Chapter 14 – Chemical Analysis
... • It is an ad hoc free parameter in the analysis, with values typically between 0.5 and 5 km/sec • Lower luminosity stars generally have lower values of microturbulence. • The microturbulence is determined as the value of x that makes the abundance independent of line ...
... • It is an ad hoc free parameter in the analysis, with values typically between 0.5 and 5 km/sec • Lower luminosity stars generally have lower values of microturbulence. • The microturbulence is determined as the value of x that makes the abundance independent of line ...
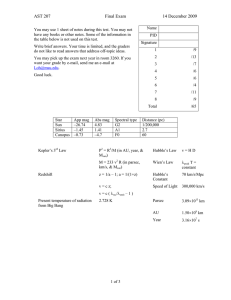
AST 207 Final Exam 14 December 2009
... c. (1 pts.) What will the sun become when it completely exhausts its fuel? (1 pt.) How big will it be? (1 pt.) What will prevent gravity from making it collapse? d. (2 pts.) The sun is losing more mass than can be accounted with the loss of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Explain how that is possi ...
... c. (1 pts.) What will the sun become when it completely exhausts its fuel? (1 pt.) How big will it be? (1 pt.) What will prevent gravity from making it collapse? d. (2 pts.) The sun is losing more mass than can be accounted with the loss of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Explain how that is possi ...
Neon and oxygen in low activity stars: towards a coronal unification
... upper limit of Ne/O = 0.18 ± 0.04 for active regions (Schmelz et al. 2005) and an analysis of transition region lines observed by the SOHO satellite suggested Ne/O = 0.17 ± 0.05 for the quiet Sun (Young 2005), both confirming the “classical” solar Ne/O ratio. Although sometimes higher Ne/O values we ...
... upper limit of Ne/O = 0.18 ± 0.04 for active regions (Schmelz et al. 2005) and an analysis of transition region lines observed by the SOHO satellite suggested Ne/O = 0.17 ± 0.05 for the quiet Sun (Young 2005), both confirming the “classical” solar Ne/O ratio. Although sometimes higher Ne/O values we ...
On Sunspot and Starspot Lifetimes - Patrick M. Hartigan
... Sun. The unit of area Micro Solar Hemisphere (MSH) is 5.8 , where 1 ≈ 725 km on the Sun. Hence, the rate of area shrinkage of the spot, W = 3.04 × 1013 m2 day−1 is the quantity encapsulating the physics that determines the lifetime of the spot and is of direct interest to us in the present work. Man ...
... Sun. The unit of area Micro Solar Hemisphere (MSH) is 5.8 , where 1 ≈ 725 km on the Sun. Hence, the rate of area shrinkage of the spot, W = 3.04 × 1013 m2 day−1 is the quantity encapsulating the physics that determines the lifetime of the spot and is of direct interest to us in the present work. Man ...
The two components of the evolved massive binary LZ Cephei
... evolution of massive stars. Methods. We analyzed a set of high-resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio optical spectra obtained over the orbital period of the system to perform a spectroscopic disentangling and derive an orbital solution. We subsequently determine the stellar properties of each compo ...
... evolution of massive stars. Methods. We analyzed a set of high-resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio optical spectra obtained over the orbital period of the system to perform a spectroscopic disentangling and derive an orbital solution. We subsequently determine the stellar properties of each compo ...
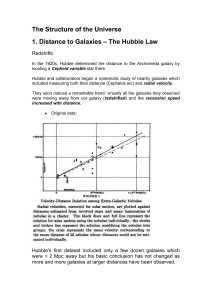
PH607 – Galaxies
... It suggests that there might be an upper ceiling to how large a galaxy can grow. Perhaps when a galaxy gets to be very large, its gravity is so strong that it rips up smaller galaxies that pass nearby before they can join it. Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many ...
... It suggests that there might be an upper ceiling to how large a galaxy can grow. Perhaps when a galaxy gets to be very large, its gravity is so strong that it rips up smaller galaxies that pass nearby before they can join it. Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many ...
Gas giants in hot water: inhibiting giant planet
... In Section 2, I estimate the temperature of embedded star clusters, and in Section 3 I estimate their protoplanetary disc temperatures. I then compare the relative importance of cluster irradiation and (1) host star irradiation in passive discs, and (2) accretion power in active discs. Generically, ...
... In Section 2, I estimate the temperature of embedded star clusters, and in Section 3 I estimate their protoplanetary disc temperatures. I then compare the relative importance of cluster irradiation and (1) host star irradiation in passive discs, and (2) accretion power in active discs. Generically, ...
Exploring the Universe
... – Hottest stars are blue, coolest are red – Hertzspurg-Russel diagram classifies stars • 90° of stars are called the main sequence • Other stars include red giants, supergiants, and dwarfs ...
... – Hottest stars are blue, coolest are red – Hertzspurg-Russel diagram classifies stars • 90° of stars are called the main sequence • Other stars include red giants, supergiants, and dwarfs ...
P7 Further Physics
... Astronomers often use the “parsec” to describe galactic distances. A parsec is roughly 3¼ light years. Angles involved in parallax measurements are often very small and are measured in seconds of an arc (arcseconds). A second of an arc is 1/60th of a minute of an arc, which is 1/60th of a degree. In ...
