Factors Affecting Deformation
... shortening of the crust, as shown in Figure 6B and 6C. Most high-angle reverse faults are small. They cause only local displacements in regions dominated by other types of faulting. Thrust faults, on the other hand, exist at all scales. In mountainous regions such as the Alps, northern Rockies, Hima ...
... shortening of the crust, as shown in Figure 6B and 6C. Most high-angle reverse faults are small. They cause only local displacements in regions dominated by other types of faulting. Thrust faults, on the other hand, exist at all scales. In mountainous regions such as the Alps, northern Rockies, Hima ...
Mountain Building at Divergent Boundaries
... shortening of the crust, as shown in Figure 6B and 6C. Most high-angle reverse faults are small. They cause only local displacements in regions dominated by other types of faulting. Thrust faults, on the other hand, exist at all scales. In mountainous regions such as the Alps, northern Rockies, Hima ...
... shortening of the crust, as shown in Figure 6B and 6C. Most high-angle reverse faults are small. They cause only local displacements in regions dominated by other types of faulting. Thrust faults, on the other hand, exist at all scales. In mountainous regions such as the Alps, northern Rockies, Hima ...
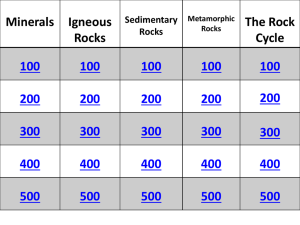
Rocks and Minerals Jeopardy
... Under enough heat and pressure, minerals can combine and recrystallize to form new minerals. 500 pts. ...
... Under enough heat and pressure, minerals can combine and recrystallize to form new minerals. 500 pts. ...
by William J. Crornie Rapidly developing technologies are
... Shallow magma bodies, like the ones under Death Valley and central New Mexico, move with the continents. Plumes, like the 300-kilometer-deep one that generates the geysers of Yellowstone National Park, remain relatively stationary as the plates drift over them, thereby serving as references for meas ...
... Shallow magma bodies, like the ones under Death Valley and central New Mexico, move with the continents. Plumes, like the 300-kilometer-deep one that generates the geysers of Yellowstone National Park, remain relatively stationary as the plates drift over them, thereby serving as references for meas ...
PDF format - GEMOC - Macquarie University
... Mantle-derived xenoliths carry direct information on SCLM composition, but the sampling they provide is limited in space and time. However, there is a good correlation between the composition of these rocks and the garnets they contain, and garnet xenocrysts are common in many volcanic rocks. The me ...
... Mantle-derived xenoliths carry direct information on SCLM composition, but the sampling they provide is limited in space and time. However, there is a good correlation between the composition of these rocks and the garnets they contain, and garnet xenocrysts are common in many volcanic rocks. The me ...
10. St. Helens
... Like the rest of the modern Cascade volcanoes, Mount St. Helens is built on older volcanic and plutonic rocks of the 36 Ma – present Cascade Arc. Locally, it also overlies older volcanic rocks (the ~40 Ma Goble Volcanics) erupted during Eocene time. Owing to only a modest degree of uplift associated ...
... Like the rest of the modern Cascade volcanoes, Mount St. Helens is built on older volcanic and plutonic rocks of the 36 Ma – present Cascade Arc. Locally, it also overlies older volcanic rocks (the ~40 Ma Goble Volcanics) erupted during Eocene time. Owing to only a modest degree of uplift associated ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Physical Geology
... This course covers the fundamentals of geology: rocks, minerals, geologic time, plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanoes, surface processes, and earth resources. The lab delves into the chemistry of minerals, how rocks form, geologic mapping with GPS, geology in the field, and other fundamental topic ...
... This course covers the fundamentals of geology: rocks, minerals, geologic time, plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanoes, surface processes, and earth resources. The lab delves into the chemistry of minerals, how rocks form, geologic mapping with GPS, geology in the field, and other fundamental topic ...
ch10_lecture_1_ - La Habra High School
... time allowing it to be eroded mainly by wind. • Since the great Dust Bowl of the 1930’s, caused by a severe drought and over-plowing for years, the development of the Soil Conservation Service ahs made the prevention of soil erosion their top priority. (now known as the National Resources ...
