Option_E_Astrophysics_
... Astronomical distances The SI unit for length, the meter, is a very small unit to measure astronomical distances. There units usually used is ...
... Astronomical distances The SI unit for length, the meter, is a very small unit to measure astronomical distances. There units usually used is ...
Lectures 19-20 The Milky Way Galaxy
... Historical Models of the Milky Way Galaxy Jacobus Kapteyn (1851-1922) used star counting to confirm the Herschel model, but with much-improved methods. Now called the Kapteyn Universe. Galaxy consists of a flattened Spheroidal system with a decreasing stellar density with increasing distance from t ...
... Historical Models of the Milky Way Galaxy Jacobus Kapteyn (1851-1922) used star counting to confirm the Herschel model, but with much-improved methods. Now called the Kapteyn Universe. Galaxy consists of a flattened Spheroidal system with a decreasing stellar density with increasing distance from t ...
FutureEnvironments
... stars typically suffer more severe effects than worlds farther away. Many starships and other pieces of technology incorporate radioactive parts and fuel cells that can flood an area with harmful radiation when ruptured or exposed. Ancient alien civilizations might leave behind powerful artifacts th ...
... stars typically suffer more severe effects than worlds farther away. Many starships and other pieces of technology incorporate radioactive parts and fuel cells that can flood an area with harmful radiation when ruptured or exposed. Ancient alien civilizations might leave behind powerful artifacts th ...
幻灯片 1
... masses: ~1.5 - 2.5 Msun • spectral type: A5 - F2. • found on the intersection of the classical instability strip and the main sequence in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram • excitation mechanism: κ mechanism ...
... masses: ~1.5 - 2.5 Msun • spectral type: A5 - F2. • found on the intersection of the classical instability strip and the main sequence in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram • excitation mechanism: κ mechanism ...
Fitting X-ray Spectra with Imperfect Models
... How complicated can it get? Star formation is pretty messy. ...
... How complicated can it get? Star formation is pretty messy. ...
Precession of Earth
... pattern rather than pointing at a single spot or staying mostly still. If you draw an imaginary line of the earth's axis and continue it up to the sky, it will make a similar path. This type of axis rotation is called precession. In the case of the earth, precession is caused by the gravitational pu ...
... pattern rather than pointing at a single spot or staying mostly still. If you draw an imaginary line of the earth's axis and continue it up to the sky, it will make a similar path. This type of axis rotation is called precession. In the case of the earth, precession is caused by the gravitational pu ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... Students know the Sun is many thousands of times closer to Earth than any other star, and billions of times closer than the far end of the Milky Way Galaxy. W/L “Space is big - really big - you just won't believe how vastly, hugely mind-bogglingly big it is. You may think it's a long way down the ro ...
... Students know the Sun is many thousands of times closer to Earth than any other star, and billions of times closer than the far end of the Milky Way Galaxy. W/L “Space is big - really big - you just won't believe how vastly, hugely mind-bogglingly big it is. You may think it's a long way down the ro ...
Think about the universe
... nebula. The name planetary nebula is misleading because it is not related to planets. But it does have the cloud-like nature of other nebulae. The name came about because astronomers using very early telescopes thought that the clouds resembled the planets Uranus and Neptune. ...
... nebula. The name planetary nebula is misleading because it is not related to planets. But it does have the cloud-like nature of other nebulae. The name came about because astronomers using very early telescopes thought that the clouds resembled the planets Uranus and Neptune. ...
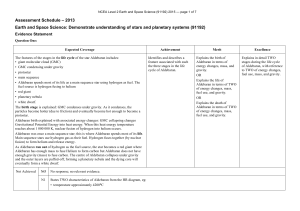
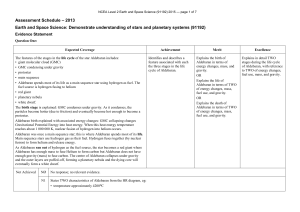
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2013
... Gravitational Potential Energy into heat energy. When this heat energy temperature reaches about 1 000 000 K, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium occurs. Aldebaran was once a main sequence star; this is where Aldebaran spends most of its life. Main sequence stars use hydrogen gas as their fuel. H ...
... Gravitational Potential Energy into heat energy. When this heat energy temperature reaches about 1 000 000 K, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium occurs. Aldebaran was once a main sequence star; this is where Aldebaran spends most of its life. Main sequence stars use hydrogen gas as their fuel. H ...
