Plate: a rigid slab of solid lithosphere rock that has defined
... 10. Describe how it is possible for one plate of rock to descend beneath another. Ie, what are the elements necessary to allow that to happen? (1 mark) -thin ocean plates with heavy basaltic rock descent into the plastic asthenosphere beneath lighter, thicker granitic rocks of continental plates -De ...
... 10. Describe how it is possible for one plate of rock to descend beneath another. Ie, what are the elements necessary to allow that to happen? (1 mark) -thin ocean plates with heavy basaltic rock descent into the plastic asthenosphere beneath lighter, thicker granitic rocks of continental plates -De ...
Notes For Chapter 9 - Folds, Faults, and Geologic Maps
... • During crustal deformation rocks are often bent into a series of wave-like undulations called folds • Most folds result from compressional stresses which shorten and thicken the crust ...
... • During crustal deformation rocks are often bent into a series of wave-like undulations called folds • Most folds result from compressional stresses which shorten and thicken the crust ...
Weathering, Erosion and Soil
... Development of Soil - Soil looses covering of broken rock particles and decaying organic matter called humus. Overlays the bedrock. Result of chemical and mechanical weathering and also biological activity. ...
... Development of Soil - Soil looses covering of broken rock particles and decaying organic matter called humus. Overlays the bedrock. Result of chemical and mechanical weathering and also biological activity. ...
Physical Geology - Geol 1330 (07610) - Spring
... c) networking 4. Some rocks may form aquifers in which groundwater is stored. Which of the following rock types would likely make the best aquifer? a) metamorphic b) sandstone c) granite d) shale 5. Which of the following rocks would likely make the best aquitard? a) conglomerate b) sandstone c) lim ...
... c) networking 4. Some rocks may form aquifers in which groundwater is stored. Which of the following rock types would likely make the best aquifer? a) metamorphic b) sandstone c) granite d) shale 5. Which of the following rocks would likely make the best aquitard? a) conglomerate b) sandstone c) lim ...
Obj - davis.k12.ut.us
... which causes: 1. rift valley – the crust reaches elastic limit and breaks creating two new edges which move away, causing the middle portion to fall, 2. depression – the crust stretches but does not reach elastic limit and break, 3. ocean ridges – from seafloor spreading. 3. Transform boundary – the ...
... which causes: 1. rift valley – the crust reaches elastic limit and breaks creating two new edges which move away, causing the middle portion to fall, 2. depression – the crust stretches but does not reach elastic limit and break, 3. ocean ridges – from seafloor spreading. 3. Transform boundary – the ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... • Most easily recognized when it occurs at the surface, or in a near-surface environment ...
... • Most easily recognized when it occurs at the surface, or in a near-surface environment ...
The diagram below shows the latitude and longitude for a city in
... which is _______________ _______________ than rock, flows upward. ...
... which is _______________ _______________ than rock, flows upward. ...
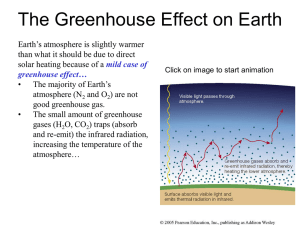
The Greenhouse Effect on Earth
... regions • Chemical weathering occurs slowly here Note: temperate regions such as at the center of the chart undergo both chemical and mechanical weathering, i.e. New York area ...
... regions • Chemical weathering occurs slowly here Note: temperate regions such as at the center of the chart undergo both chemical and mechanical weathering, i.e. New York area ...
Textbook Powerpoint
... caused by a release of potential energy along a geologic fault and usually causing a vibration or trembling at Earth’s surface. ...
... caused by a release of potential energy along a geologic fault and usually causing a vibration or trembling at Earth’s surface. ...
Chapter 8 - Soil & Mining
... The Formation of Soil • Factors that determine the formation of soil: • Parent material - what the soil is made from influences soil formation • Climate - what type of climate influences soil formation • Topography - the surface and slope can influence soil formation • Organisms - plants and animal ...