... time allowing it to be eroded mainly by wind. • Since the great Dust Bowl of the 1930’s, caused by a severe drought and over-plowing for years, the development of the Soil Conservation Service ahs made the prevention of soil erosion their top priority. (now known as the National Resources ...
CAN IMPACTS INDUCE VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS? by H. J. Melosh
... the impact (I know of no single example of such an association on any body in the solar system), some authors have opted for the idea that impacts can induce volcanism at very distant locations. The most widely discussed association is that between the K/T impact and the Deccan Traps in India [3], w ...
... the impact (I know of no single example of such an association on any body in the solar system), some authors have opted for the idea that impacts can induce volcanism at very distant locations. The most widely discussed association is that between the K/T impact and the Deccan Traps in India [3], w ...
Mass Wasting - facstaff.bucknell.edu
... D. How and why did the landslide eventually cause a flood? Debris from the slide dammed the Gros Ventre river. Once water spilled over this dam, it quickly began to erode the unconsolidated rubble, causing the dam to catastrophically fail and flooding to occur downstream. 3) How should mass wasting ...
... D. How and why did the landslide eventually cause a flood? Debris from the slide dammed the Gros Ventre river. Once water spilled over this dam, it quickly began to erode the unconsolidated rubble, causing the dam to catastrophically fail and flooding to occur downstream. 3) How should mass wasting ...
Nanaimo Group
... During the latter part of the Cretaceous Period (from around 85 to 65 million years ago), clastic sediments were deposited in a long trough-shaped basin extending from south of Duncan to north of Campbell River. Deposition probably began just after the micro-continent of Wrangellia - which comprises ...
... During the latter part of the Cretaceous Period (from around 85 to 65 million years ago), clastic sediments were deposited in a long trough-shaped basin extending from south of Duncan to north of Campbell River. Deposition probably began just after the micro-continent of Wrangellia - which comprises ...
CHAPTER 9 Weathering and Formation of Soil
... Chemical weathering is the other important type of weathering. Chemical weathering is different from mechanical weathering because the rock changes, not just in size of pieces, but in composition. That is, one type of mineral changes into a different mineral. Chemical weathering works through chemic ...
... Chemical weathering is the other important type of weathering. Chemical weathering is different from mechanical weathering because the rock changes, not just in size of pieces, but in composition. That is, one type of mineral changes into a different mineral. Chemical weathering works through chemic ...
Lab 2 - Plate TectonicsOct.2014
... The texture and mineralogic composition of a rock frequently reflect its geologic history and help us to determine whether it has an igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic origin. Texture refers to the size, shape, and interrelationship of minerals within a rock. In general, igneous rocks have a cryst ...
... The texture and mineralogic composition of a rock frequently reflect its geologic history and help us to determine whether it has an igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic origin. Texture refers to the size, shape, and interrelationship of minerals within a rock. In general, igneous rocks have a cryst ...
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics
... buckle up to create large mountain ranges like a massive car pile-up. This is called continental-tocontinental convergence, and geologically creates intense folding and faulting rather than volcanic activity. Examples of mountain ranges created by this process are the Himalayan Mountains (taken from ...
... buckle up to create large mountain ranges like a massive car pile-up. This is called continental-tocontinental convergence, and geologically creates intense folding and faulting rather than volcanic activity. Examples of mountain ranges created by this process are the Himalayan Mountains (taken from ...
chapter 9 - Geoclassroom Home
... The hypothesis rests on evidence of glaciers in tropical regions, only 11 degrees from the equator, such as Panama today. It is hypothesized that because tropical glaciers existed, it is likely that glaciers covered the landmasses of the entire globe. “Snowball Earth,” was repeated at least once mor ...
... The hypothesis rests on evidence of glaciers in tropical regions, only 11 degrees from the equator, such as Panama today. It is hypothesized that because tropical glaciers existed, it is likely that glaciers covered the landmasses of the entire globe. “Snowball Earth,” was repeated at least once mor ...
Origin of high Mg# andesite and the continental crust
... and/or metasediment in the subducting slab may leave rutile in their residue, and will thus have large Nb depletions relative to K and La [2]. Slab melts are too rich in light rare earth elements and other incompatible elements, and too poor in compatible elements, to be parental to arc magmas. Howe ...
