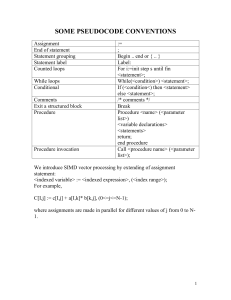
14 - Villanova Computer Science
... String: . (for concat) x (for multiple concat) String comparison: lt le eq ge gt ne Assignment: = (carries value of expression) binary assignment: += *= .= etc increment: ++$i $i++ (increment then assign vs. assign then increment) ...
... String: . (for concat) x (for multiple concat) String comparison: lt le eq ge gt ne Assignment: = (carries value of expression) binary assignment: += *= .= etc increment: ++$i $i++ (increment then assign vs. assign then increment) ...
Functional Programming Pure Functional Languages
... – variables are bound to values only through parameter associations – no side effects Functional Programming, CS314 Fall 01© BGRyder ...
... – variables are bound to values only through parameter associations – no side effects Functional Programming, CS314 Fall 01© BGRyder ...
Introduction to Programming Systems Goals CS 217
... • Systems programming language – originally used to write Unix and Unix tools – data types and control structures close to most machines – now also a popular application programming language ...
... • Systems programming language – originally used to write Unix and Unix tools – data types and control structures close to most machines – now also a popular application programming language ...
Functions 1 - Portal UniMAP
... 1.1 To apply functions as building blocks of programs. 1.2 To write C programs using functions. ...
... 1.1 To apply functions as building blocks of programs. 1.2 To write C programs using functions. ...
Decorators in Python
... before and after a function is called. A decorator takes a function object as an argument (which is called the decoratee) and returns a new function object that will be executed in its place. The function object constructed inside the decorator usually calls the decoratee. A decorator is executed ...
... before and after a function is called. A decorator takes a function object as an argument (which is called the decoratee) and returns a new function object that will be executed in its place. The function object constructed inside the decorator usually calls the decoratee. A decorator is executed ...
How to approach a computational problem
... things, but can do them perfectly,2 we understand the level of detail in which we need to develop our algorithms in order to get them to work out. What you need to do, then is to take the larger task you wish to accomplish, and break it down into a set of smaller tasks. Eventually you will wish to g ...
... things, but can do them perfectly,2 we understand the level of detail in which we need to develop our algorithms in order to get them to work out. What you need to do, then is to take the larger task you wish to accomplish, and break it down into a set of smaller tasks. Eventually you will wish to g ...
CS101 Spring 2012 LHC32
... Rules of the game A register or a RAM location can store exactly one value at any time Writing into a register or RAM location (or reading into it from the keyboard) destroys the earlier value Outputting a register or RAM location to the display is done by copying to the area reserved for the ...
... Rules of the game A register or a RAM location can store exactly one value at any time Writing into a register or RAM location (or reading into it from the keyboard) destroys the earlier value Outputting a register or RAM location to the display is done by copying to the area reserved for the ...
Learn to Program with Minecraft Plugins Extracted from:
... • castIntoBlackHole is a name we just made up; it is the name of the function, and the () characters indicate that it is a function and will take the arguments we’ve listed. You always need the parentheses, even if the function doesn’t take any arguments. In this case, it takes one argument we named ...
... • castIntoBlackHole is a name we just made up; it is the name of the function, and the () characters indicate that it is a function and will take the arguments we’ve listed. You always need the parentheses, even if the function doesn’t take any arguments. In this case, it takes one argument we named ...
Chapter Two User Operating System interface
... routines written in C and C++, although certain low-level tasks (for example, tasks where hardware must be accessed directly), may need to be written using assembly-language instructions. Before we discuss how an operating system makes system calls available, let's first use an example to illustrate ...
... routines written in C and C++, although certain low-level tasks (for example, tasks where hardware must be accessed directly), may need to be written using assembly-language instructions. Before we discuss how an operating system makes system calls available, let's first use an example to illustrate ...
Introduction (cont)
... The component of a computer that can run a program is called a processor Static body of the text of the code which is to be executed by processor is called a program Dynamic execution of a program by the processor is called a process (instruction stream, thread of execution). When multiple processes ...
... The component of a computer that can run a program is called a processor Static body of the text of the code which is to be executed by processor is called a program Dynamic execution of a program by the processor is called a process (instruction stream, thread of execution). When multiple processes ...
Binary Search
... • We call an entry of our array a candidate if, at the current stage of the algorithm, we cannot rule out that this entry has key equal to K. • We observe that a constant amount of primitive operations are executed at each recursive call of function BinarySearch. • Hence the running time is proporti ...
... • We call an entry of our array a candidate if, at the current stage of the algorithm, we cannot rule out that this entry has key equal to K. • We observe that a constant amount of primitive operations are executed at each recursive call of function BinarySearch. • Hence the running time is proporti ...
chapter7
... Operation. Controls the repetitive execution of a routine. LOOPNE and LOOPNZ are similar to LOOP, except that they terminate if the CX is zero or the ZF is 1 (zero condition, set by another instruction). Source Code. LOOPNE label LOOPNZ label Object Code. |11100000|--disp--| 7.4 High-Level Logic Str ...