... The Formation of Soil • Factors that determine the formation of soil: • Parent material - what the soil is made from influences soil formation • Climate - what type of climate influences soil formation • Topography - the surface and slope can influence soil formation • Organisms - plants and animal ...
4. Seafloor Spreading Notes
... 4. At the trenches, cooler material pulls oceanic crust down into the mantle (SLAB PULL) 5. This subducted crust (crust that is pulled underneath another type of crust) is then recycled in the mantle. ...
... 4. At the trenches, cooler material pulls oceanic crust down into the mantle (SLAB PULL) 5. This subducted crust (crust that is pulled underneath another type of crust) is then recycled in the mantle. ...
Chapter 17 Plate Tectonics - The Summer Science Safari Summer
... Sedimentary Rock – formed when rocks break down into smaller pieces by weather moved by erosion and laid down deposition. Characteristics are most common variety of rock, made of sediments; form layers/strata, usually formed by water, often contain fossils, appear dull and earthy, and are grouped b ...
... Sedimentary Rock – formed when rocks break down into smaller pieces by weather moved by erosion and laid down deposition. Characteristics are most common variety of rock, made of sediments; form layers/strata, usually formed by water, often contain fossils, appear dull and earthy, and are grouped b ...
Plate Tectonics
... a better understanding of the topic. abyssal plain – a flat stretch of the deep ocean around the margins of the continents active continental margin – continental margin that occurs along a plate boundary, marked by earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building anticline – upward fold in rock asthen ...
... a better understanding of the topic. abyssal plain – a flat stretch of the deep ocean around the margins of the continents active continental margin – continental margin that occurs along a plate boundary, marked by earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building anticline – upward fold in rock asthen ...
ENV Ch 13 Soils
... Convergent (Collision) example on land – Ural Mts, Himalayas, Where Ocean crust collides with Continental crust – Subduction occurs, example Trenches in the western Pacific. Transform boundaries. Where plates move horizontal relative to each other. Example San Francisco. Plate movement results from ...
... Convergent (Collision) example on land – Ural Mts, Himalayas, Where Ocean crust collides with Continental crust – Subduction occurs, example Trenches in the western Pacific. Transform boundaries. Where plates move horizontal relative to each other. Example San Francisco. Plate movement results from ...
3earth layers
... Beneath the ocean lies the oceanic crust. This crust is made of basalt. This crust covers more than two-thirds of the Earth. Crust is thinnest layer, It varies from 5km thick (in the ocean floor) to around 70km thick (on land where we live called the continental crust). Mantle. The mantle is much th ...
... Beneath the ocean lies the oceanic crust. This crust is made of basalt. This crust covers more than two-thirds of the Earth. Crust is thinnest layer, It varies from 5km thick (in the ocean floor) to around 70km thick (on land where we live called the continental crust). Mantle. The mantle is much th ...
PPT - Hss-1.us
... The types of rocks are: • (1) Igneous - Rocks that are formed by first heating the earth's material (elements) to a molten lava state. The when the molten lava cools it forms igneous rocks. Today we can see this happening in association with volcanoes. • (2) Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form wh ...
... The types of rocks are: • (1) Igneous - Rocks that are formed by first heating the earth's material (elements) to a molten lava state. The when the molten lava cools it forms igneous rocks. Today we can see this happening in association with volcanoes. • (2) Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form wh ...
Partial melting and the thermo-chemical evolution of terrestrial planets
... source region) of the melt sheets observed within large basins are mostly the result of the state of the mantle at the time of impact. By tuning the models to the properties of the well-studied melt sheet of the Caloris basin, our model can explain the observed properties of the major impact basins ...
