Analytical Techniques for Elemental Analysis of Minerals
... halides–carbonates–nitrates–borates–phosphates–sulfates–tungstates–silicates), Table 2 clearly shows the dominance of minerals (about 96.5%) that belong to the mineral group of the silicates. Therefore it is obvious to concentrate in this article on the elemental analysis of silicate minerals. Major ...
... halides–carbonates–nitrates–borates–phosphates–sulfates–tungstates–silicates), Table 2 clearly shows the dominance of minerals (about 96.5%) that belong to the mineral group of the silicates. Therefore it is obvious to concentrate in this article on the elemental analysis of silicate minerals. Major ...
File
... to them. The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other is called Fault. A fault is classified as a hanging wall or foot wall when it is not vertical. A hanging wall is the block of rock above the fault. A foot wall is ...
... to them. The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other is called Fault. A fault is classified as a hanging wall or foot wall when it is not vertical. A hanging wall is the block of rock above the fault. A foot wall is ...
The Earth`s layers
... The mantle is made of much denser, thicker material, because of this the plates "float" on it like oil floats on water. Many geologists believe that the mantle "flows" because of convection currents. Convection currents are caused by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, th ...
... The mantle is made of much denser, thicker material, because of this the plates "float" on it like oil floats on water. Many geologists believe that the mantle "flows" because of convection currents. Convection currents are caused by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, th ...
FCAT Review Test - Rock Cycle Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... ____ 10. Most metamorphic processes take place a. several hundred kilometers below Earth’s surface. b. a few kilometers below Earth’s surface. c. just below Earth’s surface. d. on Earth’s surface. ____ 11. Which of the following weathering processes involves the constant freezing and thawing of wate ...
... ____ 10. Most metamorphic processes take place a. several hundred kilometers below Earth’s surface. b. a few kilometers below Earth’s surface. c. just below Earth’s surface. d. on Earth’s surface. ____ 11. Which of the following weathering processes involves the constant freezing and thawing of wate ...
Objectives
... Eruption Style. They vary from mafic, intermediate, to felsic as their silica (SiO2) content increases. Mafic (basaltic) magmas are generated directly from the mantle, either within the asthenosphere or within the overlying mantle lithosphere. Many mafic-to-intermediate (basaltic-to-andesitic) magma ...
... Eruption Style. They vary from mafic, intermediate, to felsic as their silica (SiO2) content increases. Mafic (basaltic) magmas are generated directly from the mantle, either within the asthenosphere or within the overlying mantle lithosphere. Many mafic-to-intermediate (basaltic-to-andesitic) magma ...
Magmatic Ores
... Uses of Chromite: (Cr/Fe ratio and Mg and Al contents are important; cf. Evans). 1- Source of Cr, necessary for the steel industry 2- Refractory 3- Chemical industries Characteristics of Startiform deposits: Age: Precambrian Tectonic setting: cratonic, rifted continental platforms Great latera ...
... Uses of Chromite: (Cr/Fe ratio and Mg and Al contents are important; cf. Evans). 1- Source of Cr, necessary for the steel industry 2- Refractory 3- Chemical industries Characteristics of Startiform deposits: Age: Precambrian Tectonic setting: cratonic, rifted continental platforms Great latera ...
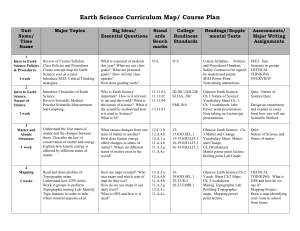
Earth Science Curriculum Map 11-12
... Locate the Ring of Fire and which plate it is situated around. Distinguish the three types of faults and how stress and strain apply to these fault types. ...
... Locate the Ring of Fire and which plate it is situated around. Distinguish the three types of faults and how stress and strain apply to these fault types. ...
Crustal Features
... Crustal Features 8.9B relate plate tectonics to the formation of crustal features ...
... Crustal Features 8.9B relate plate tectonics to the formation of crustal features ...
Modeling Faults - wbm-earth
... a breaking point and can no longer bend or stretch. As the rocks break, they move along surfaces or cracks called faults. When a fault is created, the rocks slide past or rub against each other in different directions. The energy created and released by this phenomenon creates vibrations in the Eart ...
... a breaking point and can no longer bend or stretch. As the rocks break, they move along surfaces or cracks called faults. When a fault is created, the rocks slide past or rub against each other in different directions. The energy created and released by this phenomenon creates vibrations in the Eart ...
Acid and Bases: Alkalinity and pH in Natural Waters.
... magma. These rocks are up-lifted to the surface of the earth by tectonic movements ...
... magma. These rocks are up-lifted to the surface of the earth by tectonic movements ...
Igneous Rocks - VarsityField
... If you were to drill a hole through the crust of a midmid-ocean ridge, what intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect to encounter at or near the surface? What intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect at the base of the crust? Water is abundant in the sedimentary rocks and o ...
... If you were to drill a hole through the crust of a midmid-ocean ridge, what intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect to encounter at or near the surface? What intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect at the base of the crust? Water is abundant in the sedimentary rocks and o ...