... Astronomers often use the “parsec” to describe galactic distances. A parsec is roughly 3¼ light years. Angles involved in parallax measurements are often very small and are measured in seconds of an arc (arcseconds). A second of an arc is 1/60th of a minute of an arc, which is 1/60th of a degree. In ...
DTU 8e Chap 17 Quasars and Other Active Galaxies
... speed of 5% of the speed of light. According to the Hubble law, Cygnus A is therefore 635 million light-years from Earth. Because Cygnus A is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, this remote galaxy’s energy output must be enormous. (b) An X-ray image of Cygnus A taken by the Chandra X-ray ...
... speed of 5% of the speed of light. According to the Hubble law, Cygnus A is therefore 635 million light-years from Earth. Because Cygnus A is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, this remote galaxy’s energy output must be enormous. (b) An X-ray image of Cygnus A taken by the Chandra X-ray ...
Video Lesson Information Astronomy: Observations & Theories Astronomy 1
... constellations, and brought the aspects of the sky into their buildings and structures, such as those of Chaco Canyon in the southwestern United States. Lesson 3 - Celestial Cycles This video lesson explains the motion of Earth around the sun and its yearly cycle. Astronomers explain the unique orbi ...
... constellations, and brought the aspects of the sky into their buildings and structures, such as those of Chaco Canyon in the southwestern United States. Lesson 3 - Celestial Cycles This video lesson explains the motion of Earth around the sun and its yearly cycle. Astronomers explain the unique orbi ...
Metallicity distribution for planet
... relation: occurrence of gas giant planets around FGK-type dwarfs is very sensitive to metallicity of host star. Santos et al. (2001) and Ghezzi et al. (2010) showed that there is planet-metallicity relation which means that gas giant planets host stars (FGK-type dwarfs) tend to be more metal-rich co ...
... relation: occurrence of gas giant planets around FGK-type dwarfs is very sensitive to metallicity of host star. Santos et al. (2001) and Ghezzi et al. (2010) showed that there is planet-metallicity relation which means that gas giant planets host stars (FGK-type dwarfs) tend to be more metal-rich co ...
Letter to the Editor - Max-Planck
... emission. In Cygnus X-1, strong reflection features indicate coronal emission in the X-ray band, but the jet emission may emerge in the gamma-ray band. The absence of reflection features in the spectra of the ultraluminous compact X-ray sources in nearby galaxies suggests that they are dominated by ...
... emission. In Cygnus X-1, strong reflection features indicate coronal emission in the X-ray band, but the jet emission may emerge in the gamma-ray band. The absence of reflection features in the spectra of the ultraluminous compact X-ray sources in nearby galaxies suggests that they are dominated by ...
No Slide Title
... What type of star has the mass of our Sun and the radius of the Earth but it doesn’t emit enough light or other radiation to be easily detected? ...
... What type of star has the mass of our Sun and the radius of the Earth but it doesn’t emit enough light or other radiation to be easily detected? ...
FIRST STELLAR ABUNDANCES IN THE DWARF IRREGULAR
... the star formation histories (SFH) of the galaxy over the last 15 Gyr. The analysis of bright nebular emission lines of H II regions has been the most frequent approach to modeling chemical evolution of more distant galaxies to date (Matteucci & Tosi 1985). So far, only a very limited number of elem ...
... the star formation histories (SFH) of the galaxy over the last 15 Gyr. The analysis of bright nebular emission lines of H II regions has been the most frequent approach to modeling chemical evolution of more distant galaxies to date (Matteucci & Tosi 1985). So far, only a very limited number of elem ...
Star Classification and its Connection to Exoplanets.
... the pie, so the viewer can see the result: G classified (sun-like) stars have the majority of the exoplanets, at 38%. The second pie chart uses data from the percentage of stars that have planets, so at around 6.6% of a total of around 18%, G stars make up about 37%, again the dominant planet host. ...
... the pie, so the viewer can see the result: G classified (sun-like) stars have the majority of the exoplanets, at 38%. The second pie chart uses data from the percentage of stars that have planets, so at around 6.6% of a total of around 18%, G stars make up about 37%, again the dominant planet host. ...
Inner Solar System Material Discovered in the Oort Cloud
... We have observed C/2014 S3 (PANSTARRS), a recently discovered object on a cometary orbit coming from the Oort cloud that is physically similar to an inner main belt rocky S-‐type asteroid. ...
... We have observed C/2014 S3 (PANSTARRS), a recently discovered object on a cometary orbit coming from the Oort cloud that is physically similar to an inner main belt rocky S-‐type asteroid. ...
1. Seyfert Galaxies
... These objects are AGN whose nuclear light dominates so that we can’t distinguish the host galaxy These objects are known as quasi-stellar radio sources (quasars); there are also quasi-stellar objects (QSO’s) identified via the spectra that are radio quiet Radio quiet QSO’s outnumber quasars by 10-30 ...
... These objects are AGN whose nuclear light dominates so that we can’t distinguish the host galaxy These objects are known as quasi-stellar radio sources (quasars); there are also quasi-stellar objects (QSO’s) identified via the spectra that are radio quiet Radio quiet QSO’s outnumber quasars by 10-30 ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.