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192)
... Gravitational Potential Energy into heat energy. When this heat energy temperature reaches about 1 000 000 K, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium occurs. Aldebaran was once a main sequence star; this is where Aldebaran spends most of its life. Main sequence stars use hydrogen gas as their fuel. H ...
... Gravitational Potential Energy into heat energy. When this heat energy temperature reaches about 1 000 000 K, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium occurs. Aldebaran was once a main sequence star; this is where Aldebaran spends most of its life. Main sequence stars use hydrogen gas as their fuel. H ...
Survey of Astrophysics A110 The Milky Way Galaxy
... where new stars will form. The rotation of the galaxy, which can be observed by studying stellar proper motions and Doppler shifts, then orders these concentrations of stars into a spiral-like pattern. – 2. The density wave theory of spiral structure predicts that the rotation and gravity of the mas ...
... where new stars will form. The rotation of the galaxy, which can be observed by studying stellar proper motions and Doppler shifts, then orders these concentrations of stars into a spiral-like pattern. – 2. The density wave theory of spiral structure predicts that the rotation and gravity of the mas ...
January 2015 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... tidal radius has a radius of 33 light years. However, about one-third of confirmed member stars have been observed to be well outside this boundary in the cluster's extended halo. These stars are probably in the process of escaping from the cluster’s gravitational influence. The Seven Sisters are ab ...
... tidal radius has a radius of 33 light years. However, about one-third of confirmed member stars have been observed to be well outside this boundary in the cluster's extended halo. These stars are probably in the process of escaping from the cluster’s gravitational influence. The Seven Sisters are ab ...
Cosmology with GMRT
... – Apply to a single object (optical results are averages over large redshift range) – Not subject to the same systematics – Currently probe a complementary redshift range ...
... – Apply to a single object (optical results are averages over large redshift range) – Not subject to the same systematics – Currently probe a complementary redshift range ...
Lecture 17
... detect stellar-mass lenses in the Galactic halo using stars in the Large Magellanic cloud (LMC) which is 50 kpc away, you can show that the angular separation of the lensed objects would be sub-milliarcseconds. So how would we try to use this technique to detect a large population of dark massive po ...
... detect stellar-mass lenses in the Galactic halo using stars in the Large Magellanic cloud (LMC) which is 50 kpc away, you can show that the angular separation of the lensed objects would be sub-milliarcseconds. So how would we try to use this technique to detect a large population of dark massive po ...
Examining the M67 Classification as an Open Cluster
... in the galactic field the total internal energy of a cluster should rise, ultimately leading to a complete breakup of the cluster. It turned out that the characteristic time for this process of destruction of dense stellar clusters is at most 1010 yr. Spitzer [16,17] has calculated the increase of e ...
... in the galactic field the total internal energy of a cluster should rise, ultimately leading to a complete breakup of the cluster. It turned out that the characteristic time for this process of destruction of dense stellar clusters is at most 1010 yr. Spitzer [16,17] has calculated the increase of e ...
Constellations
... The constellations are totally imaginary things that poets, farmers, sailors, and astronomers have made up over the past 6,000 years The real purpose for the constellations is to help us tell which stars are which. On a really dark night, you can see about 1000 to 1500 stars. The constellations help ...
... The constellations are totally imaginary things that poets, farmers, sailors, and astronomers have made up over the past 6,000 years The real purpose for the constellations is to help us tell which stars are which. On a really dark night, you can see about 1000 to 1500 stars. The constellations help ...
L69 CONVERSION OF NEUTRON STARS TO
... There is now compelling evidence to suggest that a substantial fraction of all gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) occur at cosmological distances (with a redshift z ∼ 1–3 ). In particular, the measured redshifts of z = 3.42 for GRB 971214 (Kulkarni et al. 1998) and z ∼ 1.6 for GRB 990123 (Kulkarni et al. 1999) ...
... There is now compelling evidence to suggest that a substantial fraction of all gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) occur at cosmological distances (with a redshift z ∼ 1–3 ). In particular, the measured redshifts of z = 3.42 for GRB 971214 (Kulkarni et al. 1998) and z ∼ 1.6 for GRB 990123 (Kulkarni et al. 1999) ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to various
... • This compares the rotation of the galaxy to the brightness (the rotation gives an indication of mass which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and so ...
... • This compares the rotation of the galaxy to the brightness (the rotation gives an indication of mass which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and so ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.