... and/or metasediment in the subducting slab may leave rutile in their residue, and will thus have large Nb depletions relative to K and La [2]. Slab melts are too rich in light rare earth elements and other incompatible elements, and too poor in compatible elements, to be parental to arc magmas. Howe ...
Grade 7 Earth/Space Pretest
... A. Forces such as weathering and erosion can change the location of rock layers, sometimes putting younger rocks above older rocks. B. Forces such as gravity and magnetism can change the location of rock layers such that older rocks are sometimes located above younger rocks. C. Forces such as tiltin ...
... A. Forces such as weathering and erosion can change the location of rock layers, sometimes putting younger rocks above older rocks. B. Forces such as gravity and magnetism can change the location of rock layers such that older rocks are sometimes located above younger rocks. C. Forces such as tiltin ...
Crust
... crust. The crust is Earth’s most external layer out of all the four layers mentioned. The crust consists of two parts the oceanic and continental crust. These crusts hover above the earth’s mantle, which is basically a river of molten rocks that is 2850 km thick. This outer most “coating” is more em ...
... crust. The crust is Earth’s most external layer out of all the four layers mentioned. The crust consists of two parts the oceanic and continental crust. These crusts hover above the earth’s mantle, which is basically a river of molten rocks that is 2850 km thick. This outer most “coating” is more em ...
VEST `96, Plate Tectonics
... THEN...knowing the ages and the distance from the ridge crest, you could figure out the spreading RATE. People did this exercise, and it turns out that there are variable spreading rates. The East Pacific Rise (EPR), which is producing the pacific plate, is spreading at 16-22 cm/year. This is what i ...
... THEN...knowing the ages and the distance from the ridge crest, you could figure out the spreading RATE. People did this exercise, and it turns out that there are variable spreading rates. The East Pacific Rise (EPR), which is producing the pacific plate, is spreading at 16-22 cm/year. This is what i ...
Deeply buried continental crust under Iceland
... the northeast Atlantic. Recent estimates of the Iceland plume flux of 40-60 km3/year indicate that it might be 4-10 times that of the Hawaii plume flux (Jones et al. 2014). Therefore, the current Iceland plume seems to be the Earth's most vigorous plume. Our inference that deeply buried fragments of ...
... the northeast Atlantic. Recent estimates of the Iceland plume flux of 40-60 km3/year indicate that it might be 4-10 times that of the Hawaii plume flux (Jones et al. 2014). Therefore, the current Iceland plume seems to be the Earth's most vigorous plume. Our inference that deeply buried fragments of ...
2013 Question of the day
... Climates near the ocean are generally milder than those further inland. ...
... Climates near the ocean are generally milder than those further inland. ...
Chapter 5: Mountain Belts and Continental Crust At this point in the
... In the Pratt model, different surface elevations are understood in terms of crustal blocks of differing density. In this case, the blocks with lower densities float higher than those with higher densities, in the same way that a block of styrofoam floats higher in a swimming pool than a block of woo ...
... In the Pratt model, different surface elevations are understood in terms of crustal blocks of differing density. In this case, the blocks with lower densities float higher than those with higher densities, in the same way that a block of styrofoam floats higher in a swimming pool than a block of woo ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Illinois State University
... Factors influencing Metamorphism Temperature • below about 150oC, most minerals are stable (little or no metamorphism) • above 150oC, reaction rate increases as temperature increases, new minerals begin to form • above 600oC, some minerals begin to melt (transition to igneous rocks) • Temperature ...
... Factors influencing Metamorphism Temperature • below about 150oC, most minerals are stable (little or no metamorphism) • above 150oC, reaction rate increases as temperature increases, new minerals begin to form • above 600oC, some minerals begin to melt (transition to igneous rocks) • Temperature ...
3.Lec3_Environmental geology and earth I
... Formation of the Earth - As the cloud condensed, its mass was greatest near the centre. This concentration of matter comprised the Sun, the planets forming from the remaining material in a disc surrounding the star, and the whole system rotated. - The inner planets formed by accretion. Small partic ...
... Formation of the Earth - As the cloud condensed, its mass was greatest near the centre. This concentration of matter comprised the Sun, the planets forming from the remaining material in a disc surrounding the star, and the whole system rotated. - The inner planets formed by accretion. Small partic ...
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.