... source region) of the melt sheets observed within large basins are mostly the result of the state of the mantle at the time of impact. By tuning the models to the properties of the well-studied melt sheet of the Caloris basin, our model can explain the observed properties of the major impact basins ...
ch08
... Photochemical dissociation - The splitting of molecules into their components by means of energy from sunlight or other light sources. In order for life to have arisen abiotically, it must have first developed under anoxic, aqueous conditions. It is possible that life arrived to this planet aboard a ...
... Photochemical dissociation - The splitting of molecules into their components by means of energy from sunlight or other light sources. In order for life to have arisen abiotically, it must have first developed under anoxic, aqueous conditions. It is possible that life arrived to this planet aboard a ...
Name____________________________
... 8. When two plates slide past each other this is a Transform boundary. 9. A Hot Spot is a place where magma works its way to the surface within a plate. 10. North America is made of Continental crust. 11. Seafloor Spreading is when oceanic crust pulls apart, forming new crust. This process forms lon ...
... 8. When two plates slide past each other this is a Transform boundary. 9. A Hot Spot is a place where magma works its way to the surface within a plate. 10. North America is made of Continental crust. 11. Seafloor Spreading is when oceanic crust pulls apart, forming new crust. This process forms lon ...
ppt - MARGINS
... et al., 1989; Hiyagon et al., 1992) and old oceanic crust and oceanic sediments (Matsuda and Nagao, 1986; Staudacher and Allègre, 1988) are shown for comparison. ...
... et al., 1989; Hiyagon et al., 1992) and old oceanic crust and oceanic sediments (Matsuda and Nagao, 1986; Staudacher and Allègre, 1988) are shown for comparison. ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... arrangement of grains within a rock Foliation – any planar arrangement of mineral grains or structural features within a rock Examples of foliation –Parallel alignment of platy and/or elongated minerals ...
... arrangement of grains within a rock Foliation – any planar arrangement of mineral grains or structural features within a rock Examples of foliation –Parallel alignment of platy and/or elongated minerals ...
File - South Sevier High School
... that Earth’s plates move is called ________________ _________________________. 2. ___________________ geologic activity is concentrated at plate boundaries, where plates move away, toward, or past each other. 3. In the early 1900’s, Alfred _____________________ hypothesized that Earth’s crustal plat ...
... that Earth’s plates move is called ________________ _________________________. 2. ___________________ geologic activity is concentrated at plate boundaries, where plates move away, toward, or past each other. 3. In the early 1900’s, Alfred _____________________ hypothesized that Earth’s crustal plat ...
GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006
... 2. Hindus regarded Earth as very old (2 billion years) 3. Earth scientists in early 1800s (Uniformitarianism): very old, >hundreds of millions of years ...
... 2. Hindus regarded Earth as very old (2 billion years) 3. Earth scientists in early 1800s (Uniformitarianism): very old, >hundreds of millions of years ...
Earth`s Interior (What`s down there below us?)
... The “lithosphere” is the crust + part of the upper mantle. It is made of rock and is brittle. The “plates” of the earth’s crust make up the lithosphere. Below the lithosphere is a softer layer called the “asthenosphere”. In the asthenosphere, The rock is near it’s melting point, and flows very slowl ...
... The “lithosphere” is the crust + part of the upper mantle. It is made of rock and is brittle. The “plates” of the earth’s crust make up the lithosphere. Below the lithosphere is a softer layer called the “asthenosphere”. In the asthenosphere, The rock is near it’s melting point, and flows very slowl ...
Basic Geology and Groundwater - well drilling school
... And then just a minute before midnight, at 11.59 P.M., humankind makes its appearance on earth, or less than two million years ago. During this entire time, 4.6 billions years, geologic processes have been continually shaping the world. As an example, the basement rocks beneath Florida were once par ...
... And then just a minute before midnight, at 11.59 P.M., humankind makes its appearance on earth, or less than two million years ago. During this entire time, 4.6 billions years, geologic processes have been continually shaping the world. As an example, the basement rocks beneath Florida were once par ...
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.