Structural Geology: Deformation and Mountain Building
... • Hangingwall: the wall and body of rock above an inclined fault • Footwall: the wall and body of rock beneath an inclined fault ...
... • Hangingwall: the wall and body of rock above an inclined fault • Footwall: the wall and body of rock beneath an inclined fault ...
+ Please click here to the package
... Some changes take place in a very short time. Floods can change the course of a river in a few days. Dust storms can carry huge amounts of soil away very rapidly. However, most of the big changes in the earth's surface take thousands of years. At various times, the earth is exposed to along periods ...
... Some changes take place in a very short time. Floods can change the course of a river in a few days. Dust storms can carry huge amounts of soil away very rapidly. However, most of the big changes in the earth's surface take thousands of years. At various times, the earth is exposed to along periods ...
The role of mafic magmatism in age specification of Devonian
... rocks and have intricate outlines (Fig. 3A). Injections of magma into the roof rocks (Fig. 3B) are often seen. A variety of this injection type is generated by the interaction of magmatic melt and a siltstone layer (Fig. 3C, D). The siltstone is thermally altered to a rock with a porcelaneous textur ...
... rocks and have intricate outlines (Fig. 3A). Injections of magma into the roof rocks (Fig. 3B) are often seen. A variety of this injection type is generated by the interaction of magmatic melt and a siltstone layer (Fig. 3C, D). The siltstone is thermally altered to a rock with a porcelaneous textur ...
File
... - the process of wearing away - Seed germinates • Sends roots into cracks / holes • Roots grow • Can break rocks in pieces - Preserve Earth’s landforms • holds soil and sand in place • Helps prevent wind & water erosion - Helps return nutrients to soil - Trees help prevent wind erosion ...
... - the process of wearing away - Seed germinates • Sends roots into cracks / holes • Roots grow • Can break rocks in pieces - Preserve Earth’s landforms • holds soil and sand in place • Helps prevent wind & water erosion - Helps return nutrients to soil - Trees help prevent wind erosion ...
MORPHOLOGY OF EARTH
... Upper mantle avg. temperature: 1100⁰ C This temperature increases as we move down The rocks are still solid because the pressure is increase at a faster rate The discontinuity is known as Rapetti Discontinuity Velocity of seismic wave is recorded as maximum in the lower mantle even more than the Inn ...
... Upper mantle avg. temperature: 1100⁰ C This temperature increases as we move down The rocks are still solid because the pressure is increase at a faster rate The discontinuity is known as Rapetti Discontinuity Velocity of seismic wave is recorded as maximum in the lower mantle even more than the Inn ...
Earth Structure, Materials, Systems, and Cycles
... Earth Structure, Materials, Systems, and Cycles ...
... Earth Structure, Materials, Systems, and Cycles ...
Chapter 9
... Origin of magma Factors that influence the generation of magma from solid rock • Role of pressure • Increase in confining pressure causes an increase in melting temperature • Drop in confining pressure can cause decompression melting • Lowers the melting temperature • Occurs when rock ascends ...
... Origin of magma Factors that influence the generation of magma from solid rock • Role of pressure • Increase in confining pressure causes an increase in melting temperature • Drop in confining pressure can cause decompression melting • Lowers the melting temperature • Occurs when rock ascends ...
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING
... Oceanic Crust – is uniformly thick throughout the worlds oceans (5 - 7 km). Assuming this is made from basaltic magma (both extrusive and intrusive) then:Volume/Year = Thickness x Spreading Rate x Length About 5 - 20 km3/year (depending on assumptions) length ~ 65,000 km thickness 5 - 7 km spreading ...
... Oceanic Crust – is uniformly thick throughout the worlds oceans (5 - 7 km). Assuming this is made from basaltic magma (both extrusive and intrusive) then:Volume/Year = Thickness x Spreading Rate x Length About 5 - 20 km3/year (depending on assumptions) length ~ 65,000 km thickness 5 - 7 km spreading ...
Magma, Igneous Rocks, and Intrusive Activity Earth, 10e
... • Granitic versus basaltic compositions • Basaltic composition – Dark silicates and calcium-rich feldspar – Termed mafic (magnesium and ferrum, for iron) in composition – Higher density than granitic rocks – Comprise the ocean floor and many volcanic islands ...
... • Granitic versus basaltic compositions • Basaltic composition – Dark silicates and calcium-rich feldspar – Termed mafic (magnesium and ferrum, for iron) in composition – Higher density than granitic rocks – Comprise the ocean floor and many volcanic islands ...
MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS
... Extensional stress (often called tensional stress) pulls rock apart and is the opposite of tectonic compression Rocks at a divergent plate boundary stretch and pull apart because they are subject to extensional stress. ...
... Extensional stress (often called tensional stress) pulls rock apart and is the opposite of tectonic compression Rocks at a divergent plate boundary stretch and pull apart because they are subject to extensional stress. ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... – Slab pull – dense ocean crust descends under its own weight – Ridge push – gravity pulls lithosphere down & away from ridge – Friction – resistance to movement from various sources ...
... – Slab pull – dense ocean crust descends under its own weight – Ridge push – gravity pulls lithosphere down & away from ridge – Friction – resistance to movement from various sources ...
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.