Lesson 13 - Oregon State University
... Big Bang Nucleosynthesis After about 30 m, nucleosynthesis ceased. The temperature was ~ 3 x 108K and the density was ~ 30 kg/m3. Nuclear matter was 76% by mass protons, 24% alpha particles with traces of deuterium, 3He and 7Li. The /n/p ratio is 109/13/87. The relative ratio of p/4He/d/3He/7Li is ...
... Big Bang Nucleosynthesis After about 30 m, nucleosynthesis ceased. The temperature was ~ 3 x 108K and the density was ~ 30 kg/m3. Nuclear matter was 76% by mass protons, 24% alpha particles with traces of deuterium, 3He and 7Li. The /n/p ratio is 109/13/87. The relative ratio of p/4He/d/3He/7Li is ...
Problem Set # 8: The Last Problem Set Due Wednesday, December
... 4) [40 points] Consider an ordinary carbon atom in your body, containing 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus. Write a brief essay describing the history of this carbon atom. Some questions your essay should answer include: When did the individual protons and neutrons first fuse? When and where ...
... 4) [40 points] Consider an ordinary carbon atom in your body, containing 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus. Write a brief essay describing the history of this carbon atom. Some questions your essay should answer include: When did the individual protons and neutrons first fuse? When and where ...
Rachel Henning
... During the first 10-43 seconds the four fundamental forces are unified (although no complete physical description of this era yet exists). Temperature 1032 Kelvin. 1043 seconds defines the time when gravity splits from the other forces (weak, strong and Electro-Magnetic). Up to 10-35 seconds, quarks ...
... During the first 10-43 seconds the four fundamental forces are unified (although no complete physical description of this era yet exists). Temperature 1032 Kelvin. 1043 seconds defines the time when gravity splits from the other forces (weak, strong and Electro-Magnetic). Up to 10-35 seconds, quarks ...
The Genesis of the Elements
... It has the lowest mass per nuclear particle of any element It can not fuse into another element without creating mass ...
... It has the lowest mass per nuclear particle of any element It can not fuse into another element without creating mass ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... explains the most facts and has the best predictive power) is that the Universe began with a Big Bang explosion ~ 13.7 billion years ago. •Time, space, and matter came into existence with this event •Since an act of creation implies space and time, most scientists do not believe it is even meaningfu ...
... explains the most facts and has the best predictive power) is that the Universe began with a Big Bang explosion ~ 13.7 billion years ago. •Time, space, and matter came into existence with this event •Since an act of creation implies space and time, most scientists do not believe it is even meaningfu ...
neutron star - Adams State University
... the proton-proton chain, allowing these larger stars to burn through their available fuel much more quickly. ...
... the proton-proton chain, allowing these larger stars to burn through their available fuel much more quickly. ...
The Story of Gold
... malleable nature, and its beauty. The rarity of the metal made it valuable and much effort would be expended to secure supplies. It’s not until recent decades that we have been able to gauge to rarity of gold in the Universe as a whole and attempt to explain why this is so. Data published at WebElem ...
... malleable nature, and its beauty. The rarity of the metal made it valuable and much effort would be expended to secure supplies. It’s not until recent decades that we have been able to gauge to rarity of gold in the Universe as a whole and attempt to explain why this is so. Data published at WebElem ...
Untitled
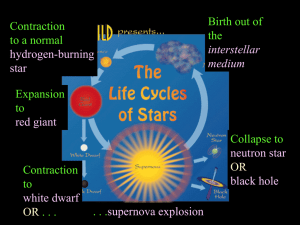
... of hydrogen and helium atoms were it not for gravity. Millions of years laterand astrophysicists argue about how many millions-gravity pulled the thin, diffuse clouds of hydrogen and helium into increasingly thicker clouds. The clouds heated_as they contracted until, at about ten million degrees, st ...
... of hydrogen and helium atoms were it not for gravity. Millions of years laterand astrophysicists argue about how many millions-gravity pulled the thin, diffuse clouds of hydrogen and helium into increasingly thicker clouds. The clouds heated_as they contracted until, at about ten million degrees, st ...
S03 from fusion to all the elements.notebook
... atom determines the type of ________ . An element can have different forms, called ________, based element neutrons on the number of ________ in the nucleus. For example, an ordinary hydrogen nucleus contains just one proton. But _________, an isotope of hydrogen, has one proton and one neutro ...
... atom determines the type of ________ . An element can have different forms, called ________, based element neutrons on the number of ________ in the nucleus. For example, an ordinary hydrogen nucleus contains just one proton. But _________, an isotope of hydrogen, has one proton and one neutro ...
Supernova
... • Broken nuclei fuse with iron to create heavy elements. • This matter goes to form new stars and planets. ...
... • Broken nuclei fuse with iron to create heavy elements. • This matter goes to form new stars and planets. ...
G030485-00 - DCC
... We are all children of the stars composed of stardustThe by-product of a blast. But the process of our creation left behind many ghosts that LIGO wants to detect. Let me tell you the story LIGO-G030485-00-D ...
... We are all children of the stars composed of stardustThe by-product of a blast. But the process of our creation left behind many ghosts that LIGO wants to detect. Let me tell you the story LIGO-G030485-00-D ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... Lithium, Beryllium, and Boron are difficult to produce in stars. (L, Be, and B are formed in the fusion chains, but they are unstable at high temperatures, and tend to break up into residues of He, which are very stable). ...
... Lithium, Beryllium, and Boron are difficult to produce in stars. (L, Be, and B are formed in the fusion chains, but they are unstable at high temperatures, and tend to break up into residues of He, which are very stable). ...
