, we would see the star grow steadily redder. Why? 1. The star moves away from us at an increasing speed. 2. The star grows steadily cooler. 3. The star's gravitational redshift increases. 4. The star becomes obscure ...
Cannot reproduce observed Log N – Log S
... The closest millisecond PSR. MNS=1.76+/-0.2 solar. Hopefully, this value will not be reconsidered. 2. The case of PSR J0751+1807. Initially, it was announced that it has a mass ~2.1 solar [astro-ph/0508050]. However, then in 2007 at a conference the authors announced that the result was incorrect. A ...
... The closest millisecond PSR. MNS=1.76+/-0.2 solar. Hopefully, this value will not be reconsidered. 2. The case of PSR J0751+1807. Initially, it was announced that it has a mass ~2.1 solar [astro-ph/0508050]. However, then in 2007 at a conference the authors announced that the result was incorrect. A ...
WFIRST-2.4: What Every Astronomer Should Know
... would be able to survey hundreds of nearby stars, enabling the characterization of dozens of known cool Jupiter-mass companions, the discovery and characterization of a similar number of cool Jupiter and Neptune companions, and the detection and characterization of debris disks in systems containin ...
... would be able to survey hundreds of nearby stars, enabling the characterization of dozens of known cool Jupiter-mass companions, the discovery and characterization of a similar number of cool Jupiter and Neptune companions, and the detection and characterization of debris disks in systems containin ...
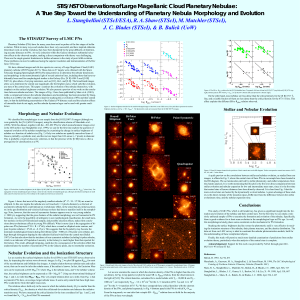
STIS/HST Observations of Large Magellanic Cloud Planetary
... J. C. Blades (STScI), & B. Balick (UoW) The STIS/HST Survey of LMC PNs Planetary Nebulae (PNs) have for many years been used as probes of the late stages of stellar evolution. While in many ways such studies have been very successful, and have inspired elaborate theoretical work on stellar evolution ...
... J. C. Blades (STScI), & B. Balick (UoW) The STIS/HST Survey of LMC PNs Planetary Nebulae (PNs) have for many years been used as probes of the late stages of stellar evolution. While in many ways such studies have been very successful, and have inspired elaborate theoretical work on stellar evolution ...
Galaxies - WordPress.com
... It provides us with many of the images we have of space. It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our ...
... It provides us with many of the images we have of space. It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our ...
Disk Galaxies and problem 3
... • Tidal origin of spiral arms. Spiral arms are induced by tidal perturbation of a nearby galaxy. This is observationally seen in grand-design spirals, such as M51. The tidal arms are also easily produced in numerical simulations, see Fig. 7. • Bar spiral arms. A rotating bar at the centre of galaxie ...
... • Tidal origin of spiral arms. Spiral arms are induced by tidal perturbation of a nearby galaxy. This is observationally seen in grand-design spirals, such as M51. The tidal arms are also easily produced in numerical simulations, see Fig. 7. • Bar spiral arms. A rotating bar at the centre of galaxie ...
The Luminosity-Metallicity Relations for Star
... Abstract We have carried out an Ha and R-band imaging survey of a volume-limited sample of 340 spiral and irregular galaxies within a distance of 11 Mpc. Our goal is to fully characterize the star formation properties of complete samples of galaxies in the local universe. In particular, we are using ...
... Abstract We have carried out an Ha and R-band imaging survey of a volume-limited sample of 340 spiral and irregular galaxies within a distance of 11 Mpc. Our goal is to fully characterize the star formation properties of complete samples of galaxies in the local universe. In particular, we are using ...
File - the ridgeway ASTRONOMY page
... measurement of the spectrum of light produced when matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation. In astronomy, spectroscopy is a very useful tool because telescopes can easily ...
... measurement of the spectrum of light produced when matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation. In astronomy, spectroscopy is a very useful tool because telescopes can easily ...
Earth Motions and the Heavens
... South Pole This is another picture of the South Pole, but shorter. Two nearby galaxies are visible in this image. The large fuzzy one, just above the roof of the Commons Building, is the Large Magellanic Cloud, and the smaller fuzzy patch near the top of the image is the Small Magellanic Cloud. The ...