... Operation. Controls the repetitive execution of a routine. LOOPNE and LOOPNZ are similar to LOOP, except that they terminate if the CX is zero or the ZF is 1 (zero condition, set by another instruction). Source Code. LOOPNE label LOOPNZ label Object Code. |11100000|--disp--| 7.4 High-Level Logic Str ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... Setting up the data structure: you need to ask yourself questions such as: 1. Will the data be in memory or register? 2. Is the data of type byte, word or double word? 3. How many data items are there? 4. Does the data represents only positive numbers, or does it represents positive and negative num ...
... Setting up the data structure: you need to ask yourself questions such as: 1. Will the data be in memory or register? 2. Is the data of type byte, word or double word? 3. How many data items are there? 4. Does the data represents only positive numbers, or does it represents positive and negative num ...
lect_2_handout
... functions. Anything you can do with vectors, you can do with functions. This includes assigning them to variables, storing them in lists, passing them as arguments to other functions. Functions don’t even have to be named or stored. Functions remove redundancy and duplication in your code. The motiv ...
... functions. Anything you can do with vectors, you can do with functions. This includes assigning them to variables, storing them in lists, passing them as arguments to other functions. Functions don’t even have to be named or stored. Functions remove redundancy and duplication in your code. The motiv ...
CS2403 Programming Language Class Sildes
... • Usually presented as a parse tree • Expressed by recursive rules – Any identifier is an expression – Any number is an expression – If exp1 and exp2 are expressions, then so are ...
... • Usually presented as a parse tree • Expressed by recursive rules – Any identifier is an expression – Any number is an expression – If exp1 and exp2 are expressions, then so are ...
lecture1 2016 - UWC Computer Science
... – .model small : Lines that start with a "." are used to provide the assembler with information. The word(s) behind it say what kind of info. In this case it just tells the assembler the program is small and doesn't need a lot of memory. I'll get back on this later. – .stack : Another line with info ...
... – .model small : Lines that start with a "." are used to provide the assembler with information. The word(s) behind it say what kind of info. In this case it just tells the assembler the program is small and doesn't need a lot of memory. I'll get back on this later. – .stack : Another line with info ...
lecture1 v2 - UWC Computer Science
... – .model small : Lines that start with a "." are used to provide the assembler with information. The word(s) behind it say what kind of info. In this case it just tells the assembler the program is small and doesn't need a lot of memory. I'll get back on this later. – .stack : Another line with info ...
... – .model small : Lines that start with a "." are used to provide the assembler with information. The word(s) behind it say what kind of info. In this case it just tells the assembler the program is small and doesn't need a lot of memory. I'll get back on this later. – .stack : Another line with info ...
MP 2014 UNIT 2
... You must set the SP correctly before using CALL CALL 5000H – Push the PC value onto the stack – Load PC with 16‐bit address supplied CALL ins. RET : Load PC with stack top; POP PC ...
... You must set the SP correctly before using CALL CALL 5000H – Push the PC value onto the stack – Load PC with 16‐bit address supplied CALL ins. RET : Load PC with stack top; POP PC ...
public static void nameAndAddress()
... Methods that Use a Single Argument • Methods that do not require any arguments are simple to write and can be used in certain situations. • However, they are limited because they have no communication with the calling class. Ex. Suppose you are writing a program to create restaurant reservations. W ...
... Methods that Use a Single Argument • Methods that do not require any arguments are simple to write and can be used in certain situations. • However, they are limited because they have no communication with the calling class. Ex. Suppose you are writing a program to create restaurant reservations. W ...
Introduction Slides
... to compute the gcd, and was not completely object-oriented (integers aren’t objects). • The Scheme code used sequencing to do I/O, an imperative feature. ...
... to compute the gcd, and was not completely object-oriented (integers aren’t objects). • The Scheme code used sequencing to do I/O, an imperative feature. ...
Assembly Programming - University of the Western Cape
... – .model small : Lines that start with a "." are used to provide the assembler with information. The word(s) behind it say what kind of info. In this case it just tells the assembler the program is small and doesn't need a lot of memory. I'll get back on this later. – .stack : Another line with info ...
... – .model small : Lines that start with a "." are used to provide the assembler with information. The word(s) behind it say what kind of info. In this case it just tells the assembler the program is small and doesn't need a lot of memory. I'll get back on this later. – .stack : Another line with info ...
Stacks - Courses
... • The names of the methods supported by an ADT • How those methods are to be declared and used – e.g., what order the parameters are listed in ...
... • The names of the methods supported by an ADT • How those methods are to be declared and used – e.g., what order the parameters are listed in ...