The Stars, the Elements and You
... it suggests it is: the mass of the atom. The reason that the atomic mass is not a whole number is that most atoms have versions of themselves called isotopes which have more or less neutrons, but always the same number of protons (very important point!). Isotopes are critical in providing evidence f ...
... it suggests it is: the mass of the atom. The reason that the atomic mass is not a whole number is that most atoms have versions of themselves called isotopes which have more or less neutrons, but always the same number of protons (very important point!). Isotopes are critical in providing evidence f ...
Origin of the Elements and their Isotopes
... the atomic number (element). • Number of neutrons + protons determines atomic mass (isotope). • Protons are positively charged, neutrons are neutral and electrons are negatively charged. ...
... the atomic number (element). • Number of neutrons + protons determines atomic mass (isotope). • Protons are positively charged, neutrons are neutral and electrons are negatively charged. ...
Can the sun make it rain, or (Will astronomy help us
... • Proton and neutron target practice, making He • Atomic differentiation, rice and bb’s for H and Fe ...
... • Proton and neutron target practice, making He • Atomic differentiation, rice and bb’s for H and Fe ...
Study Notes for Integrated Science Astronomy Unit These notes will
... universe is expanding and cooling. This expansion and the microwave radiation left behind from its origins is how the theory was formulated and then scientifically observed. The Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe is based on evidence that all galaxies are rushing apart from one another. T ...
... universe is expanding and cooling. This expansion and the microwave radiation left behind from its origins is how the theory was formulated and then scientifically observed. The Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe is based on evidence that all galaxies are rushing apart from one another. T ...
Document
... Abundance in number of an atomic species Z is the ratio between the number of atoms of this species and that of another species, X, chosen as a reference nZ=N(Z)/N(X) In the study of stellar photospheres one refers generally to Hydrogen, as this is the most abundant element. The quantity nZ=N(Z)/N(H ...
... Abundance in number of an atomic species Z is the ratio between the number of atoms of this species and that of another species, X, chosen as a reference nZ=N(Z)/N(X) In the study of stellar photospheres one refers generally to Hydrogen, as this is the most abundant element. The quantity nZ=N(Z)/N(H ...
Where Did the Elements Come From?
... Nuclear Reactions • Rxn involving a change in the composition of the nucleus of an ...
... Nuclear Reactions • Rxn involving a change in the composition of the nucleus of an ...
Elements in our universe
... the nucleus of an atom Atomic mass is the mass of an atom measured in atomic mass units, when the atom is at rest at its lowest energy level. Isotopes are elements of different forms. This is caused by the varying number of neutrons in each atom. Isotopes may have the same atomic number but diff ...
... the nucleus of an atom Atomic mass is the mass of an atom measured in atomic mass units, when the atom is at rest at its lowest energy level. Isotopes are elements of different forms. This is caused by the varying number of neutrons in each atom. Isotopes may have the same atomic number but diff ...
Serway_PSE_quick_ch45
... have too many neutrons for the nucleus to be stable. Beta decay in which electrons are ejected decreases the number of neutrons and increases the number of protons in order to stabilize the nucleus. ...
... have too many neutrons for the nucleus to be stable. Beta decay in which electrons are ejected decreases the number of neutrons and increases the number of protons in order to stabilize the nucleus. ...
Evolution and the Big Bang, ET Life Lec. 6, Jan 18, 2002
... Neutron star spins 30 times a second and emits pulses of radio waves pulsar. ...
... Neutron star spins 30 times a second and emits pulses of radio waves pulsar. ...
Appendix 2
... galaxies. Observation shows that overall movement of the galaxies is to move away from each other. The speed of any two galaxies is greater the further they are apart. This is understood to be the result of space expanding. Working backwards in time it is thought that all the matter of which the pre ...
... galaxies. Observation shows that overall movement of the galaxies is to move away from each other. The speed of any two galaxies is greater the further they are apart. This is understood to be the result of space expanding. Working backwards in time it is thought that all the matter of which the pre ...
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons, primarily protons and neutrons. The first nuclei were formed about three minutes after the Big Bang, through the process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis. It was then that hydrogen and helium formed to become the content of the first stars, and this primeval process is responsible for the present hydrogen/helium ratio of the cosmos.With the formation of stars, heavier nuclei were created from hydrogen and helium by stellar nucleosynthesis, a process that continues today. Some of these elements, particularly those lighter than iron, continue to be delivered to the interstellar medium when low mass stars eject their outer envelope before they collapse to form white dwarfs. The remains of their ejected mass form the planetary nebulae observable throughout our galaxy.Supernova nucleosynthesis within exploding stars by fusing carbon and oxygen is responsible for the abundances of elements between magnesium (atomic number 12) and nickel (atomic number 28). Supernova nucleosynthesis is also thought to be responsible for the creation of rarer elements heavier than iron and nickel, in the last few seconds of a type II supernova event. The synthesis of these heavier elements absorbs energy (endothermic) as they are created, from the energy produced during the supernova explosion. Some of those elements are created from the absorption of multiple neutrons (the R process) in the period of a few seconds during the explosion. The elements formed in supernovas include the heaviest elements known, such as the long-lived elements uranium and thorium.Cosmic ray spallation, caused when cosmic rays impact the interstellar medium and fragment larger atomic species, is a significant source of the lighter nuclei, particularly 3He, 9Be and 10,11B, that are not created by stellar nucleosynthesis.In addition to the fusion processes responsible for the growing abundances of elements in the universe, a few minor natural processes continue to produce very small numbers of new nuclides on Earth. These nuclides contribute little to their abundances, but may account for the presence of specific new nuclei. These nuclides are produced via radiogenesis (decay) of long-lived, heavy, primordial radionuclides such as uranium and thorium. Cosmic ray bombardment of elements on Earth also contribute to the presence of rare, short-lived atomic species called cosmogenic nuclides.