... South Pole This is another picture of the South Pole, but shorter. Two nearby galaxies are visible in this image. The large fuzzy one, just above the roof of the Commons Building, is the Large Magellanic Cloud, and the smaller fuzzy patch near the top of the image is the Small Magellanic Cloud. The ...
Dark-matter halo mergers as a fertile environment for low
... Our approach is divided in different steps. We first run a DM-only low-resolution simulation to study the evolution and the merging history of the haloes. A single box of 1.0 comoving Mpc with a top grid resolution of 1283 cells is employed. The parameters for creating the initial conditions and the ...
... Our approach is divided in different steps. We first run a DM-only low-resolution simulation to study the evolution and the merging history of the haloes. A single box of 1.0 comoving Mpc with a top grid resolution of 1283 cells is employed. The parameters for creating the initial conditions and the ...
Bonnell_2015_MNRAS_Early - St Andrews Research Repository
... a rate substantially slower than the freefall rate in the dense gas. This decoupling is due to the weakening of, and expulsion of gas from, the deepest parts of the clouds’ potential wells where most of the star formation occurs in the control simulations. This results in large fractions of the stel ...
... a rate substantially slower than the freefall rate in the dense gas. This decoupling is due to the weakening of, and expulsion of gas from, the deepest parts of the clouds’ potential wells where most of the star formation occurs in the control simulations. This results in large fractions of the stel ...
Gas fraction and star formation efficiency at z< 1.0
... to drive the gas quickly to galaxy centers and to trigger starbursts. Locally Ultra-Luminous Infra-Red Galaxies (ULIRGs), with LFIR > 1012 L⊙ , are in the majority starbursts caused by galaxy major mergers (e.g. Sanders & Mirabel 1996, Veilleux et al. 2009). The overall gas fraction in those systems ...
... to drive the gas quickly to galaxy centers and to trigger starbursts. Locally Ultra-Luminous Infra-Red Galaxies (ULIRGs), with LFIR > 1012 L⊙ , are in the majority starbursts caused by galaxy major mergers (e.g. Sanders & Mirabel 1996, Veilleux et al. 2009). The overall gas fraction in those systems ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Why does the North Star appear to be fixed in the sky while all other object move? What would be the view of the night sky from the North pole? Why can't we see the same constellations in the evening sky throughout the year? Why haven’t constellation patters changed since they have been established ...
... Why does the North Star appear to be fixed in the sky while all other object move? What would be the view of the night sky from the North pole? Why can't we see the same constellations in the evening sky throughout the year? Why haven’t constellation patters changed since they have been established ...
Do high-velocity clouds trace the dark matter subhalo population?⋆
... subhalos. Since intergalactic gas is accreted by massive galaxies, observable e.g. as high-velocity clouds (HVCs) around the Milky Way, with extremely low metallicities, these can represent the baryonic content of primordial dark matter (DM) subhalos. Another possibility of their origin is that they ...
... subhalos. Since intergalactic gas is accreted by massive galaxies, observable e.g. as high-velocity clouds (HVCs) around the Milky Way, with extremely low metallicities, these can represent the baryonic content of primordial dark matter (DM) subhalos. Another possibility of their origin is that they ...
Rearrangement of gas in disc galaxies
... that amply change their host environments. They are present in a significant number of galaxies at all redshifts. In this thesis, we aim toward a better understanding of the physical processes that allow for the formation and maintenance of these two phenomena. We focus on the study of the physical ...
... that amply change their host environments. They are present in a significant number of galaxies at all redshifts. In this thesis, we aim toward a better understanding of the physical processes that allow for the formation and maintenance of these two phenomena. We focus on the study of the physical ...
Lectures 19-20 The Milky Way Galaxy
... Historical Models of the Milky Way Galaxy Jacobus Kapteyn (1851-1922) used star counting to confirm the Herschel model, but with much-improved methods. Now called the Kapteyn Universe. Galaxy consists of a flattened Spheroidal system with a decreasing stellar density with increasing distance from t ...
... Historical Models of the Milky Way Galaxy Jacobus Kapteyn (1851-1922) used star counting to confirm the Herschel model, but with much-improved methods. Now called the Kapteyn Universe. Galaxy consists of a flattened Spheroidal system with a decreasing stellar density with increasing distance from t ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.